If you have been recently diagnosed with elevated liver enzymes or struggling with liver conditions as fatty liver disease, then one of the best ways to begin healing your liver is with Ayurvedic treatment. A holistic system of medicine, Ayurveda involves liver healing herbs, changes in diet, lifestyle and application of yoga therapy to cleanse the liver and provide relief from liver diseases.
Liver enzymes such as ALT and AST levels are often tested to check the health and functioning of your liver. These enzymes are normally produced by the liver and they are vital for its functioning. That’s why when there is any change in the levels of liver enzymes in your blood, it often indicates liver disease or liver dysfunction.
Treating high liver enzymes involves identifying the underlying cause and addressing it. In some cases, lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, reducing alcohol consumption, and avoiding certain medications can help to lower elevated liver enzymes within a month. However, more severe cases may require medical intervention or even surgery.
If you’re looking for more information on treating high liver enzymes, you’re in the right place! In this article, we will dive deeper into the symptoms and causes of high liver enzymes, the best Ayurvedic herbs to treat liver conditions and effective natural ways to manage liver enzymes. Let’s begin!
What are Liver Enzymes?
Liver enzymes are proteins produced by the liver that help it perform various essential functions such as breaking down toxins, processing nutrients, and producing bile. When the liver is under stress or damaged, it releases more enzymes into the bloodstream, thus leading to elevated liver enzymes in your test reports.
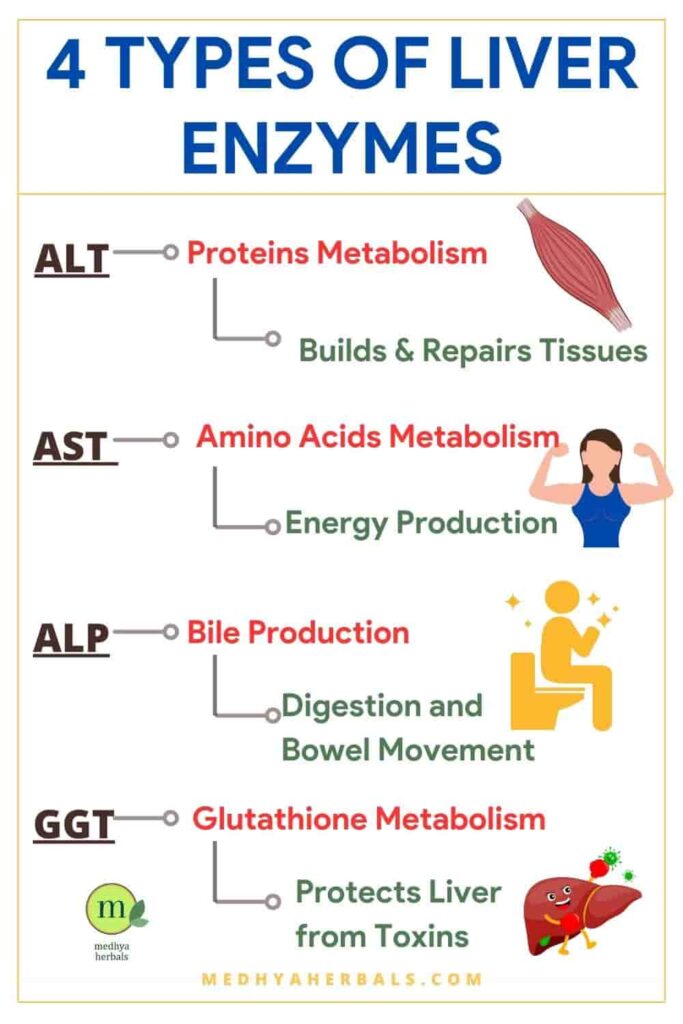
Here’s a closer look at the function of some common liver enzymes:
- Alanine transaminase (ALT): This enzyme helps the liver break down proteins and amino acids, which are essential for building and repairing tissues in the body. Elevated levels of ALT in the blood can indicate liver disease. ALT is also known as serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, or SGPT.
- Aspartate transaminase (AST): This enzyme helps the liver metabolize amino acids and produce energy. Elevated levels of AST in the blood can indicate liver damage, but can also be a sign of muscle or heart damage. AST is also known as serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, or SGOT.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): This enzyme is involved in the production of bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats in the small intestine. Elevated levels of ALP in the blood can indicate liver or bone disease.
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): This enzyme is involved in the metabolism of glutathione, an antioxidant that helps protect the liver from damage caused by toxins. Elevated levels of GGT in the blood can indicate liver disease, but can also be a sign of alcohol abuse.
Normal Levels of Liver Enzymes
Liver enzyme levels can vary depending on age, gender, and other factors. Here’s a table of the normal range of liver enzymes in the blood:
| Liver Enzyme | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| ALT | 7-56 U/L |
| AST | 10-40 U/L |
| ALP | 44-147 U/L |
| GGT | 9-48 U/L |
It’s important to note that the normal range of liver enzymes can vary slightly between different laboratories and testing methods. Any significant deviation from the normal range should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to identify and address the underlying cause.
Causes of High Liver Enzymes
High liver enzymes can occur due to a variety of factors, ranging from mild to severe. Here are some common causes of high liver enzymes:
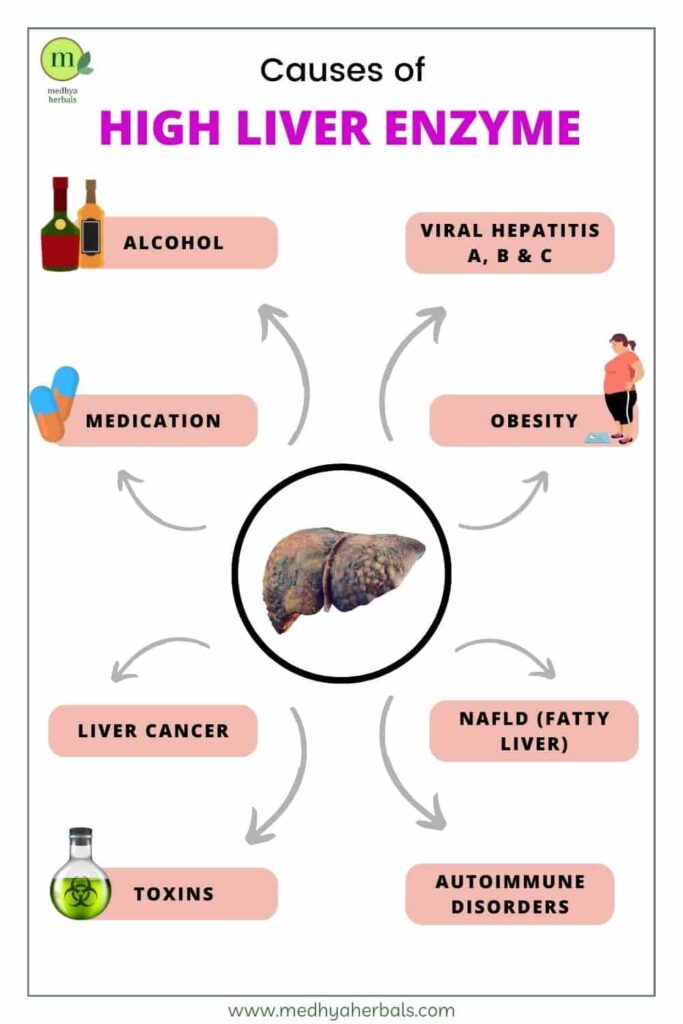
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive consumption of alcohol can damage liver cells and cause inflammation, leading to elevated levels of liver enzymes.
- Viral Hepatitis: Hepatitis A, B, and C are viruses that can cause liver inflammation and damage, leading to elevated liver enzyme levels.
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver, leading to liver inflammation and damage, and subsequently high liver enzyme levels.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as statins, antibiotics, and anti-seizure drugs, can cause liver damage and lead to elevated levels of liver enzymes.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune disorders, such as autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis, can cause inflammation and damage to the liver, resulting in high liver enzyme levels.
- Liver Cancer: Liver cancer can cause liver damage, leading to elevated levels of liver enzymes.
- Other Factors: Other factors that can cause high liver enzyme levels include obesity, exposure to toxins, and genetic liver disorders.
It’s essential to identify and address the underlying cause of high liver enzymes to prevent further damage to the liver and avoid serious health problems. A healthcare provider can conduct tests and recommend appropriate treatment based on your medical history and condition.
Symptoms of High Liver Enzymes
High liver enzymes do not typically cause specific symptoms, but they can indicate underlying liver damage or disease. In some cases, individuals with high liver enzyme levels may experience the following symptoms:

- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes is a common symptom of liver disease. Jaundice occurs when the liver is unable to process bilirubin, a waste product that is excreted through bile.
- Fatigue: Liver damage can cause a decrease in energy levels, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Inflammation and scarring of the liver can cause pain and swelling in the abdominal area.
- Dark Urine: Liver damage can cause bilirubin to accumulate in the urine, leading to dark-colored urine.
- Pale Stools: Light-colored or gray stools can indicate a lack of bile in the digestive system, which may be due to liver damage.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with high liver enzyme levels experience symptoms. Additionally, some symptoms of liver disease, such as fatigue and abdominal pain, can be caused by various other conditions.
Ayurvedic Herbs to Treat High Liver Enzymes
In Ayurveda, the liver is called “pittashaya”, which means it is the seat of the pitta or the energy of transformation and metabolism. When our liver is stressed or inflamed, it leads to build up of heat inside the liver and the blood tissues, thus causing high body heat.

That’s why the best Ayurvedic herbal remedies for liver health include bitter and cooling herbs that dissipate off the liver heat and heal liver tissues. These liver healthy Ayurvedic herbs also repair and rejuvenate the liver so that it stops leaking the liver enzymes and starts to function well. Here are the best Ayurvedic herbs to treat high liver enzymes:
1. Kutki
- Benefits: Kutki is known for its ability to promote healthy liver function, reduce inflammation, and improve bile flow. It is also believed to have antioxidant properties that can help protect the liver from damage.
- Properties: Kutki contains compounds such as kutkin and picrorhizin, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Kutki can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
2. Bhumi Amla
- Benefits: Bhumi Amla is believed to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can help protect the liver from damage, reduce inflammation, and improve liver function.
- Properties: Bhumi Amla contains compounds such as lignans and flavonoids, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Bhumi Amla can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
3. Amla
- Benefits: Amla is known for its ability to improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and protect the liver from damage caused by toxins. It is also believed to have antioxidant properties that can help prevent liver cell damage.
- Properties: Amla contains compounds such as polyphenols and flavonoids, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Amla can be consumed fresh, dried, or in capsule form.
4. Guduchi
- Benefits: Guduchi is believed to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help protect the liver from damage, reduce inflammation, and improve liver function.
- Properties: Guduchi contains compounds such as alkaloids and flavonoids, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Guduchi can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
5. Punarnava
- Benefits: Punarnava is known for its ability to reduce inflammation, improve liver function, and protect the liver from damage caused by toxins.
- Properties: Punarnava contains compounds such as flavonoids and alkaloids, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Punarnava can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
6. Licorice
- Benefits: Licorice is believed to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help protect the liver from damage, reduce inflammation, and improve liver function.
- Properties: Licorice contains compounds such as glycyrrhizin and flavonoids, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Licorice can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
7. Bhringraj
- Benefits: Bhringraj is known for its ability to improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and protect the liver from damage caused by toxins.
- Properties: Bhringraj contains compounds such as wedelolactone and demethylwedelolactone, which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Bhringraj can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
8. Triphala
- Benefits: Triphala is a combination of three fruits (Amla, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki) that are known for their ability to improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and protect the liver from damage caused by toxins.
- Properties: Triphala contains compounds such as tannins and flavonoids,
- which are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties.
- Consumption: Triphala can be consumed in capsule or powder form, or brewed into a tea.
Do note that while these Ayurvedic herbs have many benefits for liver health, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating them into your diet or supplement routine. Some herbs may interact with medications or have potential side effects, and dosages may vary based on individual factors such as age, gender, and medical history. An Ayurvedic practitioner can provide guidance on safe and effective use of these herbs for liver health.
The Best Foods to Bring Down High Liver Enzymes
While there is no specific food that can lower liver enzymes, a balanced and healthy diet can help support liver function and promote overall health. Here are some foods that can be beneficial for liver health:
- Leafy Greens: Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that can help protect the liver from damage caused by toxins.
- Berries: Berries such as blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries are rich in antioxidants and may help reduce inflammation in the liver.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds that can help detoxify the liver and promote healthy liver function.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are high in healthy fats and antioxidants that can help protect the liver from damage.
- Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and tuna are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation in the liver.
- Green Tea: Green tea is high in antioxidants and may help reduce inflammation in the liver.
In addition to incorporating these foods into your diet, it’s important to avoid or limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and alcohol, which can all contribute to liver damage and elevated liver enzymes. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise can also help support liver function and promote overall health.
Natural Ways to Lower Elevated ALT Levels
Making lifestyle changes can be an effective way to lower high liver enzyme levels and promote liver health. Here are some lifestyle changes that can help:

- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and being overweight can increase the risk of fatty liver disease and liver damage. Losing weight through healthy diet and exercise can help reduce liver enzyme levels and improve liver health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and increase liver enzyme levels. Limiting or avoiding alcohol can help reduce inflammation and allow the liver to heal.
- Avoid Unhealthy Foods: Processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats can all contribute to liver damage and high liver enzyme levels. Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote liver health.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can help reduce inflammation, improve liver function, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure can contribute to liver damage and high liver enzyme levels. Managing these conditions through proper medication and lifestyle changes can help improve liver health.
- Avoid Toxins: Exposure to toxins such as chemicals and pollutants can contribute to liver damage and high liver enzyme levels. Avoiding exposure to toxins and wearing protective gear when working with chemicals can help reduce the risk of liver damage.
Conclusion
High liver enzymes can indicate underlying liver damage or disease and should be taken seriously. Making diet and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding unhealthy foods, can help lower high liver enzyme levels and promote liver health.
Incorporating Ayurvedic herbs and other natural remedies can also be beneficial for liver health. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment of high liver enzyme levels, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
At Medhya Herbals, we can help you find the right treatment and support to improve your liver function. So, take the first step towards a healthier life today and make the necessary changes to support your liver health!
FAQ
How long does it take for liver enzymes to return to normal?
The amount of time it takes for liver enzymes to return to normal depends on the underlying cause of the elevated levels. In some cases, liver enzyme levels may return to normal on their own, while in other cases, medical treatment may be required.
For example, if high liver enzymes are due to alcohol abuse, stopping alcohol consumption can help reduce inflammation and allow the liver to heal. Liver enzyme levels may return to normal within a few weeks to a few months after stopping alcohol consumption.
If high liver enzymes are due to medication use, stopping or switching to a different medication may be necessary. Liver enzyme levels may return to normal within a few weeks to a few months after stopping or switching medication.
In cases of viral hepatitis or NAFLD, treatment may involve lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications, weight loss, and exercise, as well as medication. The length of time it takes for liver enzyme levels to return to normal will depend on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the treatment.
It’s important to note that in some cases, elevated liver enzyme levels may indicate chronic liver disease, which may require ongoing treatment and monitoring. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment of high liver enzyme levels.
When to worry about high alt levels?
ALT, or alanine aminotransferase, is an enzyme found primarily in the liver. It’s important to note that ALT levels can fluctuate based on various factors, such as age, gender, and medications. However, if your ALT levels are consistently high, it may be an indication of liver damage or disease.
Generally, ALT levels higher than the upper limit of normal range (which is typically 30-65 IU/L for men and 19-50 IU/L for women) should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Additionally, if you’re experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, or jaundice, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Other factors that may warrant concern for high ALT levels include a family history of liver disease, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to toxins or drugs known to cause liver damage.
References
- Mayo Clinic. “High liver enzymes: Causes.” Mayo Clinic, 2021, https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/high-liver-enzymes/basics/causes/sym-20050830. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. “Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).” NIDDK, 2019, https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.
- Wong, Vincent W-S, and Grace L-H Wong. “Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Epidemic of the 21st Century.” Advances in Pediatrics., vol. 60, no. 1, 2013, pp. 1-25.
- Sharma, Vishal et al. “Herbal medicine: A natural anti-inflammatory therapy for liver disorders.” Hepatitis Monthly, vol. 12, no. 10, 2012, pp. e7238.
- Kim, Han-Jung et al. “Effect of green tea on liver function and fat accumulation in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, vol. 59, no. 15, 2011, pp. 8085-8091.
- Khurana, Sandhya and Manjul Mishra. “Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of Amla (Emblica officinalis) on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats.” Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, vol. 54, no. 1, 2010, pp. 81-88.
- European Medicines Agency. “Assessment report on Glycyrrhiza glabra L., radix and its preparations.” EMA, 2013, https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-glycyrrhiza-glabra-l-radix-its-preparations_en.pdf. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.
- Yan, Hui et al. “Bhringraj (Eclipta prostrata) in liver disease: A review.” Pharmacognosy Reviews, vol. 11, no. 21, 2017, pp. 70-77.
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. “Alcohol’s Effects on the Body.” NIAAA, 2021, https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohols-effects-health/alcohols-effects-body. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Toxic Substances Portal – Carbon Tetrachloride.” CDC, 2021, https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/substances/toxsubstance.asp?toxid=18. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.


You have not mentioned Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata) in your list. Milk thistle, even though not an Ayurvedic herb is also beneficial for liver. What about Dugdhapheni (dandelion)?
Hello! Thanks for the suggestion, indeed both of these herbs are very helpful for liver function, spleen (an integral part of liver’s detox and metabolic functions) and to support bile juice quality (which affects gall bladder function).