Your liver is a silent hero, quietly performing over 500 essential tasks for your body every single day. But how do you know if this vital organ is functioning at its best? Well, this what is indicated by levels of ALT (Alanine aminotransferase), a key enzyme found primarily in your liver. When your liver is healthy, ALT levels remain within a certain range. But if they rise, it could be an early sign of liver damage or disease.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore when you should worry about your ALT levels. We’ll delve into specific symptoms associated with high ALT levels, understand how these levels fluctuate by age, and what it means when your ALT level crosses 100. With a wealth of expert insights derived from years of research in the realm of women’s health and wellness, you can trust us to provide the in-depth knowledge you need.
Curious about how to lower ALT levels or how they link to your liver’s health? Or maybe you’ve wondered if there are any natural treatments to help maintain your ALT levels. Whatever your questions, stick with us. By the end of this article, you’ll be well-armed with the knowledge you need to support your liver’s health and overall wellness.
In our quest for healthier lives, every piece of information matters. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
Understanding ALT Levels
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is a crucial enzyme mostly found in your liver cells. Its primary function is to facilitate the conversion of proteins into energy for the liver. But when your liver is injured or inflamed, ALT can leak into your bloodstream, causing ALT levels to rise. This is why ALT is commonly used as a marker for liver health.
Normal ALT Levels by Age
In general, the reference range for ALT levels can vary depending on the laboratory that analyzes the blood sample, but most typically, it’s approximately 7 to 56 units per liter (U/L) for adult males and 7 to 45 U/L for adult females. In children, ALT levels can be slightly higher, typically less than 50 U/L for newborns and less than 60 U/L for children under the age of six months. It’s worth noting that these values can also vary based on factors like sex and age.
As we age, it’s typical to see some fluctuation in ALT levels. It’s essential to have regular checks and understand the ‘normal’ level for your specific age group. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of any significant changes that might indicate a potential health issue.
When Should You Be Worried About ALT Levels?
ALT levels are a spectrum, and it’s important to understand that the degree of increase can indicate different health implications. For instance:
- ALT 75 or 80: An ALT level in this range is above the typical upper limit of normal. While it’s not dramatically high, it’s still a cause for attention. If your ALT level remains at this range persistently, it may signal a mild but ongoing liver issue, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- ALT 200: An ALT level at this point is significantly high and often indicates more severe liver inflammation or damage. Causes could range from viral hepatitis to drug-induced liver injury, alcohol-related liver damage, or even autoimmune liver diseases.
High ALT Levels (ALT Over 100)
Liver health is crucial to your overall well-being. Because of the liver’s capacity for silent suffering, symptoms might not surface until liver damage is advanced. By monitoring your ALT levels, you can identify potential liver health issues early.
When ALT levels exceed 100 U/L, it usually signifies some form of liver damage. It could be a result of various conditions, including hepatitis, fatty liver disease, alcohol-related liver damage, or even certain medications. An ALT level over 100 is typically considered high, but levels can reach into the thousands in acute hepatitis.
However, it’s important to note that having an ALT level over 100 doesn’t automatically imply a severe liver condition. It’s the persistent high levels of ALT that are often a cause for concern, suggesting chronic liver disease. In such cases, further investigation is usually warranted to determine the specific cause and implement appropriate treatment.
Temporary vs. Chronic High ALT
Sometimes, ALT levels can temporarily spike due to factors such as intense exercise, alcohol consumption, or medication use. This short-term increase usually isn’t a cause for alarm and often resolves on its own without treatment.
On the other hand, chronic high ALT levels, especially those twice or thrice the upper normal limit persisting for several months, may indicate a more serious, ongoing issue with liver health. Chronic high ALT could be a sign of conditions like chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or other forms of liver disease. If you have persistently high ALT levels, it’s critical to consult with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, ALT is a valuable indicator of liver health. Understanding your ALT levels and knowing when to worry can play a significant role in preventing and managing potential liver diseases.

Symptoms of High ALT Levels
ALT is an enzyme that leaks into your bloodstream when your liver cells are damaged. High ALT levels are typically a symptom themselves indicating liver damage. They don’t usually manifest in visible symptoms, and most people discover their elevated ALT levels through routine blood work or tests for other conditions.
While elevated ALT levels primarily indicate liver damage, their impact on health can extend beyond the liver, affecting your overall wellness and daily functioning. Here are some ways that high ALT levels—and the liver issues causing them—can manifest:
Physical Health
- Excessive perspiration and body odor: Your body may try to expel toxins through sweat, leading to excessive perspiration and body odor.
- Weight gain or unexplained weight loss: With a toxic liver, you may struggle with weight gain, especially around the abdominal area. For some people, however it can lead to excessive weight loss.
- Skin issues: Conditions like acne, rashes, or eczema could indicate liver toxicity.
- Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms associated with high ALT levels is a persistent sense of tiredness or fatigue. You may feel a general lack of energy or get tired more easily.
- Dark urine: Your urine might be dark or amber-colored due to excess bilirubin excretion.
- Abdominal discomfort: You may experience discomfort or pain in the upper right section of your abdomen, directly under your ribs where your liver is located.
- Easy bruising or bleeding: A damaged liver produces fewer of the proteins necessary for blood clotting, leading to easy bruising or bleeding.
Mental Health
- Cognitive symptoms: In severe cases, when liver disease has progressed, you might experience symptoms like confusion, memory loss, altered sleeping habits, and difficulty concentrating.
- Nausea or loss of appetite: Liver issues can lead to a feeling of nausea or a loss of appetite, which can also result in unintentional weight loss.
Metabolism and Nutrition
- Digestive issues: You may experience frequent indigestion, constipation, diarrhea, bloating or discomfort in the abdominal area
- Nutritional impact: The liver plays a crucial role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Liver damage can thus lead to nutritional deficiencies, impacting overall health.
Liver Health
- Jaundice: This condition causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow, indicating a problem with your liver’s ability to filter out bilirubin.
- Ascites: If your liver is damaged, you may experience an uncomfortable swelling in your abdomen due to a build-up of fluid known as ascites.
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. If you notice any of these symptoms persistently, especially along with high ALT levels, you should seek medical advice to identify the root cause and receive proper treatment.
Understanding the impact of high ALT levels can inspire early action, timely treatment, and lifestyle modifications. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and limiting alcohol consumption are some lifestyle choices that can keep ALT levels in check, ensuring a healthier liver and overall well-being.
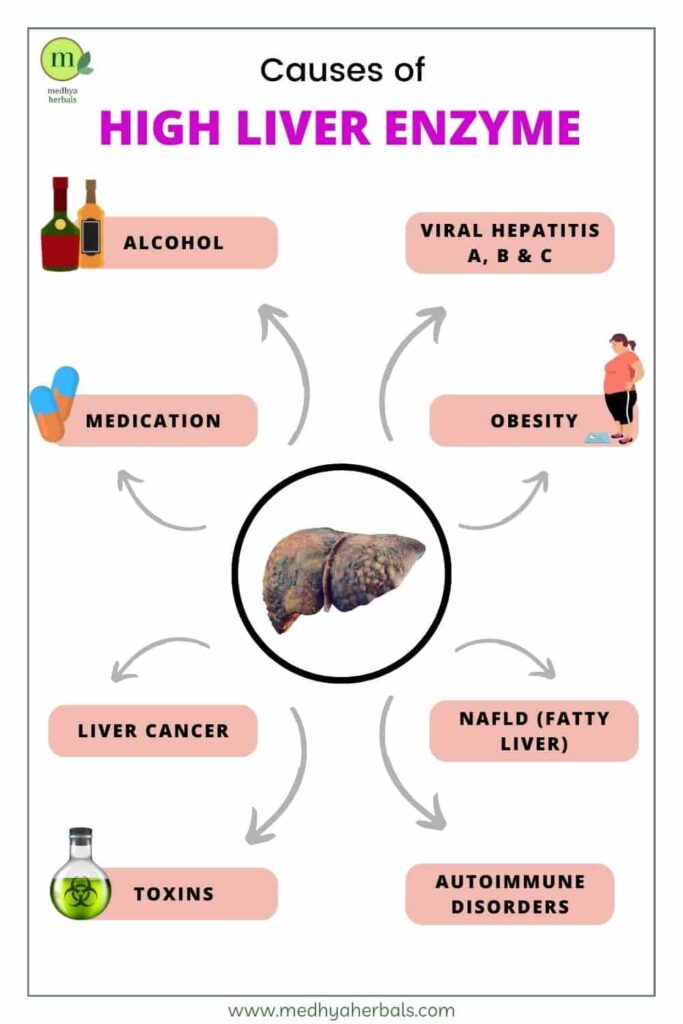
Causes of High ALT Levels
ALT, or Alanine Aminotransferase, is an enzyme primarily found in the liver. It’s released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged, so high levels of ALT in a blood test could indicate some form of liver disease. Let’s take a detailed look at what might cause high ALT levels.
Liver Diseases
Various liver diseases can result in high ALT levels, including:
- Hepatitis: Hepatitis A, B, and C are viral infections that can cause inflammation and damage to the liver, leading to increased ALT levels.
- Cirrhosis: This is a late-stage liver disease where healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, reducing liver function.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This is a condition where fat builds up in the liver, causing inflammation and damage. It’s often associated with obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- Alcoholic liver disease: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage liver cells, leading to inflammation and increased ALT levels.
Medications and Supplements
Certain medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), statins (used to control cholesterol), and some antibiotics can increase ALT levels. Overuse of certain dietary supplements, like iron or vitamin A, could also result in elevated ALT.
Other Health Conditions
Other health conditions that can cause high ALT levels include:
- Heart failure: A severe form of this condition can lead to liver damage and higher ALT levels.
- Celiac disease: This autoimmune disorder can cause liver inflammation, thus increasing ALT levels.
- Thyroid disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can result in elevated ALT levels.
Addressing High ALT Levels
Unlike most organs in the body, the liver can regenerate new cells to replace damaged ones. This regenerative ability allows it to recover from a certain amount of damage. However, this process isn’t infinite. If the liver is repeatedly injured and scar tissue continually forms, it could lead to cirrhosis, a condition where the liver function is significantly impaired due to extensive scar tissue.
If you’ve discovered that your ALT levels are elevated, it’s important to understand the factors influencing these levels and the ways you can manage them.
Natural Ways to Lower ALT Levels Quickly
There are several natural and medical approaches to lowering ALT levels:
- Adopt a healthy diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support liver health. Foods like garlic, berries, grapes, beetroot juice, cruciferous vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish have been shown to be particularly beneficial for the liver.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help to burn triglycerides for fuel and reduce liver fat, which in turn can help to lower ALT levels.
- Maintain a healthy weight: If you’re overweight or obese, reducing your weight in a healthy way can help to decrease your ALT levels and improve your liver health.
- Limit alcohol and avoid illicit substances: Alcohol and illicit substances can cause significant liver damage and elevate ALT levels. It’s best to avoid these substances or consume them in moderation.
- Regular check-ups: Regular health check-ups and liver function tests can help catch any increase in ALT levels early before it leads to significant liver damage.
- Avoid unnecessary medications: Certain over-the-counter and prescription medications can harm the liver if taken in large amounts or for prolonged periods. Always follow your doctor’s instructions when taking medication.
In addition to these natural ways, your healthcare provider may recommend specific medications or interventions based on the underlying cause of the elevated ALT levels.
How Diet Impacts ALT Levels and Your Liver
Your diet can significantly impact your ALT levels. The foods and beverages you consume can either support or harm your liver’s ability to perform its essential functions.
A diet high in saturated fats, sugars, and alcohol can lead to weight gain, which can, in turn, lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) — a common cause of elevated ALT. NAFLD can cause the liver to swell, leading to damage and increased ALT levels.
On the other hand, a diet rich in liver healthy foods such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help maintain normal ALT levels. Let’s explore which ones to embrace and which ones to avoid.
Foods to Take to Lower ALT Levels
1. Leafy Greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and Brussels sprouts are high in antioxidants that can help protect the liver from damage.
2. Fruits: Berries, grapes, and citrus fruits are rich in antioxidants. Additionally, fruits like papaya and banana are high in fiber and can help in maintaining a healthy weight, thus reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
3. Lean Protein: Proteins are essential for liver repair. Include lean sources like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes in your diet.
4. Whole Grains: Foods like oatmeal, brown rice, and whole grain bread are rich in fiber, which can help control your weight and thus reduce your risk of fatty liver disease.
5. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are rich in healthy fats and vitamin E, known for their liver-protective effects.
6. Coffee and Green Tea: Studies suggest that coffee and green tea can lower the risk of developing liver disease and also slow its progression if the disease is already present. Howver, they should be taken in moderation.
7. Stay hydrated: Water plays a vital role in detoxifying the body and supporting liver function. Ensure you’re drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Foods to Avoid for High ALT Levels
1. Alcohol: Excessive consumption of alcohol can lead to liver damage, thus increasing ALT levels.
2. Fried and Fatty Foods: Foods high in saturated fats can lead to weight gain, increasing the risk of fatty liver disease.
3. Sugary Foods and Drinks: These can also lead to weight gain and fatty liver disease. Avoid soda, candy, and foods with added sugars.
4. Salt: High sodium intake can cause fluid retention and exacerbate liver complications. Avoid processed foods that often contain hidden sodium.
5. Red and Processed Meats: These can be high in saturated fats and may increase inflammation in the liver.

Ayurvedic Natural Remedies for High ALT Levels
Ayurveda, a holistic medical science, has been addressing liver health for thousands of years. It offers a range of natural remedies to help maintain optimal liver function and manage conditions that lead to high ALT levels.
Triphala
Triphala, a traditional Ayurvedic formulation consisting of three fruits: Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Bibhitaki (Terminalia belerica), and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), is renowned for its detoxifying and rejuvenating properties. It promotes digestion, eliminates toxins, and helps in maintaining a healthy liver.
Turmeric
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant herb. Its active compound, curcumin, protects the liver from damage and has been shown to reduce ALT levels in certain studies.
Licorice
Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) is another herb widely used in Ayurvedic medicine. It has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help in protecting the liver and reducing ALT levels.
Bhumyamalaki
Bhumyamalaki (Phyllanthus niruri) is known for its hepatoprotective properties. It has been used traditionally for liver disorders, and research suggests it can lower ALT levels.
Kutki
Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa) is a potent hepatoprotective herb, highly respected in Ayurvedic medicine for its impact on liver health. It helps detoxify the liver and maintain healthy ALT levels.
While these remedies can support liver health and help manage high ALT levels, it’s essential to remember that they should be used under the supervision of a trained Ayurvedic practitioner, particularly because liver issues can be complex and may require a personalized approach to treatment.
Conclusion
We understand that navigating health concerns such as elevated ALT levels can be overwhelming. The wealth of information available may seem daunting and it’s challenging to discern which advice to follow for your unique situation. You may have tried various remedies, perhaps without seeing the progress you hoped for. It’s essential to remember that everyone’s body is different, and what works for one person may not work for another.
That’s where the experienced team of Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals comes in. With their comprehensive understanding of Ayurvedic medicine and its root-cause approach to treatment, they can guide you on a personalized path towards improved health. Our approach acknowledges that your body is a complex interconnected system. By understanding the underlying causes of elevated ALT levels, our team can offer treatment strategies that bring long-term relief, not just temporary fixes.
We invite you to schedule a consultation with our Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals. They will work closely with you, considering your unique circumstances and tailoring a treatment plan that not only addresses your immediate health concerns but also promotes overall wellness. Let us walk this journey to better health with you – because you don’t have to navigate it alone.
FAQ
Does ALT Change Daily?
Yes, ALT levels can fluctuate daily due to a variety of factors. These can include diet, exercise, hydration status, alcohol consumption, medication use, and the presence of any liver-damaging conditions. However, significant and persistent increases in ALT are typically an indication of liver disease or damage, and should not be taken lightly.
How Quickly Can ALT Levels Drop?
The speed at which ALT levels drop can vary widely depending on the cause of the elevation and the measures taken to address it. In cases where the high ALT is due to temporary factors like alcohol consumption or medication side effects, ALT levels might normalize within a few days to weeks once these factors are addressed. In other instances, particularly with chronic liver disease, it may take several weeks to months of consistent treatment and lifestyle modification to see a significant decrease in ALT levels.
Does High ALT Always Indicate Liver Damage?
While a high ALT level is often associated with liver damage, it doesn’t always indicate a severe liver condition. The liver is a resilient organ that can often manage minor damages without significantly impacting its function. Thus, a temporary rise in ALT levels can sometimes occur due to non-severe causes such as intense physical activity, short-term medication use, or alcohol consumption.
However, a persistently high ALT level—particularly when it’s more than twice the upper limit of the normal range—generally suggests ongoing liver inflammation or damage. Conditions such as chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or even some forms of cancer can lead to sustained high ALT levels.
It’s also essential to note that some people with liver diseases might still have ALT levels within the normal range. Therefore, while high ALT is a strong indicator of liver health issues, a normal ALT level does not definitively rule out liver disease.
What vitamins help the liver?
Certain vitamins play key roles in maintaining liver health and function. Vitamin A has antioxidant properties that help protect the liver from damage. B vitamins, particularly B12, aid in liver detoxification processes. Vitamin C, known for its antioxidant properties, helps in preventing oxidative damage to liver cells. Vitamin D, besides its role in bone health, may have protective effects on the liver and help prevent liver diseases. Vitamin E is another powerful antioxidant that can help reduce inflammation and damage in the liver, particularly useful in managing conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Always remember to get your vitamins from a balanced diet, or consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Can I reverse my liver damage?
Depending on the extent and cause of the damage, liver damage can often be reversed or at least halted. The liver is an organ with remarkable regenerative abilities. If the cause of liver damage—like excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, or exposure to certain toxins—is removed early enough, the liver can repair and regenerate itself over time. Even in the case of diseases like Hepatitis B and C, early and appropriate treatment can help stop or slow the damage and reduce complications. However, severe or advanced stages of liver diseases such as cirrhosis may be irreversible, underscoring the importance of early detection and treatment. As always, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your individual circumstances.
How do I keep my ALT levels down?
Keeping your ALT levels down largely involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking care of your liver. Incorporate a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your daily routine, while limiting consumption of alcohol, saturated fats, and sugars. Regular exercise can help manage your weight and reduce the risk of conditions like fatty liver disease, which can lead to elevated ALT levels. Moreover, avoid exposure to toxins that can harm liver cells, including those in some cleaning products, pesticides, and certain medications. Regular check-ups allow for early detection and management of any liver issues, and it’s important to follow any treatment plans prescribed by your healthcare professional. Remember, your liver health is integral to your overall well-being, so treating your liver kindly will have wide-ranging benefits.
Can high ALT be fixed?
Yes, high ALT levels can often be managed and even brought back to normal. Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme found mostly in your liver, and high levels typically signal liver damage. The key to fixing high ALT levels is to address the underlying cause, whether that’s a viral infection, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, or a reaction to certain medications. Depending on the cause, changes in diet, lifestyle modifications, or specific medical treatments might be recommended. For instance, if the elevated ALT is due to alcohol, ceasing consumption can help. If it’s due to obesity, weight loss and regular exercise can often help reduce ALT levels. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to identify the cause of the high ALT and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Time Frame for ALT Levels to Return to Normal After Liver Damage
The time frame for ALT levels to return to normal after liver damage can vary greatly depending on the severity and cause of the damage. In mild cases, if the damaging factor (such as alcohol, drugs, or a virus) is removed, ALT levels can decrease within weeks to months. In more severe or chronic cases, it may take several months or even longer for ALT levels to fully normalize. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will be needed to monitor your liver function and ALT levels during this recovery period.

