With a staggering 88 million people in the U.S. estimated to have pre-diabetes, a condition characterized by insulin resistance, understanding how to manage this health issue has never been more critical. Especially for women, where the impact extends beyond diabetes, affecting hormonal balance and potentially leading to conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). As a seasoned Ayurvedic Doctor, my experience with countless patients has reiterated one fact: a strategic approach to diet can be a game-changer in restoring insulin sensitivity.
If you find yourself perpetually fatigued, constantly battling hunger pangs, struggling with an expanding waistline, or having difficulty concentrating, you may be facing the invisible challenge of insulin resistance. Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Herein lies your roadmap to managing insulin resistance, filled with practical insights derived from Ayurveda’s age-old wisdom and cutting-edge nutritional science.
Join me as we delve into the intricacies of the insulin resistance diet, uncover the best and worst foods for your blood sugar, unravel the mysteries surrounding weight loss with insulin resistance, and explore potential strategies for restoring insulin sensitivity. With the right knowledge and tools at your disposal, you can retake control of your well-being, and I’m here to guide you every step of the way.
Below you can also download 7 days Insulin Resistance diet plan pdf version to make healthy diet a pillar of success for your treatment! This is your ultimate guide to reverse Insulin Resistance with your diet.
Understanding Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose for energy or storage.
In insulin resistance, due to the decreased response, the body needs higher amounts of insulin to help glucose enter cells. This causes the pancreas to produce more insulin, leading to higher levels of insulin in the blood, a condition known as hyperinsulinemia.
Over time, insulin resistance can lead to prediabetes and eventually type 2 diabetes, as the pancreas may not be able to keep up with the body’s increased demand for insulin. Besides, insulin resistance is often associated with other health conditions, such as heart disease and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
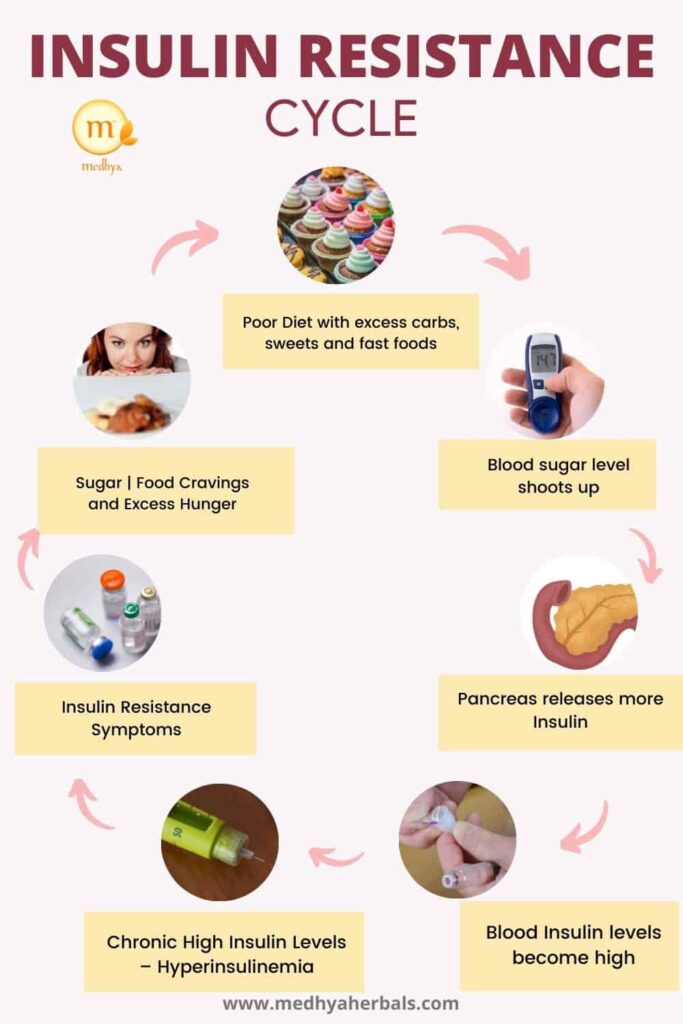
Main Causes of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is not triggered by a single cause but is instead a cumulative result of several factors:
-
- Excessive weight: Obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor. Extra fat in your body makes it harder for cells to respond to insulin.
-
- Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise leads to weight gain and a higher risk of insulin resistance.
-
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugars contributes to insulin resistance.
-
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt your body’s hormonal balance, leading to insulin resistance.
-
- Sleep deprivation: Lack of sleep can affect your body’s insulin needs.
-
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can increase your risk.
-
- Age and family history: Your risk increases as you age and if insulin resistance or diabetes runs in your family.
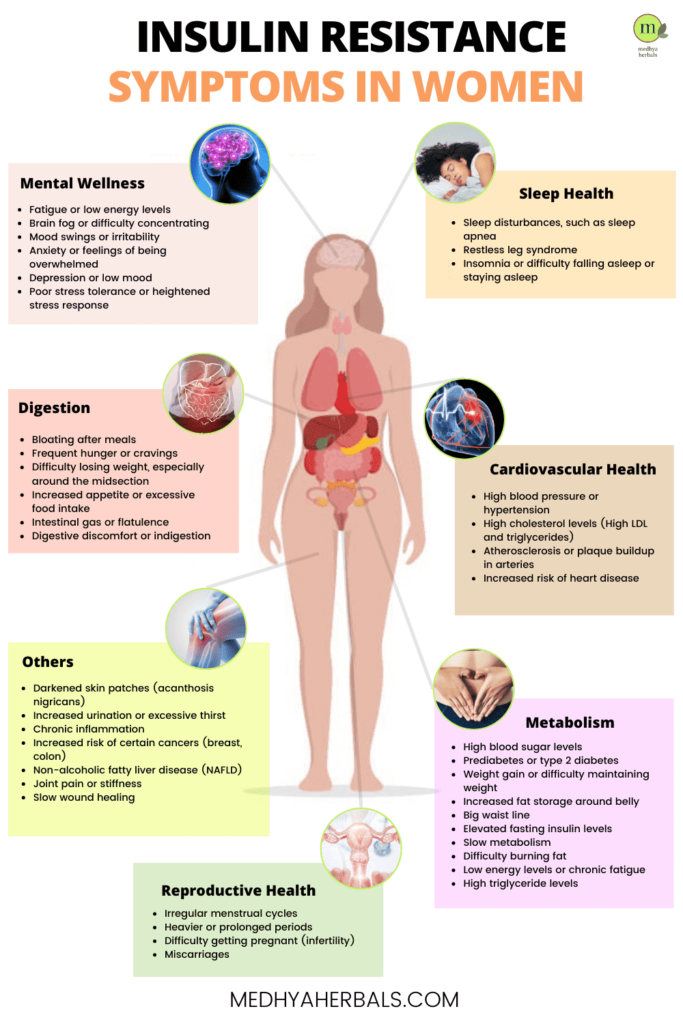
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance can be the first step towards managing this condition. Here are the symptoms you should be aware of:
-
- Fatigue: You may feel tired and drained out most of the time, even when you’ve had adequate rest.
-
- Constant Hunger: You might experience frequent bouts of hunger, even shortly after eating.
-
- Difficulty Concentrating: Also known as ‘brain fog,’ this symptom can make it challenging to focus and complete tasks.
-
- Weight Gain: Especially around the middle, weight gain is a common sign of insulin resistance.
-
- Cravings for carbs and sugars: Insulin resistance can lead to cravings for sugary foods and complex carbohydrates.
-
- High blood pressure: Insulin resistance can often coexist with high blood pressure.
While insulin resistance is indeed a serious condition, the silver lining is that it’s manageable, and in some cases, reversible. The key lies in understanding how lifestyle choices, especially diet, can influence your insulin sensitivity. As you continue to read, you will discover the Ayurvedic approach to dietary changes that can help balance your blood sugar levels.
The Role of Diet in Managing Insulin Resistance
The food you consume plays a significant role in managing insulin resistance. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, causing blood sugar levels to rise. In response, your pancreas releases insulin to help cells absorb this glucose. In the case of insulin resistance, your cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, causing your pancreas to produce more insulin and blood sugar levels to remain high.
A diet high in refined carbs and sugars can exacerbate this situation, causing rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. On the other hand, a balanced diet with whole foods, fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain steady blood sugar and insulin levels.
Understanding the Glycemic Index
The glycemic index ranks food based on their immediate effect on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI value (70 or higher) are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a quicker and more significant rise in blood sugar levels, contributing to insulin resistance. These are typically refined foods, such as white bread, most white rice, and sugary drinks.
On the other hand, foods with a low GI value (55 or less) are slowly digested and absorbed, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar and insulin levels. These foods are usually rich in fiber, protein, or fat. Thus low-GI foods can help manage blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Examples include whole fruits and vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
The glycemic index is particularly relevant for individuals managing insulin resistance or diabetes. While the glycemic index is a useful tool, it’s not the only factor to consider when planning a diet for insulin resistance. Other aspects, such as the overall nutritional content of the food, the amount consumed, and the cooking method, can also influence blood sugar responses.

What to Eat with Insulin Resistance
It’s possible for anyone to experience temporary insulin resistance, but if it persists, it can evolve into more serious conditions like prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Fortunately, making changes to your diet and incorporating specific foods into your meals can significantly enhance your insulin sensitivity.
This way your muscle, fat, and liver cells can absorb glucose more effectively with lesser amounts of insulin, thus helping you to reverse insulin resistance eventually. Here’s a detailed list of some powerful food choices on an insulin resistance diet:
Fibre-Rich Foods
Foods high in fibre help slow the digestion and absorption of sugars, thus preventing blood sugar spikes and promoting better insulin sensitivity. Examples of fibre-rich foods include:
-
- Whole grains like brown rice, oats, barley, and quinoa
-
- Fruits and vegetables, particularly with their skin
-
- Legumes like lentils and beans
-
- Nuts and seeds
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins are not only essential for cell repair and growth but can also help regulate blood sugar levels. Including them in your diet can provide a sense of satiety, preventing overeating, which can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance. Some lean proteins to consider are:
-
- Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines
-
- Skinless chicken and turkey
-
- Eggs
-
- Plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, and tofu
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, particularly mono and polyunsaturated fats, can improve insulin sensitivity and provide a slow, steady source of energy. They can also reduce inflammation, which is often linked with insulin resistance. Here are some sources of healthy fats:
-
- Avocadoes
-
- Nuts and seeds
-
- Fatty fish
-
- Olive oil
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants combat inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which can contribute to insulin resistance. Foods rich in antioxidants can, therefore, help improve insulin sensitivity. These include:
-
- Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries
-
- Green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale
-
- Nuts and seeds
-
- Dark chocolate
Probiotic-Rich Foods
Probiotics can improve the health of your gut microbiome, which in turn can influence your insulin sensitivity. Foods rich in probiotics include:
-
- Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi
-
- Miso and tempeh
Remember, the key to a healthy diet for insulin resistance is balance and variety. Consuming a range of these beneficial foods, alongside regular physical activity and lifestyle changes, can go a long way in managing and potentially reversing insulin resistance.
Worst Foods to Avoid for Insulin Resistance
Successfully managing insulin resistance involves mindful dietary choices. There are several foods and beverages that, when consumed frequently or in large quantities, can exacerbate insulin resistance. Understanding these can help you make more informed and healthful decisions.
Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates are processed to remove fiber and other nutrients, leaving a food product that rapidly increases blood sugar levels. This group includes white bread, white pasta, white rice, and most pastries and desserts.
High Sugar Foods and Drinks
High-sugar foods and drinks can cause rapid spikes in insulin and blood sugar levels, thus contribute to insulin resistance. These include:
-
- Sweetened coffee or tea
-
- Candy and chocolates
-
- Desserts and baked goods
-
- Sports Drinks
-
- Soda
-
- Processed juices
Trans Fats
Trans fats, typically found in partially hydrogenated oils, are known to increase insulin resistance. These can be found in numerous processed foods, including pastries, packaged snacks, and certain margarines. They’re commonly found in:
-
- Fried foods
-
- Fast food
-
- Processed snacks like chips and crackers
-
- Baked goods
-
- Full-fat dairy and fatty cuts of meat
-
- Certain margarines
Processed Meats
Regular consumption of processed meats, like sausages, bacon, and hot dogs, has been associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, a condition closely tied to insulin resistance.
Alcohol
While moderate alcohol consumption may not lead to insulin resistance, excessive drinking can. Additionally, many alcoholic beverages are high in sugar and can cause significant spikes in blood glucose levels.
Remember, moderating the intake of these foods and drinks is key in managing insulin resistance effectively. It’s crucial to balance your diet with nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods that support healthy blood sugar levels and enhance insulin sensitivity.
Insulin Resistance Diet Chart
Now that you have an understanding of the choice of foods, let’s dive into the details of an Insulin resistance diet chart.

As you saw above, one of the key ingredients of insulin resistance diet is variety of wholesome fresh foods that are cooked in an easy to digest way. Here is your diet chart on meal proportion and distribution:
30% Meal Portion should be Fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods.
30% Meal Portion should be Complex Carbs as Whole grains, cereals, and starch-based food products
30% Meal Portion should be Lean proteins such as lentils, beans, fermented soy products
10% Meal Portion should be Healthy Fats
Natural Ways to Reverse Insulin Resistance
Implementing healthy lifestyle changes can be a powerful tool in improving insulin resistance, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin. As you navigate your journey towards better health, it’s important to understand that alongside a balanced diet, there are several other natural ways that can play a significant role in reversing insulin resistance.
Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity. Exercise helps your muscles use glucose more efficiently and decreases insulin resistance even without weight loss. Activities such as brisk walking, running, cycling, swimming, or strength training can all be beneficial. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for hormone regulation, including insulin. Studies have found that sleep deprivation can lead to increased insulin resistance. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and consider practices such as a regular sleep schedule, a cool and dark bedroom, and a pre-bedtime relaxation routine to improve sleep quality.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance and lead to increased insulin resistance. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep-breathing exercises, and other relaxation practices can help manage stress levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help keep your blood sugar levels within healthy limits and promote kidney health, helping them eliminate excess sugar in the blood.
Quit Smoking
Smoking has been linked to insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. If you’re a smoker, quitting can significantly improve your insulin sensitivity.
Limit Alcohol
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits, excessive drinking can lead to insulin resistance and many other health problems. It’s advisable to limit alcohol to moderate levels – up to one drink per day for women and two for men.
Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and routine blood work can help monitor blood sugar levels, ensuring that any changes in insulin sensitivity are caught early and managed appropriately.
Conclusion
Managing insulin resistance may seem challenging, but remember that you’re not alone on this journey. Every individual’s body responds differently to changes in diet and lifestyle, making it important to seek personalized advice for your unique situation. While the comprehensive insights provided in this article serve as a guide, it’s important to remember that the journey to improved health is often paved with personalization and understanding of one’s own body.
We know how hard it can be to find relief from conditions like insulin resistance. It can feel frustrating and overwhelming at times, but rest assured that there are solutions available. Ayurveda, with its focus on treating the root cause of health issues, can provide lasting relief. Through Ayurvedic treatments, we aim to restore the balance in your body, enhance your insulin sensitivity, and help you lead a healthier and more energetic life.
At Medhya Herbals, our experienced Ayurvedic doctors are ready to guide you on your path to better health. We invite you to schedule a consultation with us, so we can provide a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs, lifestyle, and goals. Together, we can work towards managing and potentially reversing insulin resistance, enabling you to live your life to the fullest. Let’s embark on this healing journey together.
Below you can download 7 Days Insulin Resistance Plan pdf version for reference. If you need further support to follow the diet plan, lose weight or considering Ayurvedic treatment to manage or treat Insulin Resistance Naturally, do contact us here, we will help you out.
FAQ
How Long Does it Take to Fix Insulin Resistance?
There's no one-size-fits-all answer to this as it varies depending on individual health status, the degree of insulin resistance, and the consistency of lifestyle changes. Some might see improvements in a few weeks, while for others, it could take a few months. The key is consistency in maintaining positive lifestyle changes.
Remember, the journey towards reversing insulin resistance permanently is a gradual process. It requires persistence, patience, and a holistic approach. It might seem daunting, but with the right steps, it is an achievable goal.
Why It's Hard to Lose Weight with Insulin Resistance
Losing weight when dealing with insulin resistance is challenging due to the pivotal role insulin plays in body's metabolism. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, aids in glucose uptake from our bloodstream into cells for energy.
When insulin resistance occurs, cells aren't as responsive to insulin, causing inefficient glucose uptake. This prompts the body to produce more insulin, leading to an excess that triggers the body to store more calories as fat, particularly around the abdomen.
Additionally, elevated insulin levels disrupt the brain's satiety signals, often leading to overeating and consequent weight gain. Essentially, a complex cycle between insulin resistance and weight gain ensues, with each condition exacerbating the other. However, this cycle can be interrupted through dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss, leading to improved insulin sensitivity.
Can You Reverse Insulin Resistance Permanently?
While insulin resistance can be a challenging condition to manage, with the right strategies, it's possible to improve insulin sensitivity significantly. With a combination of diet changes, regular exercise, weight management, stress management, and enough sleep, it is possible to reverse insulin resistance.
However, maintaining these lifestyle changes long-term is necessary to ensure the condition doesn't return. It's essential to remember that it isn't about quick fixes but consistent, long-term changes in your diet, physical activity, and overall lifestyle.
Are Eggs Bad for Insulin Resistance?
Eggs, when consumed as part of a balanced diet, are not inherently bad for insulin resistance. They are a nutrient-dense food, offering high-quality protein and essential micronutrients that can support overall health.
Studies have shown mixed results on the impact of eggs on insulin resistance, with some indicating potential benefits while others suggest possible harm when consumed in excess.
However, how eggs are prepared and what they're paired with can significantly affect their nutritional impact. For instance, eggs cooked without added fats or oils and served with vegetables can be a healthy choice. As with any food, moderation is key, and it's crucial to consider eggs as part of the broader diet and lifestyle when addressing insulin resistance.
Role of Oats in an Insulin Resistance Diet
Oats play a significant role in an insulin resistance diet due to their high fiber content, specifically a type of soluble fiber known as beta-glucan. This fiber slows the rate at which carbohydrates are absorbed by the body, resulting in a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. Consequently, this prevents sharp spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, promoting better insulin sensitivity. Moreover, the fiber in oats contributes to feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management, an important factor in managing insulin resistance. Additionally, oats are a source of many other nutrients, such as magnesium, which has been associated with improved insulin response.
Can probiotics help with insulin resistance?
Yes, probiotics, beneficial bacteria, can potentially assist with insulin resistance. The gut microbiome, housing a vast collection of bacteria in our digestive tract, significantly influences our metabolic and weight management processes. Imbalances in these bacteria may contribute to insulin resistance, and probiotics can aid in restoring this microbial balance. Certain strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have been studied for their beneficial impact on insulin resistance, with promising preliminary results like improved blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Consuming probiotics through fermented foods or supplements, combined with a high-fiber diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management, can contribute to a comprehensive approach to managing insulin resistance. However, more robust research is needed to firmly establish the role of probiotics in managing insulin resistance.
The best supplements for insulin resistance
Supplements can potentially support insulin sensitivity alongside a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, though it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any regimen.
Some beneficial supplements include magnesium, which plays a role in insulin secretion and glucose use; chromium, involved in carbohydrate and fat metabolism; alpha-lipoic acid, an antioxidant studied for enhancing insulin sensitivity; Omega-3 fatty acids, known to reduce inflammation and improve cell function; probiotics, which can promote gut health and impact insulin sensitivity; berberine, a plant compound that could lower blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity; cinnamon, potentially helpful in lowering blood sugar and enhancing insulin sensitivity, though research results have been mixed; and vitamin D, deficiency of which is associated with insulin resistance. Nonetheless, these supplements should not replace a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle.
Effect of coffee on insulin levels
The effect of coffee on insulin levels is somewhat complex and depends on various factors, including the amount consumed, whether it's caffeinated or decaffeinated, and individual metabolic responses.
Some research suggests that moderate consumption of caffeinated coffee may temporarily reduce insulin sensitivity and raise blood sugar levels, which could be a concern for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Conversely, other studies indicate that long-term coffee consumption, especially decaffeinated coffee, might be associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, suggesting a potential improvement in insulin sensitivity over time.
However, given the mixed findings and individual variations, it's important to pay attention to your body's responses and discuss your coffee consumption with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about insulin resistance or diabetes.
References
- Insulin resistance & prediabetes. (2018). https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
- Low-glycemic index diet may improve insulin sensitivity in obese children. Pediatric Research. (2015). https://www.nature.com/articles/pr2015142
- Marine omega-3 (N-3) fatty acids for cardiovascular health: an update for 2020. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. (2020). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7072971/
- Nutrition therapy for adults with diabetes or prediabetes: a consensus report. Diabetes Care. (2019). https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/42/5/731/40480/Nutrition-Therapy-for-Adults-With-Diabetes-or
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. FoodData Central. [Internet 2019] Available: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/ Accessed October 6th, 2022.
- Hadipour E, Taleghani A, Tayarani-Najaran N, Tayarani-Najaran Z. Biological effects of red beetroot and betalains: A review. Phytother Res. 2020 Aug;34(8):1847-1867. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6653. Epub 2020 Mar 14. PMID: 32171042.
- Russo B, Picconi F, Malandrucco I, Frontoni S. Flavonoids and Insulin-Resistance: From Molecular Evidences to Clinical Trials. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2061. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092061. PMID: 31027340; PMCID: PMC6539502.
- Xavier AA, Pérez-Gálvez A. Carotenoids as a Source of Antioxidants in the Diet. Subcell Biochem. 2016;79:359-75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-39126-7_14. PMID: 27485230.
- Atkinson FS, Brand-Miller JC, Foster-Powell K, Buyken AE, Goletzke J. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values 2021: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 Nov 8;114(5):1625-1632. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab233. PMID: 34258626.
- Toi PL, Anothaisintawee T, Chaikledkaew U, Briones JR, Reutrakul S, Thakkinstian A. Preventive Role of Diet Interventions and Dietary Factors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients. 2020 Sep 6;12(9):2722. doi: 10.3390/nu12092722. PMID: 32899917; PMCID: PMC7551929.


Excellent information sir . Thanque very much