Hormonal imbalances are more than just an inconvenience; they can be the underpinning cause of numerous health issues affecting millions of women worldwide. Symptoms can vary from subtle to debilitating, with common indicators such as persistent fatigue, mood swings, sleep disturbances, and inexplicable weight changes. As an experienced Ayurvedic practitioner at Medhya Herbals, I understand how these symptoms can profoundly disrupt your everyday life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will journey through the realm of hormonal health. We will demystify hormonal imbalances, uncover their causes, and learn how to identify the signs in your own body. Drawing upon the rich tradition of Ayurveda, I will share 6 most effective strategies on how to balance hormones, including the role of diet, essential vitamins, and lifestyle adaptations.
Hormonal imbalances are a significant health issue, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can reclaim your well-being. Ready to unlock the secrets of hormonal balance? Dive in, and let’s begin this journey of discovery together.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones are complex. They’re powerful chemicals produced by your endocrine glands for regulating most major bodily processes, including body temperature, appetite, mood, stress levels, sleep cycles, metabolic rate, and reproductive cycles. They serve as an internal communication system between cells throughout the body. They coordinate everything from digestion and growth to appetite, immune function, mood, and libido.
What is Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormonal imbalances occur when there is too much or too little of a hormone in the bloodstream. Because of their essential role in the body, even small hormonal imbalances can cause severe effects throughout the body.
Estrogen dominance, for example, can lead to symptoms such as weight gain, mood swings, and heavy menstrual cycle. Low thyroid function can cause fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, can lead to excessive hunger and weight gain. High cortisol levels, often caused by chronic stress, can result in anxiety, sleep disturbances, and other symptoms.
It’s important to remember that hormonal imbalances are common, and they can occur during natural life stages like puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. However, hormonal imbalances can also be caused by external factors such as stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and certain medical conditions.
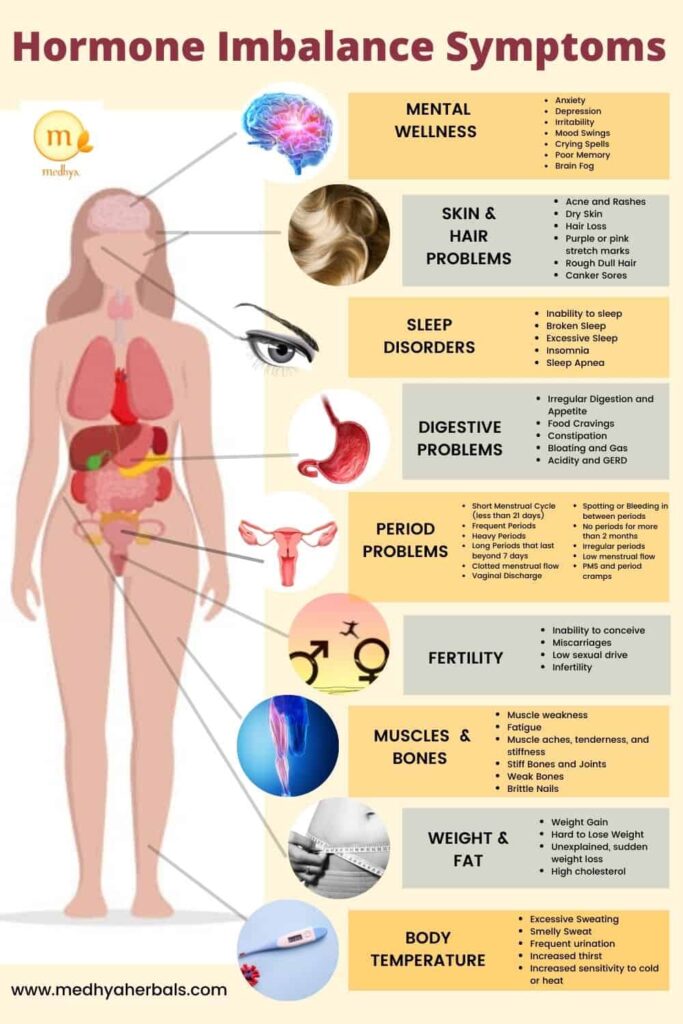
Hormonal Imbalance Symptoms in Females
Hormonal imbalances can result in a wide range of symptoms depending on which hormones are out of balance. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Persistent Fatigue: Even after adequate sleep, you may feel constantly tired.
- Sleep Irregularities: You may experience insomnia or find that you’re more tired than usual.
- Mood Swings and Emotional Instability: Hormones can affect your emotional well being, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and irritability.
- Unexplained Weight Changes: You may experience sudden weight loss or weight gain that’s not due to changes in diet or exercise.
- Skin Issues: Acne, dry skin, and skin rashes are common indicators of hormonal imbalance.
- Body Temperature Changes: Feeling unusually hot or cold can be a sign of hormonal imbalance.
- Changes in Heart Rate: Hormonal imbalances can cause your heart rate to change, often leading to palpitations.
- Trouble Concentrating and Memory Issues: Hormones help regulate cognitive functions, so imbalances may result in difficulty focusing or remembering things.
- Digestive Issues: Digestive problems like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea can also indicate a hormonal imbalance.
- Changes in Appetite: You may experience increased hunger or a lack of appetite.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: For women, changes in the menstrual cycle, such as irregular periods or heavy bleeding, can be a sign of a hormonal imbalance.
- Decreased Libido: A decrease in sexual desire can be caused by hormonal changes.
Remember, you may not experience all of these symptoms. In fact, the specific symptoms you might experience depends on which glands and hormones are affected.
What is Hormonal Balance?
Hormonal balance refers to the optimal regulation and interaction of hormones within the body’s endocrine system. Hormones play an instrumental role in virtually every process in our body. When they are balanced, our bodies operate like a well-oiled machine. This balance aids in maintaining our mood, weight, digestion, and overall energy levels stable. Optimal hormonal balance can result in improved mental clarity, a feeling of vitality, and an overall sense of well being.
Hormonal balance is crucial for overall health and well being. When hormones are in balance, individuals often experience good energy levels, a strong immune system, healthy skin, and a generally positive mood. They sleep well, have a healthy libido, and find it relatively easy to maintain their weight.
The time it takes for hormones to balance naturally can vary widely from person to person. It depends on several factors, including the degree of the hormonal imbalance, the specific hormones involved, and how rigorously the lifestyle changes are implemented. It’s also important to note that while lifestyle modifications can significantly improve hormone balance, some conditions might require additional medical treatments or interventions.
How to Naturally Balance Your Hormones
Balancing the hormones involves a combination of lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management. Here are the top 6 ways that will give you best results at any age and for all health conditions:
1. Foods that Balance Hormones in Females

A hormone balancing diet is essentially an eating plan that promotes optimal hormonal balance in your body. This type of diet involves incorporating foods that support hormone health and limiting those that can disrupt it. Hormones play a crucial role in regulating many of your body’s processes, including metabolism, reproduction, mood, and sleep, to name a few. Thus, eating a hormone-friendly diet is key to overall wellness.
Here are some key components of a hormone balancing diet:
Balanced Macronutrients
Each meal should contain a balance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Proteins provide the building blocks for hormone production, while healthy fats are crucial for creating the structure of hormones. Carbohydrates, particularly complex carbs from whole foods, provide energy and can help regulate the body’s insulin response.
Quality Protein
Protein provides essential amino acids that your body can’t produce on its own, which are necessary for hormone production. Foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and seeds are great sources of high-quality protein.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, fatty fish, olives, nuts, seeds, and coconut, play a key role in hormone production. In particular, omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for hormonal health because they can reduce inflammation and help balance hormone levels.
High-Fiber Foods
Fiber, particularly from whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help manage your body’s insulin response, a key factor in hormone balance. Fiber can also support a healthy gut microbiome, which is connected to hormone regulation.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants can protect your body from oxidative stress, which can disrupt hormone balance. Foods rich in antioxidants include colorful fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, spices, and quality dark chocolate.
Adequate Hydration
Water is essential for every process in your body, including hormone production and function. Drinking enough water can help ensure that your body has what it needs to produce hormones effectively.
Limited Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain added sugars and unhealthy fats, which can disrupt your body’s insulin response and overall hormone balance. Limiting these foods and replacing them with whole, nutrient-dense options can support hormonal health.
Controlled Caffeine
While a moderate amount of caffeine can be part of a healthy diet, too much can increase cortisol levels and disrupt hormone balance. If you’re sensitive to caffeine or struggling with hormonal imbalances, it may be worth considering reducing your caffeine intake.
Remember, a hormone balancing diet isn’t about strict restrictions or dieting. Instead, it’s about nourishing your body with nutrient-dense foods that support hormonal health.
2. Nutritional Supplements and Vitamins to Balance Hormones for Females
Alongside a balanced diet, certain supplements can support your hormonal health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s are essential for hormone production. They can help reduce inflammation and are known to support mood and brain health.
- Vitamin D: Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin”, vitamin D plays a crucial role in hormone production and regulation. It’s also essential for bone health, immune function, and inflammation control.
- Magnesium: This mineral is crucial for a multitude of bodily functions. For hormones, it can help manage PMS symptoms, improve sleep, and support mood.
- B-Vitamins: B-vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for hormone regulation. They’re particularly important for women of reproductive age.
- Probiotics: A healthy gut microbiome can significantly influence your hormones. Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut flora, supporting not only your digestion but also hormone regulation.
- Adaptogens: Apart from ashwagandha and rhodiola, there are other adaptogenic supplements like holy basil (tulsi) and ginseng that help your body adapt to stress, supporting overall hormonal balance.
Remember, while nutritional supplements can support hormonal health, they’re not a replacement for a healthy diet and lifestyle.
3. Natural Remedies for Hormonal Imbalance in Females

Herbs have been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda for their potent healing properties. Here are some herbs that have been shown to support hormonal balance:
- Ashwagandha: This adaptogenic herb has been used in Ayurveda for centuries. It helps your body manage stress by reducing cortisol levels. It can also help in improving thyroid function, reducing anxiety and depression, and enhancing mood.
- Chaste Tree Berry (Vitex): Vitex is widely recognized for its benefits in women’s hormonal health. It can help alleviate premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms, regulate menstrual cycles, and reduce menopause symptoms.
- Black Cohosh: Used traditionally to relieve menopausal symptoms, black cohosh may help manage hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, and mood swings.
- Maca: This Peruvian plant may help balance estrogen and progesterone levels. It’s known to enhance energy, mood, and also support fertility.
- Rhodiola Rosea: This adaptogen helps your body respond to stress better, whether it’s physical or emotional. It has been shown to reduce cortisol levels and support thyroid function.
Remember, while herbs can be powerful, they can also interact with medications and aren’t suitable for everyone. Always consult with a healthcare provider or an Ayurvedic expert before starting any herbal remedy.
4. Quality Sleep for Hormonal Balance
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of hormonal balance. During sleep, your body works to restore and repair various functions such as your immune system, muscle tissue, and memory. This restorative process is governed by certain hormones, which are released or suppressed during different stages of sleep.
When we sleep, our body regulates the production of several key hormones:
- Cortisol, often called the stress hormone, follows a natural daily (circadian) rhythm where it’s higher in the morning to help you wake up and gradually decreases throughout the day. However, a lack of sleep or poor-quality sleep can disrupt this rhythm, leading to higher cortisol levels at night, which can make it harder to fall asleep.
- Melatonin is known as the sleep hormone. Its primary function is to signal to your body that it’s time for sleep. When it’s dark, your body produces more melatonin, making you sleepy. Conversely, light suppresses melatonin production. Lack of quality sleep or irregular sleep-wake cycles can disrupt melatonin production, impacting your ability to fall asleep and the quality of your sleep.
- Growth hormone is primarily released during deep sleep. It plays a crucial role in bodily growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration, making it vital for healing and restoration.
- Leptin and ghrelin are two hormones that regulate hunger and satiety. Leptin decreases hunger, while ghrelin increases it. When you don’t get enough sleep, leptin levels drop, and ghrelin levels rise, leading to increased hunger and appetite, which can disrupt hormonal balance and potentially lead to weight gain and other health problems.
How to get Good Sleep for Hormonal Balance?
To maintain hormonal balance, it’s not just the number of hours you sleep that matters but the quality of your sleep as well. Here are some strategies to improve sleep quality:
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate your body’s internal clock, known as your circadian rhythm. This consistency can improve the quality of your sleep.
- Create a Restful Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using eye shades, earplugs, or a white noise machine if necessary. A comfortable mattress and pillows can also enhance sleep quality.
- Limit Exposure to Screens Before Bed: The light emitted by phones, tablets, computers, and TVs can interfere with the production of melatonin, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Mind Relaxing Activities: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your nighttime routine. This might include reading, meditating, listening to calm music, or taking a warm bath.
- Be Mindful of Eating Habits: Try not to go to bed too hungry or too full. Both can disrupt your sleep. Also, limit how much you drink before bed to prevent disruptive middle-of-the-night trips to the toilet.
- Avoid Stimulants: Stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine can interfere with the ability to fall asleep.
Remember, it’s normal for your sleep patterns to change occasionally due to factors like stress or illness. However, if you regularly have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, it may be worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
5. Stress Management to Balance Hormones Naturally
Stress is an inevitable part of life, but chronic stress can disrupt your hormonal balance and negatively impact your overall health. It’s crucial to understand the role of stress and hormones in your body and the importance of effective stress management techniques.
The primary hormone involved in the stress response is cortisol, produced in the adrenal glands. In times of stress, cortisol levels rise to help your body deal with the perceived threat. This is part of the “fight or flight” response, which prepares your body for action. While this response is essential in truly threatening situations, chronic stress can lead to consistently high levels of cortisol, which can disrupt your overall hormonal balance.
Consistently high cortisol levels can interfere with the function of other hormones, including insulin (the hormone regulating blood sugar levels), thyroid hormones (which regulate metabolism), sex hormones (like estrogen and testosterone), and melatonin (the sleep hormone). This can lead to a variety of health issues, including poor sleep, weight gain, mood swings, and even more serious conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
How to Manage Stress for Hormonal Balance?
To manage stress and maintain hormonal balance, consider incorporating the following stress management techniques:
Mindfulness and Meditation
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help manage stress and lower cortisol levels. These practices encourage relaxation and can help you stay focused on the present moment, reducing feelings of anxiety and stress. Even a few minutes of meditation each day can make a difference.
Yoga and Breathing Exercises
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, which can all help reduce stress. Specific breathing exercises, like deep abdominal breathing or alternate nostril breathing, can activate your body’s relaxation response, reducing stress and lowering cortisol levels.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is a great stress reliever. It helps reduce cortisol levels and stimulates the production of endorphins, your body’s natural mood lifters. This doesn’t have to be intense exercise; even gentle activities like walking or cycling can be beneficial.
Healthy Diet
A diet rich in whole foods, especially fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates, can help your body better cope with stress. These foods provide the nutrients your body needs to function properly and maintain hormonal balance.
Adequate Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is essential for stress management and hormonal balance. Lack of sleep can increase cortisol levels and disrupt other hormones, leading to increased stress and anxiety.
Social Connections
Staying connected with friends and family, or participating in social activities, can help manage stress. Social connections can offer emotional support, improve your mood, and act as a natural stress reliever.
Professional Help
If you’re struggling with chronic stress and having difficulty managing it on your own, consider seeking professional help. Therapists and counselors can provide techniques and strategies to manage stress effectively.
6. Regular Exercise for Hormonal Balance
Regular exercise is a powerful tool for maintaining hormonal balance. Not only does it impact your physique and mood, but it also plays a crucial role in regulating various hormones in your body. From insulin to growth hormones, cortisol to endorphins, regular exercise can influence these hormones in beneficial ways.
Here’s a closer look at how regular physical activity aids in hormonal balance:
Insulin Sensitivity
Exercise increases your sensitivity to insulin by promoting the uptake of glucose into your muscles for energy. This means that your body needs less insulin to lower your blood glucose levels, reducing the risk of insulin resistance, which is associated with conditions like diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Cortisol Regulation
Cortisol is often referred to as the ‘stress hormone’. While acute spikes in cortisol are necessary in situations of immediate danger, chronic elevations due to stress can have negative health impacts. Exercise, particularly mindful activities like yoga and Tai Chi, can help reduce cortisol levels, assisting in managing stress and promoting a feeling of calm and relaxation.
Endorphin Release
Endorphins are often termed ‘feel-good’ hormones. These are neurotransmitters that produce a feeling of happiness and euphoria. Regular physical activity, particularly high-intensity exercises or endurance exercises, can trigger the release of endorphins, uplifting your mood and promoting a sense of well-being.
Growth Hormone and Testosterone
Regular exercise, particularly resistance and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), stimulates the release of growth hormone and testosterone. These hormones play a crucial role in muscle growth and repair, bone health, and metabolism.
Estrogen and Progesterone
For women, regular physical activity can help regulate the menstrual cycle and balance levels of estrogen and progesterone. Regular exercise can also alleviate symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause.
To enjoy these hormonal benefits, try to incorporate a mix of different types of exercise into your routine:
- Aerobic Exercise: Also known as cardio, aerobic exercises like walking, running, swimming, or cycling are great for heart health and weight management.
- Resistance Training: This includes weightlifting or bodyweight exercises. Resistance training is great for building and maintaining muscle mass and bone density.
- Flexibility Exercises: Incorporate activities like yoga or Pilates to maintain flexibility and balance, and to aid in stress relief.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise alternated with low-intensity recovery periods. HIIT is a great way to improve cardiovascular health and insulin sensitivity and stimulate the release of growth hormones.
Remember, it’s important to listen to your body and choose a form of exercise that you enjoy and that suits your current fitness level.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of hormonal imbalance can feel like walking through a maze, especially when symptoms cloud our everyday life. We understand how challenging it can be to find relief from the myriad of symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances. But rest assured, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right support and guidance, achieving hormonal balance is not only attainable but can bring about transformative changes to your health and well-being.
The ancient wisdom of Ayurveda provides a holistic approach, offering not just symptomatic relief, but targeting the root cause of the imbalance. By harnessing the power of nature, through dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, and nutritional supplements, Ayurveda aims to restore the natural balance in your body, creating a ripple effect of wellness throughout your life.
At Medhya Herbals, our team of experienced Ayurvedic doctors is ready to guide you on your path to hormonal balance. We invite you to schedule a consultation with us. Together, we will create a personalised treatment plan, tailored specifically to your needs. Embrace the promise of Ayurveda, and take the first step towards a healthier, happier, hormonally balanced you today.
FAQ
How Serious is Hormonal Imbalance?
The seriousness of a hormonal imbalance is dependent on its cause, the specific hormones involved, and how the imbalance manifests within an individual’s body. Hormones regulate numerous bodily functions, including metabolism, reproduction, mood, growth, and development. Therefore, an imbalance can lead to a variety of health issues, some of which can be quite severe.
For instance, imbalances in insulin can lead to diabetes, a chronic condition that can have significant long-term effects on the body if not properly managed. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), another condition related to hormonal imbalance, can lead to infertility, metabolic syndrome, and increased risk of endometrial cancer if left untreated. Thyroid hormone imbalances can cause issues with metabolism, energy levels, and body temperature regulation, among other symptoms. Prolonged periods of stress can also lead to hormonal imbalances that may contribute to anxiety disorders or depression.
It’s also essential to remember that the effects of hormonal imbalances aren’t only physical. They can also cause emotional distress and impact an individual’s quality of life. Nevertheless, with appropriate diagnosis and treatment, many people with hormonal imbalances can effectively manage their symptoms and lead healthy lives. The key lies in early detection, understanding the root cause, and following a comprehensive treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, medication, or in some cases, surgery.
How Can I Check if My Hormones are Balanced?
Suspecting a hormonal imbalance and wondering how to check it is the first step towards understanding your body’s internal workings. If you’re experiencing persistent, unexplained symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, weight fluctuations, or sleep disturbances, you may want to consider having your hormones checked.
A specialist in hormone-related conditions or an endocrinologist can help assess your hormone levels. They’ll start by discussing your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. It’s crucial to provide a detailed account of your symptoms and any changes you’ve noticed in your body. This might include changes in your menstrual cycle if you’re a woman, changes in mood, sleep patterns, appetite, weight, and energy levels. Here’s a 2 mins hormone imbalance test quiz that you can take to know which hormones might be out of balance for you.
How are Hormone Levels Tested?
If a hormonal imbalance is suspected based on your symptoms and medical history, the doctor will likely order certain diagnostic tests. Blood tests are the most common method used to measure hormone levels. Depending on your symptoms, you may be tested for levels of hormones related to the thyroid, estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, insulin, or others.
In some cases, a saliva test or urine test may be used instead of, or in addition to, a blood test. These tests can be particularly useful for monitoring how hormone levels fluctuate throughout the day. Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, might also be used to check for any abnormalities in the endocrine glands.
Remember, only a healthcare professional can accurately diagnose a hormonal imbalance. If you suspect that your hormones may be out of balance, it’s important to seek medical advice rather than trying to diagnose or treat the problem yourself. Hormonal imbalances can usually be managed with the right treatment, leading to improved symptoms and quality of life.
How to Balance Your Hormones in a Week?
Balancing hormones is a gradual process and it usually takes more than a week for significant changes to take effect. However, adopting certain lifestyle and dietary changes can initiate the process and help you feel better in a week’s time. Starting with a nutrient-rich diet, make sure you’re consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds can be particularly beneficial for hormonal balance. Also, consuming fibre-rich foods can aid digestion and regulate insulin levels.
Moreover, engage in regular physical activity to regulate various hormones such as insulin and cortisol. Exercise aids in better sleep, which is a crucial element in hormonal balance. Implement stress management techniques like deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness, as chronic stress can wreak havoc on your hormonal balance. Limit your caffeine intake and establish a healthy sleep routine to ensure adequate rest. Please note that while these steps can initiate hormonal balance, they are part of a longer journey towards overall well-being and must be maintained for a sustained period for significant results.
References
- The Relationship between Diet and Hormones
- Hormonal and Neuroendocrine Regulation of Energy Balance
- Hormone Imbalance
- http://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/really-acne/adult-acne
- https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/cushing-syndrome/
- http://www.hormone.org/diseases-and-conditions/breast-cancer
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7432488/
- https://medlineplus.gov/hyperthyroidism.html
- http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/hypothyroidism
- http://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/home-use-tests/menopaus
- http://www.womenshealth.gov/menopause/menopause-basics
- http://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/polycystic-ovary-syndrome
- https://medlineplus.gov/primaryovarianinsufficiency.html
- https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/primary-ovarian-insuffiency
- https://medlineplus.gov/puberty.html
- http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/puberty
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279105/#gynecomastia-etiolog.INTRODUCTION
- https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/testosterone-levels-test

