Are you eating healthy but your weight isn’t going down? Have you been doing intermittent fasting for long, yet it hasn’t gotten you much weight loss results! Are you exercising regularly, but your waistline is still growing? The culprit could be stubborn weight gain due to hormones!
Hormonal weight gain is a common problem among both men and women. It is caused by an imbalance in hormones that can lead to an increase in appetite, fat storage, and decreased metabolism.
In this post, I will explain exactly which hormones are involved when you experience hard to lose weight and stubborn belly fat. Then I will share tips on how to balance hormones naturally to feel more motivated, get healthy, and burn stubborn body fat.
What Hormones Cause Weight Gain?
Research has proven that fat loss and weight gain are controlled at a cellular level by hormones in your body. Often these hormones are intricately interconnected such that if one is imbalanced, it disturbs others too.
While, there are multiple hormones that play a role in regulating our weight and metabolism, the most important hormones are Cortisol, Estrogen, Thyroid, Insulin and Leptin. Together these 5 hormones really decide the areas of body where fat deposits are placed, your metabolism and the rate at which you will gain or lose weight.
That’s why, if you can balance these hormones, you can reverse hormonal weight gain and also get rid of the hormonal imbalance symptoms.

Estrogen
Estrogen is a hormone that plays a key role in regulating the menstrual cycle, bone density, and fat distribution in women. However, a decrease in esrogen levels during menopause can lead to an increase in visceral fat, which is the type of fat that surrounds the organs and can increase the risk of several health problems such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Thyroid
Thyroid hormone plays a key role in regulating metabolism and energy production in the body. When thyroid hormone levels are low, metabolism slows down, which can lead to an increase in weight. Symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland include weight gain, fatigue, constipation, and feeling cold.
Cortisol
Cortisol is a hormone that is produced in response to stress and helps the body respond to a threat or danger. However, chronic stress can lead to an increase in cortisol levels, which can cause an increase in appetite and fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels by helping glucose enter the cells to be used for energy. However, insulin resistance, which is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin, can lead to an increase in blood sugar levels and weight gain.
Leptin
Leptin is a hormone that is produced by fat cells and helps regulate appetite and metabolism. However, leptin resistance, which is a condition where the body becomes resistant to leptin, can lead to an increase in appetite and weight gain.
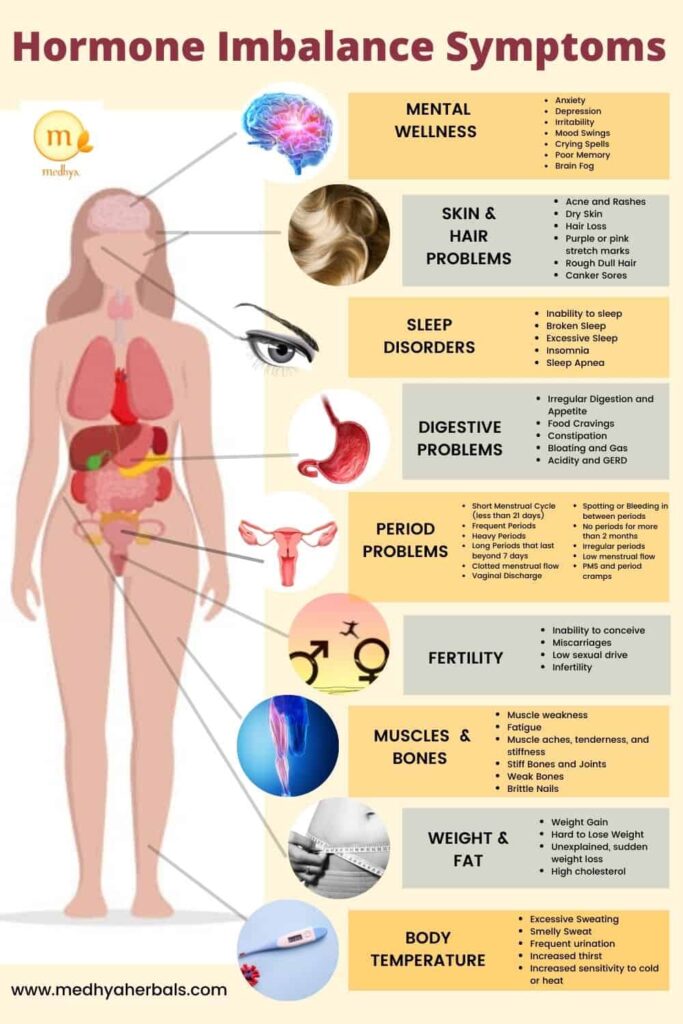
Hormonal Weight Gain Symptoms
Weight gain due to hormones is commonly associated with the creation of visceral fat which surrounds the internal organs like the pancreas and liver. Visceral belly fat is highly dangerous as it increases the possibility of metabolic syndrome and acquiring chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes and heart conditions.
The symptoms of hormonal weight gain can vary depending on the underlying hormonal imbalance, but some common signs and symptoms include:

- Increase in appetite: Hormonal imbalances can cause an increase in appetite, which can lead to overeating and weight gain.
- Cravings for sweets and carbohydrates: Hormonal imbalances can also cause cravings for sweets and carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain.
- Difficulty losing weight: Hormonal imbalances can make it difficult to lose weight, even with a healthy diet and exercise.
- Fatigue: Hormonal imbalances can cause fatigue and decreased energy levels, which can make it difficult to exercise and lead to a sedentary lifestyle.
- Insomnia: Hormonal imbalances can disrupt sleep patterns and cause insomnia, which can lead to weight gain due to decreased metabolism and increased appetite.
- Mood swings: Hormonal imbalances can cause mood swings and irritability, which can contribute to overeating and weight gain.
- Decreased libido: Hormonal imbalances can also decrease libido and sexual function, which can lead to decreased physical activity and weight gain.
- Constipation: Hormonal imbalances can disrupt digestive function and cause constipation, which can contribute to weight gain due to decreased metabolism.
- Depression: Hormonal imbalances can also lead to symptoms of depression and mood swings, which can contribute to overeating and weight gain.
- Brain fog: Hormonal imbalances can cause symptoms of brain fog, including difficulty concentrating and memory problems, which can make it difficult to make healthy choices and lead to overeating and weight gain.
- Irregular menstrual cycle: Hormonal imbalances can cause irregular menstrual cycles, which can be a sign of underlying health problems and contribute to weight gain due to hormonal fluctuations.
Which Areas are affected by Hormonal Weight Gain?
Hormonal weight gain can affect several areas of the body, including:

- Abdomen: Hormonal imbalances can cause an increase in fat storage in the abdominal area, which can lead to a “muffin top” or a protruding belly.
- Hips and thighs: Hormonal imbalances can also cause an increase in fat storage in the hips and thighs, which can lead to a “pear-shaped” body type.
- Face and neck: Hormonal weight gain can also cause an increase in fat storage in the face and neck, which can lead to a double chin and facial puffiness.
- Arms: Hormonal imbalances can cause an increase in fat storage in the arms, leading to a “bat wing” appearance.
- Breast: Hormonal weight gain can also cause an increase in breast size due to an increase in fat storage.
What Causes Hormonal Weight Gain?
Hormonal weight gain results from hormonal fluctuations in the body. This can occur due to several reasons, including menopause, stress, medication, and hormonal imbalance disorders:
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to an increase in cortisol levels, which can cause an increase in appetite and fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
- Medication: Certain medications such as antidepressants, corticosteroids, and antipsychotics can cause weight gain as a side effect by disrupting hormone levels and metabolism.
- Hormonal therapy (HRT): HRT is often prescribed to women during menopause to help relieve symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness. However, HRT can also lead to weight gain due to an increase in estrogen levels.
- Birth control pills: Birth control pills can also cause weight gain as a side effect, especially in women who are sensitive to hormonal fluctuations.
- Hysterectomy: Hysterectomy, which is the surgical removal of the uterus, can also lead to hormonal weight gain due to the disruption of hormone levels and metabolism.
Health Conditions that Cause Hormonal Weight Gain
- Thyroid problems: An under active thyroid gland can lead to a decrease in metabolism, which can cause weight gain due to a decrease in the thyroid hormone, which plays a key role in regulating metabolism and energy production in the body.
- Menopausal weight gain: Menopause is a natural process that occurs in women typically between the ages of 45-55. During menopause, there is a decrease in estrogen levels, which can lead to an increase in visceral fat, decreased metabolism, and weight gain.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by an imbalance in hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, which can lead to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. Women with PCOS also have an increased risk of developing insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and discomfort. Hormonal imbalances, particularly in estrogen and progesterone, can contribute to the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus. This can cause weight gain due to the disruption of hormone levels and metabolism.
How to Lose Hormonal Weight Gain?
It is important to note that losing hormonal weight gain may take time and patience. While, you may not see immediate results, consistent efforts with proper guidance will help you to lose weight, balance hormones and prevent future health risks. Here are 5 most important steps you need to take to being losing weight due to hormonal imbalance:
Eat a balanced diet
Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate hormones and prevent weight gain. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats can also help reduce inflammation and promote a healthy metabolism.
Exercise regularly
Regular exercise can help regulate hormones, increase metabolism, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, five days a week. Resistance training such as weight lifting can also help build muscle mass and increase metabolism.
Manage stress
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to weight gain. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness can help regulate hormones and promote weight loss.
Get enough sleep
Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormone levels, decrease metabolism, and increase appetite. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night to regulate hormone levels and promote weight loss.
Consider medication or therapy
In some cases, medication or therapy may be necessary to regulate hormones and promote weight loss. Consult a doctor who can recommend appropriate treatment options.
Do note that it is also important to consult a doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of hormonal weight gain or have a health condition that may be contributing to hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
Hormonal weight gain can be a frustrating and discouraging problem to deal with, but it is not something that you have to live with. By making positive changes to your lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding triggers, you can regulate hormones and prevent weight gain due to hormonal imbalances.
Remember, small changes can lead to big results. It’s never too late to start taking care of yourself and making positive changes to your lifestyle. Don’t let hormonal weight gain hold you back from living your best life. Take control of your health, and start making positive changes today.
If you need help in making diet and lifestyle changes, contact Medhya Herbals to prepare your personalised Ayurvedic treatment plan. With the guidance of our highly experienced Ayurvedic doctors, you can overcome hormonal weight gain and achieve your health goals. So, let’s take the first step towards a healthier and happier you!
References
- Stress and Obesity: Are There More Susceptible Individuals?
- Cortisol, obesity and the metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study of obese subjects and review of the literature
- More evidence linking stress to obesity
- Hyperinsulinemia: a Cause of Obesity?
- Estrogen Deficiency and the Origin of Obesity during Menopause

