The journey to motherhood can be paved with uncertainties, especially when whispers of “low egg quality” and declining fertility cloud your path. You might be experiencing irregular periods, struggling to conceive, or facing the anxieties of AMH levels painting a less-than-rosy picture. Don’t lose hope! I’m here to guide you through the empowering world of Ayurveda, where ancient wisdom meets modern solutions to unlock your full fertility potential. Join me as we delve into the fascinating science of egg quality, demystify AMH’s role, and explore powerful Ayurvedic secrets to reclaim your reproductive health, naturally.
In the next few paragraphs, we will guide you through evidence-backed methods to identify and address these concerns, providing you with tangible steps to increase eggs in your ovaries, improve overall egg quality, and navigate fertility treatments like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) with confidence. Get ready to embrace a holistic approach that combines ancient wisdom with modern understanding, as we embark on a path toward improved reproductive well-being.
Understanding Egg Quality and its Impact on Fertility
Egg quality refers to the health and viability of a woman’s eggs, or oocytes, which significantly influences her fertility potential. The quality of eggs is crucial because it directly affects the chances of successful fertilization, embryo development, implantation, and ultimately, a healthy pregnancy.
When eggs are of good quality, they have the necessary genetic material and cellular machinery to undergo fertilization and early embryonic development successfully. However, poor egg quality can lead to difficulties in conception, increased risk of miscarriage, and higher chances of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
Several factors contribute to egg quality, including age, genetics, lifestyle, and hormonal balance. Among these, age is one of the most significant determinants. As women age, the number and quality of their eggs naturally decline, primarily due to a decrease in ovarian reserve, which refers to the number of remaining follicles containing eggs in the ovaries. This decline in egg quality is a major reason why fertility decreases with advancing age.
AMH and Its Role in Assessing Ovarian Reserve
AMH, or Anti-Müllerian Hormone, is a hormone produced by cells in ovarian follicles, and its levels in the blood can provide valuable insights into a woman’s ovarian reserve. Ovarian reserve refers to the quantity and quality of a woman’s remaining eggs.
AMH levels serve as a useful marker for assessing ovarian reserve because they reflect the number of follicles present in the ovaries. Higher levels of AMH generally indicate a larger number of follicles and, consequently, a better ovarian reserve. Conversely, lower levels of AMH suggest a reduced number of remaining follicles and may indicate diminished ovarian reserve.
By measuring AMH levels, fertility specialists can estimate a woman’s reproductive potential and tailor fertility treatment plans accordingly. For example, women with low AMH levels may require different approaches to ovarian stimulation during in vitro fertilization (IVF) or may be advised to consider alternative options, such as egg donation.
Poor Egg Quality Symptoms in Women
Identifying subtle indicators of bad egg quality is essential for those navigating fertility concerns. While not always overt, certain signs may suggest potential issues. Here are some subtle indicators to be aware of:
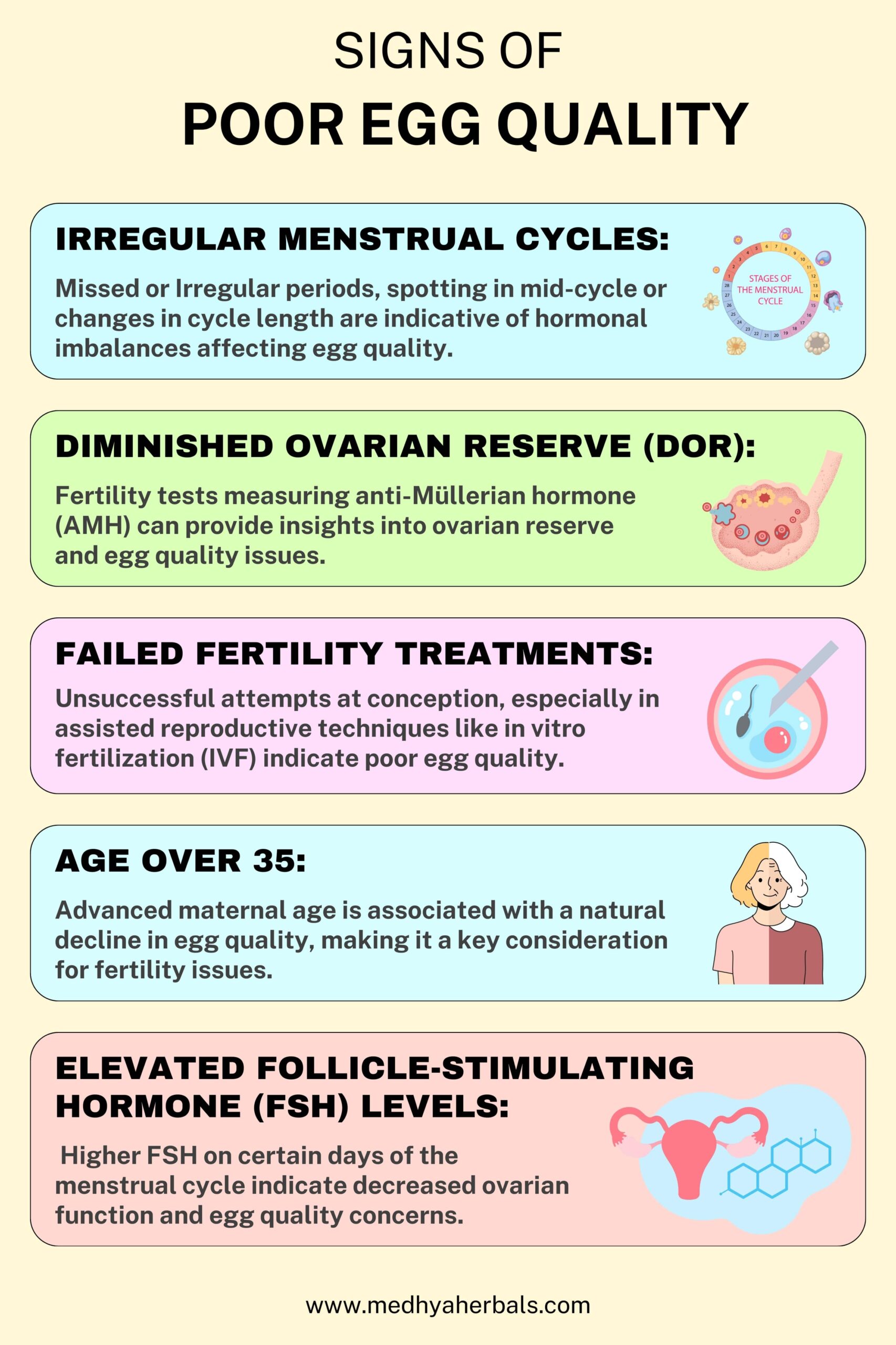
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Inconsistencies in menstrual cycles, such as irregular periods or changes in cycle length, can be indicative of hormonal imbalances affecting egg quality.
- Diminished Ovarian Reserve (DOR): Fertility tests measuring the quantity of remaining eggs, like anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) testing, can provide insights into ovarian reserve and potential egg quality issues.
- Failed Fertility Treatments: Unsuccessful attempts at conception, especially in assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF), may signal underlying problems with egg quality.
- Poor Response to Ovarian Stimulation: In fertility treatments requiring ovarian stimulation, a limited response in terms of follicle development may suggest compromised egg quality.
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Experiencing multiple miscarriages may point to chromosomal abnormalities in the eggs, impacting overall quality.
- Age Over 35: Advanced maternal age is associated with a natural decline in egg quality, making it a key consideration for fertility issues.
- Elevated Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Levels: Higher FSH levels on certain days of the menstrual cycle can indicate decreased ovarian function and potential egg quality concerns.
Impact of Stress and Emotions on Bad Egg Quality in Women
The impact of emotions on egg quality in women is a complex and interconnected aspect of reproductive health. Stress, anxiety, and negative emotions can potentially influence fertility and egg quality through various mechanisms:
- Hormonal Disruption: Emotional stress can trigger the release of stress hormones like cortisol, affecting the delicate balance of reproductive hormones. This imbalance may interfere with the maturation and release of healthy eggs.
- Blood Flow and Oxygenation: Chronic stress can lead to increased muscle tension and reduced blood flow to reproductive organs. Insufficient blood flow may compromise the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to the ovaries, impacting egg quality.
- Inflammation: Prolonged stress can contribute to chronic inflammation in the body. Inflammation has been linked to reproductive issues and may affect the overall health of eggs.
- Disruption of Ovulation: Emotional distress may disrupt regular ovulatory cycles, potentially leading to irregularities and impacting the quality of released eggs.
- Impact on Lifestyle Choices: Emotional challenges can influence lifestyle choices, such as poor dietary habits, lack of exercise, and unhealthy coping mechanisms like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. These factors can contribute to diminished egg quality.
Factors Contributing to Diminished Egg Quality in Women
Several factors can contribute to diminished egg quality in women, impacting fertility and reproductive health:
- Age: Advanced maternal age is a significant factor, as the number and quality of eggs decline with age.
- Genetics: Inherited genetic factors can influence egg quality, affecting fertility outcomes.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and other hormonal disorders can disrupt normal ovulation and compromise egg quality.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to environmental pollutants and toxins can have detrimental effects on egg health.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor nutrition, lack of exercise, and high levels of stress can contribute to suboptimal egg quality.
- Medical Treatments: Certain medical treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation, can negatively impact ovarian function and egg quality.
- Smoking and Substance Abuse: Tobacco and substance use have been linked to decreased fertility and poor egg quality.
- Reproductive Tract Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs may affect the maturation and release of eggs.
Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals seeking to optimize their reproductive health, and addressing them through holistic approaches can positively impact egg quality and overall fertility.
Relation between Egg Quality and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can have implications for egg quality in women. PCOS is a common endocrine disorder characterized by hormonal imbalances, enlarged ovaries containing small cysts, and irregular menstrual cycles. Here’s how PCOS may impact egg quality:
- Anovulation: Women with PCOS often experience irregular ovulation or anovulation (lack of ovulation). This irregularity can result in eggs not fully maturing, potentially affecting their quality.
- Hormonal Imbalances: PCOS is associated with elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance. These hormonal imbalances can disrupt the normal ovarian function, affecting the development and maturation of eggs.
- Quality of Ovulatory Cycles: Even when ovulation occurs in women with PCOS, the quality of the ovulatory cycles may be compromised. The eggs released during these cycles may be of lower quality, which can impact fertility.
- Hyperandrogenism: Elevated androgen levels in PCOS can contribute to the development of small follicles in the ovaries. These follicles may not mature properly, leading to a potential decrease in egg quality.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Some studies suggest that women with PCOS may have a slightly higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities in their eggs, which can impact the overall quality of the eggs.
Despite these potential challenges, many women with PCOS can still achieve successful pregnancies. It often requires a comprehensive and personalized approach to address the specific needs associated with PCOS and fertility.
How to Improve Egg Quality Naturally
Improving egg quality naturally involves adopting holistic lifestyle changes and incorporating practices that promote overall reproductive health. Here are key steps to enhance egg quality in women:
Diet for Fertility and Egg Quality
- Balanced Nutrition: Include a variety of nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Focus on antioxidants, found in berries, leafy greens, and nuts, which help combat oxidative stress and support egg health.
- Adequate Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to support optimal blood flow to reproductive organs and aid in the removal of toxins from the body.
- Supplements and Herbs: Consider supplements like folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, and CoQ10, known to support reproductive health.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Quit smoking, as it can accelerate egg aging and negatively impact fertility. Limit alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption may affect ovarian function.
- Limit Caffeine Intake: Moderate caffeine consumption, as high levels may be associated with fertility issues.
Lifestyle Practices for Fertility
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness to lower cortisol levels and promote hormonal balance.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate, regular exercise to improve blood circulation and promote overall well-being.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight, as extremes in weight, whether underweight or overweight, can impact reproductive health.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene to support hormonal balance and overall health.
- Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental pollutants, toxins, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals that may impact reproductive health.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor reproductive health and address any underlying issues.
Foods to Improve Female Egg Quality
Including certain nutrient-rich foods in your diet can support and potentially improve female egg quality. Here’s a list of foods that are known for their positive impact on reproductive health:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in folate, which is crucial for DNA synthesis and repair.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds provide essential fatty acids and antioxidants.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and trout contain omega-3 fatty acids, which support overall reproductive health.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources like chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes for essential amino acids.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients.
- Avocado: Rich in healthy monounsaturated fats and vitamin E, supporting overall fertility.
- Colorful Vegetables: Bell peppers, carrots, and sweet potatoes are high in antioxidants and vitamins.
- Greek Yogurt: A good source of protein and probiotics, promoting gut health, which is linked to fertility.
- Eggs: Eggs contain choline, a nutrient important for cell membrane structure.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons provide vitamin C, essential for collagen formation and absorption of iron.
- Broccoli: Rich in folate and fiber, supporting reproductive health.
- Pomegranate: Packed with antioxidants, it may enhance blood flow to the uterus.
- Dairy or Fortified Plant Milk: Ensure sufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
- Beans and Lentils: High in protein, iron, and folate, supporting overall health.

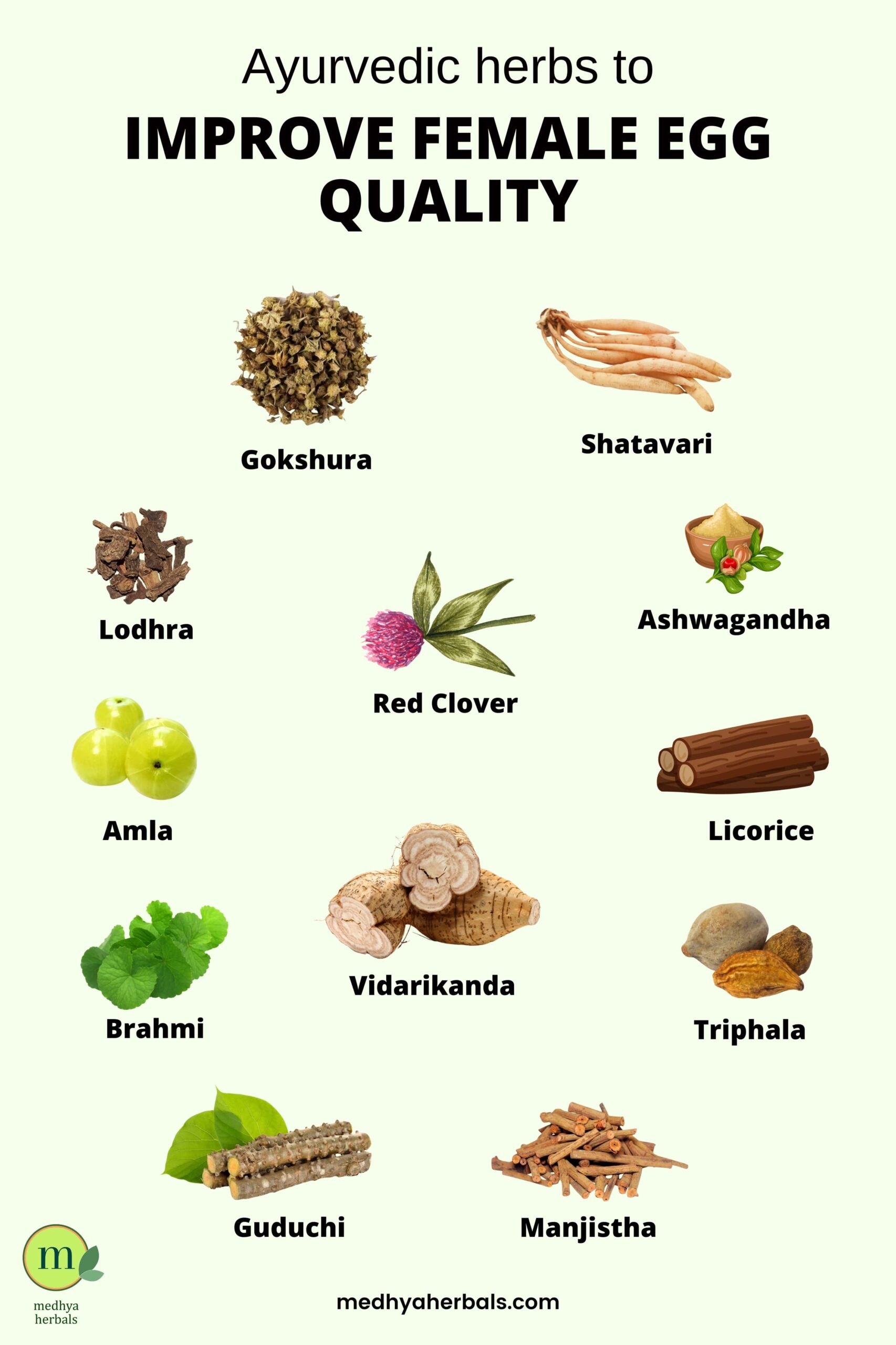
Ayurvedic Herbs to Improve Female Egg Quality
Ayurveda, the traditional system of medicine, offers various herbs that are believed to support female reproductive health and may contribute to improving egg quality. Here are some Ayurvedic herbs that are commonly used for this purpose:
- Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus): Shatavari is traditionally used to support female reproductive organs and hormonal balance.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): An adaptogenic herb, Ashwagandha helps manage stress and promotes hormonal harmony, potentially enhancing overall fertility.
- Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris): Gokshura is believed to support the reproductive system, balance hormones, and improve ovarian function.
- Amla (Emblica officinalis): A rich source of vitamin C and antioxidants, Amla helps in detoxification and supports overall reproductive health.
- Lodhra (Symplocos racemosa): Lodhra is traditionally used to balance female hormones and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Known for its calming effects, Brahmi may help reduce stress and anxiety, contributing to improved reproductive well-being.
- Triphala: A combination of three fruits (Amla, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki), Triphala is used for detoxification and promoting digestive health, indirectly supporting reproductive processes.
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Guduchi is believed to boost immunity and has anti-inflammatory properties, potentially supporting reproductive health.
- Red Clover (Trifolium pratense): Although not native to Ayurveda, Red Clover is sometimes included for its potential to support female reproductive health.
- Vidarikanda (Pueraria tuberosa): Vidarikanda is used to balance hormones and support the female reproductive system.
- Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra): Known for its adaptogenic properties, Licorice may help balance hormones and reduce stress.
- Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia): Manjistha is traditionally used for its blood-purifying properties, potentially supporting reproductive health.
Always consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner or healthcare professional before incorporating these herbs into your routine, if you have underlying health conditions. Ayurvedic approaches are individualized, and the suitability of herbs varies from person to person.

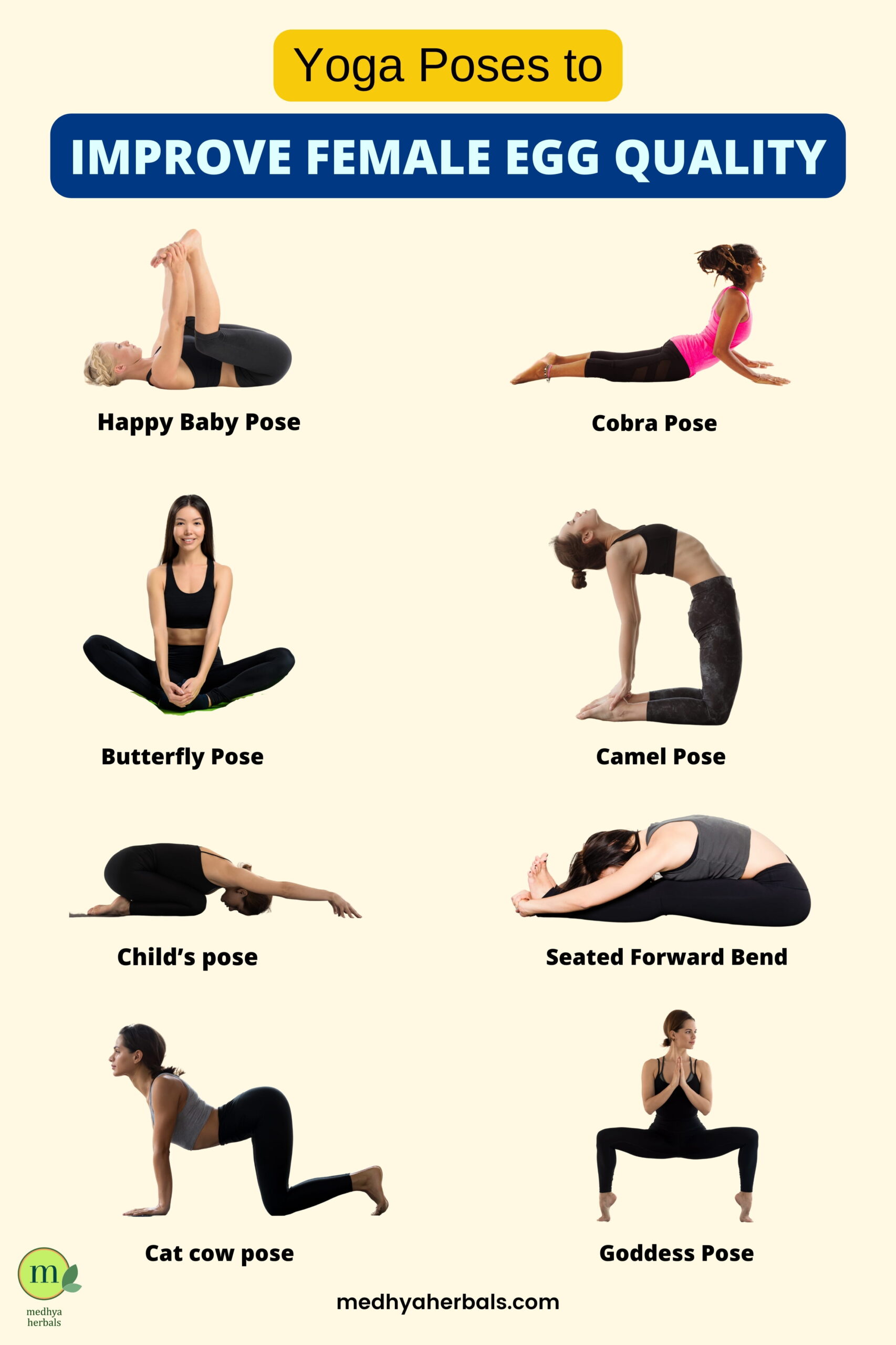
Yoga Poses to Improve Female Egg Quality
While yoga is not a direct cure for improving egg quality, it can contribute to overall reproductive health by reducing stress, promoting hormonal balance, and enhancing blood circulation to the pelvic region. Here are some yoga poses that are believed to support female reproductive health:
- Butterfly Pose (Baddha Konasana): Stimulates the ovaries and improves flexibility in the hip region.
- Supported Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana): Enhances blood circulation to the pelvic area and stimulates the abdominal organs.
- Legs Up the Wall Pose (Viparita Karani): Promotes relaxation, reduces stress, and increases blood flow to the pelvic region.
- Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana): Strengthens the reproductive organs, stimulates the ovaries, and helps improve digestion.
- Seated Forward Bend (Paschimottanasana): Stretches the spine, hamstrings, and pelvic region, promoting blood flow to the reproductive organs.
- Camel Pose (Ustrasana): Opens up the chest and abdomen, stimulates the ovaries, and improves flexibility.
- Reclining Bound Angle Pose (Supta Baddha Konasana): A restorative pose that helps relax the pelvic muscles and promotes a sense of calm.
- Goddess Pose (Supta Baddha Konasana): Similar to the butterfly pose, this variation involves reclining, promoting relaxation and flexibility.
- Child’s Pose (Balasana): Relieves stress and tension, promoting relaxation and overall well-being.
- Happy Baby Pose (Ananda Balasana): Opens up the hips and stretches the groin, promoting flexibility in the pelvic region.
- Cat-Cow Pose (Marjaryasana-Bitilasana): A gentle flow that improves spine flexibility, massages the reproductive organs, and stimulates hormonal balance.
- Mountain Pose (Tadasana): Focuses on grounding and balancing, promoting a sense of stability and calm.

Conclusion
The path to optimal egg health can seem long and winding, but know this – you are not alone. Millions of women navigate similar uncertainties, and the good news is, you don’t have to walk this path blindfolded. Ayurveda offers a profound understanding of women’s unique needs, unlocking a treasure trove of powerful solutions tailored to your individual journey. Remember, healing isn’t just about suppressing symptoms; it’s about addressing the root cause.
Our expert Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals are here to guide you every step of the way. Imagine personalized consultations delving into your unique health tapestry, crafting a bespoke plan that nourishes your body and mind from within. Picture dietary adjustments that spark vitality, herbal formulations that gently nudge your system towards balance, and practices that weave serenity into your daily life. We believe in empowering you to become the architect of your well-being, and our personalized approach ensures you get the support you deserve.
Take the first step today. Schedule a consultation with one of our Ayurvedic doctors and embark on a transformative journey towards vibrant egg health and a future brimming with possibility. Remember, you hold the power to rewrite your story – let Ayurveda be your guiding light.
FAQ
How can I improve my egg quality naturally for pregnancy?
Improving egg quality naturally for pregnancy involves adopting a holistic approach to enhance overall reproductive health. Focus on a balanced, nutrient-rich diet rich in antioxidants, incorporating foods like berries, leafy greens, and nuts. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by staying physically active, managing stress through practices like yoga or meditation, and ensuring sufficient sleep. Consider supplements such as folic acid, CoQ10, and omega-3 fatty acids, known to support reproductive well-being. Additionally, avoid harmful substances like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on optimizing your fertility journey.
What can damage woman’s eggs?
Several factors can potentially damage a woman’s eggs, impacting fertility and reproductive health. Advanced maternal age is a significant contributor, as the quantity and quality of eggs naturally decline over time. Genetic factors can play a role, with inherited conditions affecting egg development. Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), can disrupt regular ovulation and impact egg quality. Environmental factors, including exposure to toxins and pollutants, may also contribute to egg damage. Lifestyle choices such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition can further impact egg health. Medical treatments like chemotherapy or radiation can have detrimental effects on ovarian function and egg quality. Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals seeking to preserve and optimize their reproductive health, and addressing them through lifestyle changes and medical guidance can positively impact egg quality and overall fertility.
How can I improve egg quality in 2 weeks?
Improving egg quality in a short timeframe, such as two weeks, is a challenging task as the development and maturation of eggs typically occur over a longer duration. However, adopting certain lifestyle changes during this period can positively influence overall reproductive health. Focus on a nutrient-rich diet with antioxidants, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Stay adequately hydrated and prioritize sufficient sleep to support hormonal balance. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises. While significant improvements in egg quality may take time, these short-term adjustments can create a conducive environment for reproductive health and lay the foundation for long-term well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
What destroys egg quality?
Several factors can adversely impact egg quality in women. Advanced maternal age is a key contributor, as the number and quality of eggs naturally decline over time. Hormonal imbalances, particularly conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), can disrupt regular ovulation and affect egg development. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known to accelerate ovarian aging and decrease egg quality. Exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants may also contribute to egg damage. Additionally, certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation can have detrimental effects on egg quality. Understanding and addressing these factors through lifestyle changes and medical guidance is crucial for preserving and optimizing egg quality for overall reproductive health.
What are 5 foods that improve egg quality?
Certain foods are believed to contribute to improved egg quality by providing essential nutrients and antioxidants. Here are five foods that are commonly associated with supporting reproductive health:
- Berries
- Leafy Greens
- Nuts and Seeds
- Fatty Fish
- Whole Grains
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into a well-balanced diet is key for overall reproductive health. However, consultation with a healthcare professional or a nutritionist can provide personalized advice based on individual needs and health conditions.
References
- Impact of egg quality on fertilization and pregnancy rates: A review of factors affecting human embryo development: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3805019/ by Rienk AA et al. (2013) – Discusses the impact of chromosomal abnormalities and DNA damage on embryo development and pregnancy success.
- Age-related decline in egg quality: Age-related changes in human follicular oocytes: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1281758/ by Keefe DL (2004) – Explains the biological processes leading to decreased egg quality with age.
- AMH as a marker of ovarian reserve: The role of anti-Müllerian hormone in assessing ovarian reserve: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3250754/ by Broens PA et al. (2011) – Reviews the use of AMH as a tool for assessing ovarian reserve and its limitations.
- Genetic factors influencing egg quality: Mitochondrial DNA mutations and human oocyte quality: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2907171/ by Van Blerkom J et al. (2009) – Explores the link between mitochondrial DNA mutations and reduced egg quality.
- Lifestyle factors affecting egg quality: Lifestyle and environmental factors associated with female infertility: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3924315/ by Sifer LL et al. (2013) – Examines the negative impact of smoking, alcohol, and stress on egg quality.
- Medical conditions and egg quality: Endometriosis and ovarian reserve: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3054615/ by Agarwal R et al. (2010) – Discusses how endometriosis can affect ovarian function and egg quality.