Thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism, can significantly impact a woman’s fertility and lead to pregnancy complications if left unmanaged. As a woman trying to conceive, it’s essential to understand the challenges of hypothyroidism and pregnancy.
While the journey can be daunting, you should know that with proper management and care, women with hypothyroidism can have similar chances of getting pregnant as women without thyroid disorders. A study found that women with well-controlled hypothyroidism had a pregnancy rate of 84%, compared to 87% for women without thyroid disorders.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the impact of hypothyroidism on fertility, pregnancy, and post-pregnancy. I’ll also share with you Ayurvedic tips to help you support your fertility and confidently embark on this life-changing journey.
Understanding Thyroid Disease
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It produces thyroid hormones, which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development in the body. Thyroid hormones, mainly T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine and released into the bloodstream. They regulate the body’s metabolism, including heart rate, temperature, and energy production. Thyroid hormones also play a critical role in brain development, bone health, and muscle control.
Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, is a condition where the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in metabolism, growth, and development. An imbalance in thyroid hormones due to an under active thyroid or inflammation of thyroid gland can lead to various health issues, including potential complications during pregnancy.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism symptoms can be mild to severe. Since your metabolism is affected, the following symptoms may be noticed:
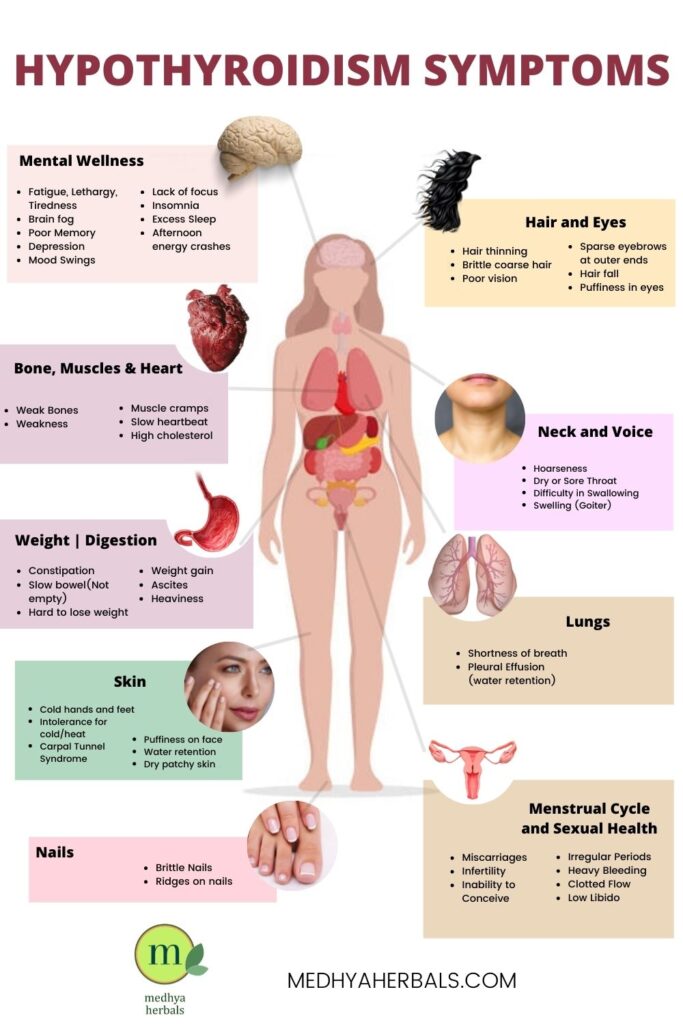
- Fatigue – One consequence of reduced metabolism is that you have less energy produced.
- Weight gain – If nutrients are not effectively metabolized, then can store up as fat, causing weight gain.
- Feeling cold when others are hot – metabolic activities generate heat and help you keep warm. If these activities are reduced however, then you have less heat.
- Joint and muscle pain
- Constipation
- Puffiness in the face
- Dry and thinning hair
- Dry skin
- Decreased sweating
- Heavy or irregular menstrual periods
- Impaired fertility
- Depression
- Reduced heart rate
What are the Causes of Hypothyroidism?
The following can cause a person’s thyroid gland to produce less thyroid hormones than needed:
- Hashimoto’s disease: This is an auto-immune disease. The immune system is supposed to protect you from disease. However, sometimes, it gets so overzealous, or confused, that it begins attack the body itself. In the case of Hashimoto’s disease, the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. The gland gets damaged, and it produces less thyroid hormones.
- Inflammation of the thyroid: this is called thyroiditis. Here, thyroid hormones leaks out of the gland. This will temporarily raise thyroid hormone levels, causing hyperthyroidism. Eventually, due to continuous leakage, hypothyroidism results.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: This is present at birth, and it may be fatal in a new born baby. This is why it is important to screen new born babies.
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland also causes hypothyroidism
- Radiation treatment of the thyroid: Radiation therapy can be given for some conditions like cancer. The radiation can damage the thyroid gland and cause problems also.
- Medications: Some medications can interfere with the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism and Infertility
Hypothyroidism can cause elevated levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which can interfere with ovulation and decrease fertility. High TSH levels can lead to increased prolactin secretion, which can suppress ovulation and interfere with the menstrual cycle. Prolactin is a hormone that stimulates milk production in lactating women. High prolactin levels outside of pregnancy and lactation can cause menstrual irregularities, decreased libido, and infertility.
Low Thyroid Hormone Levels and Implantation
Inadequate levels of thyroid hormones can also impact the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. Thyroid hormones play a critical role in the development and function of the endometrium, the lining of the uterus. An imbalance of thyroid hormones can lead to a thin endometrium, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant and develop.
Thyroid Antibodies and Infertility
Thyroid autoantibodies are antibodies produced by the immune system that target the thyroid gland. Women with thyroid autoantibodies are at increased risk of infertility and pregnancy loss. Thyroid antibodies can interfere with ovulation and cause inflammation in the reproductive tract, which can impact fertility.
How Hypothyroidism Affects Pregnancy
Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, can impact pregnancy in several ways, leading to potential complications for both the mother and baby.
Risk of Complications During Pregnancy
Untreated or poorly managed hypothyroidism during pregnancy increases the risk of various complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, preeclampsia, low birth weight, and placental abruption. The risk of these complications is particularly high in women with pre-existing hypothyroidism and those with thyroid autoantibodies.
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis is a type of thyroid disorder that affects some women after giving birth. It occurs due to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can lead to hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism. Women with pre-existing hypothyroidism are at higher risk of developing postpartum thyroiditis. It can cause fatigue, weight gain, depression, and other symptoms, and requires careful monitoring and management.
Developmental Issues in the Baby
Inadequate thyroid hormone levels during pregnancy can affect the baby’s brain development, leading to cognitive and developmental delays. The first trimester is particularly critical for the baby’s brain development, and maternal thyroid hormone levels play a crucial role in this process.
Thyroid Disorders That Can Start During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of significant changes in a woman’s body, including changes in thyroid function. Thyroid disorders can also develop during pregnancy, making it important to monitor thyroid function throughout pregnancy.
Subclinical Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy
Gestational hypothyroidism is a type of thyroid disorder that can develop during pregnancy. It occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the increased demand during pregnancy. It is characterized by mildly elevated levels of TSH and normal levels of thyroid hormones. Gestational hypothyroidism can lead to adverse outcomes such as gestational diabetes, preterm birth, low birth weight, and cognitive impairment in the baby.
Thyroiditis and Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders
Thyroiditis is a type of thyroid disorder that can develop during pregnancy due to inflammation of the thyroid gland. It can cause hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism, thus complicating pregnancy.
In addition, thyroiditis can lead to autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Graves’ disease in which the immune system attacking the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Autoimmune thyroid disorders can increase the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes such as preterm birth and miscarriage.
Steps to Take for Getting Pregnant with Hypothyroidism
If you are trying to conceive, there are several steps you can take to optimize your chances of getting pregnant with hypothyroidism and having a healthy pregnancy outcome:
Consult with Your Healthcare Provider
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider before trying to conceive. Your healthcare provider can monitor your thyroid hormone levels and adjust medication doses as needed to optimize thyroid function before and during pregnancy. Your healthcare provider may also recommend preconception care, such as taking supplements to help support a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Monitor Your Menstrual Cycle
Women with hypothyroidism may experience irregular menstrual cycles, which can make it difficult to determine when ovulation occurs. Monitoring your menstrual cycle, either through tracking basal body temperature or using an ovulation predictor kit, can help identify when ovulation occurs and optimize timing for conception.
Optimize Thyroid Function
Optimizing thyroid function before and during pregnancy is crucial for a healthy pregnancy outcome. Working with your healthcare provider to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust medication doses as needed can help ensure adequate thyroid function. Eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding exposure to toxins can also help support thyroid function.
Address Any Underlying Fertility Issues
In addition to hypothyroidism, there may be other underlying fertility issues that are impacting your ability to conceive. Addressing any underlying fertility issues, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis, can help optimize your chances of getting pregnant and having a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Thyroid Levels and TSH Level for Getting Pregnant
Adequate thyroid hormone levels can help regulate menstrual cycles, promote ovulation, and support a healthy pregnancy. The target thyroid hormone levels during pregnancy may differ from non-pregnant levels. The American Thyroid Association recommends a TSH level of 0.1-2.5 mIU/L in the first trimester and 0.2-3.0 mIU/L in the second and third trimesters. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate target levels for your unique situation.
Managing Hypothyroidism during Pregnancy with Ayurveda
As an Ayurvedic doctor, I believe that a holistic approach that addresses the mind, body, and spirit can support optimal health and wellbeing during pregnancy. Here are some Ayurvedic tips for managing hypothyroidism during pregnancy:
Balancing Kapha Dosha
In Ayurveda, hypothyroidism is associated with an imbalance of Kapha dosha. Balancing Kapha dosha through dietary and lifestyle modifications can help improve thyroid function. Eating warm, cooked foods and avoiding cold, raw foods can help balance Kapha dosha. Engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can also help balance Kapha dosha and improve thyroid function.
Herbal Remedies
Several Ayurvedic herbs have been traditionally used to support thyroid function, such as ashwagandha, guggulu, and shilajit. These herbs can help improve thyroid hormone levels and support overall health during pregnancy. However, it is important to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner before taking any herbal remedies during pregnancy.

Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to Ayurvedic remedies, making lifestyle modifications can also help manage hypothyroidism during pregnancy. Avoiding exposure to toxins, such as cigarette smoke and environmental pollutants, can help protect thyroid function. Engaging in stress-reducing practices, such as meditation and yoga, can also help support thyroid function.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to manage hypothyroidism during pregnancy. Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and adjustment of medication doses as needed can help ensure adequate thyroid function. Ayurvedic remedies can complement conventional medical treatment, but should not be used as a substitute for medical advice and treatment.
Diet Tips for a Healthy Pregnancy with Hypothyroidism
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for a healthy pregnancy outcome, especially for women with hypothyroidism. Here are some diet tips to support thyroid function and optimize pregnancy outcomes:
Increase Iodine Intake
Iodine is an essential mineral required for the production of thyroid hormones. Women with hypothyroidism may have a higher risk of iodine deficiency, which can further impair thyroid function. Including iodine-rich foods in the diet, such as seaweed, iodized salt, and fish, can help support thyroid function during pregnancy.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help support overall health and wellbeing during pregnancy. Including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide essential nutrients for both the mother and baby.
Limit Goitrogenic Foods
Goitrogenic foods, such as cruciferous vegetables, soy, and millet, can interfere with thyroid function by blocking iodine uptake. Women with hypothyroidism may need to limit their intake of goitrogenic foods. Cooking cruciferous vegetables can reduce their goitrogenic effect, while fermented soy products, such as tempeh and miso, have a lower goitrogenic effect than soy milk and tofu.
Avoid Gluten
Some women with hypothyroidism may also have an autoimmune condition called celiac disease, which is triggered by gluten. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Women with hypothyroidism who have celiac disease should avoid gluten to prevent further damage to the thyroid gland.
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial for a healthy pregnancy outcome. Drinking enough water can help support thyroid function, regulate body temperature, and prevent constipation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hypothyroidism can impact pregnancy outcomes and make it difficult for women to conceive. Proper diagnosis and management of hypothyroidism are crucial for optimizing fertility and achieving a successful pregnancy.
If you are experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism or have been diagnosed with hypothyroidism during pregnancy, it is important to take proper treatment in time. At Medhya Herbals, we offer personalized Ayurvedic treatment plans for hypothyroidism during pregnancy. Our highly experienced Ayurvedic doctors specialize in natural treatment methods that complement conventional medical treatment.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Medhya Herbals for a personalized Ayurvedic treatment plan that meets your unique needs. Remember, taking care of your health during pregnancy can help ensure a healthy environment for your baby to grow and develop.
References

