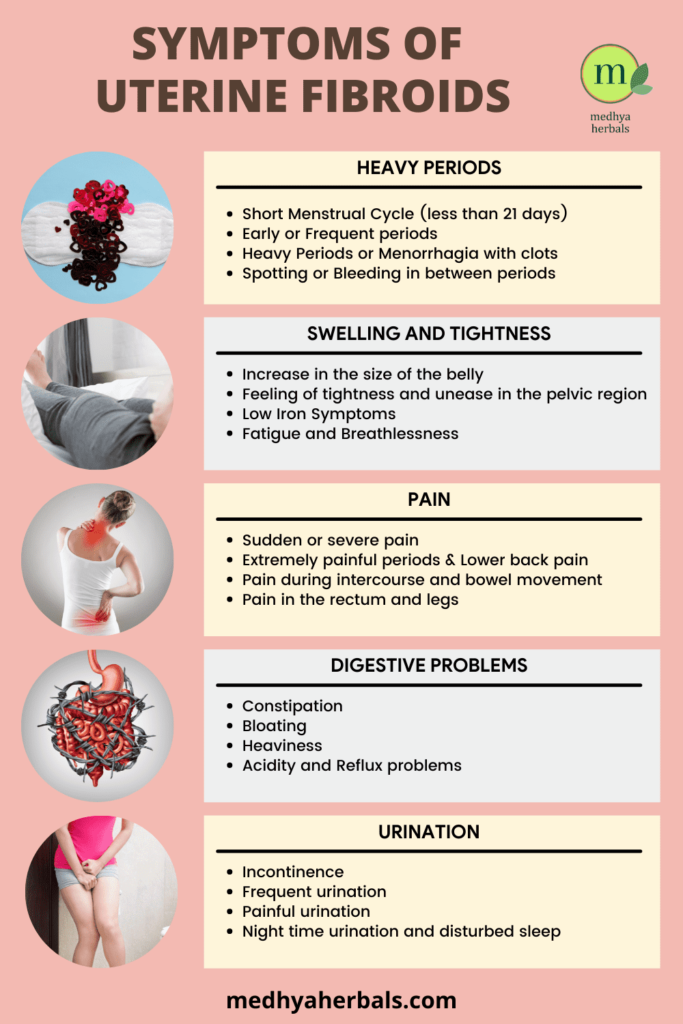
Fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on the bladder and bowels. It’s essential to address these symptoms promptly so as to avoid the health risks of uterine fibroids
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the most effective natural remedies for shrinking fibroids. By following the health tips outlined here, you can prevent invasive procedures as hysterectomy and find relief from fibroid-related discomfort. From understanding what makes fibroids shrink naturally to exploring the fastest ways to control the fibroid symptoms, you will discover practical ways to for fibroids natural treatment.
Throughout this article, we will answer burning questions like: Can you actually shrink fibroids? How fast can you expect results? What signs indicate that fibroids are shrinking? By addressing these queries and more, I aim to provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed decisions about your health.
Rest assured that the information presented here is backed by scientific research and the wisdom of Ayurveda, a time-tested holistic healing system. Our approach combines evidence-based practices with natural remedies, ensuring you receive comprehensive care without compromising your well-being.
So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey towards fibroid healing and reclaim your vitality, join me as we explore the most effective fibroids natural treatments, herbs, and lifestyle modifications to shrink fibroids naturally. Your health is our priority, and together we will navigate this path towards lasting relief and wellness.
What Causes Fibroids to Grow Fast?
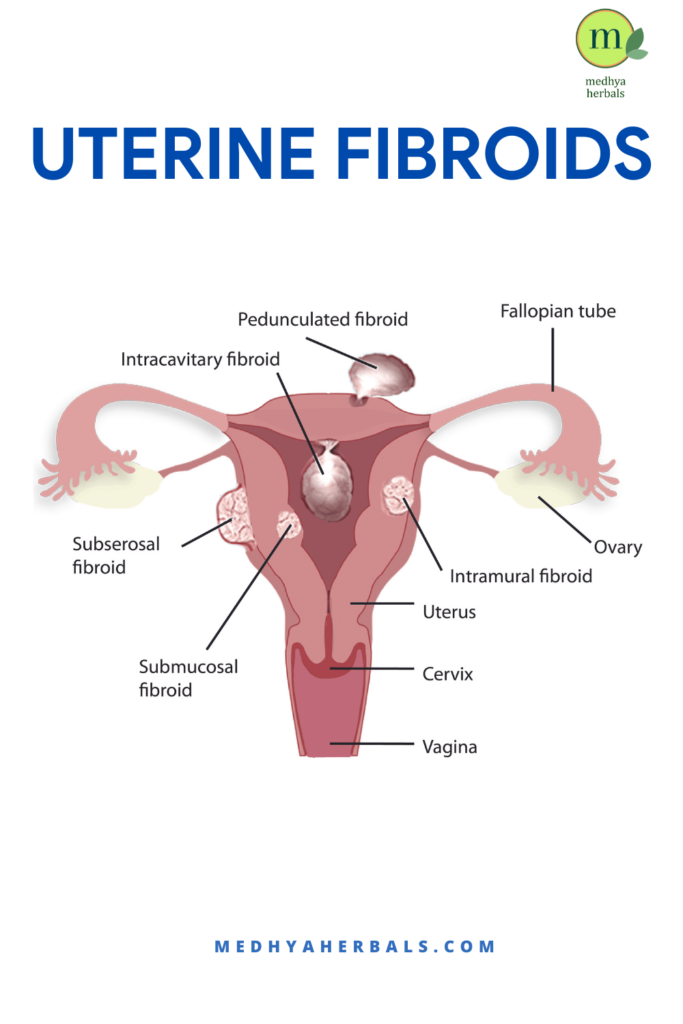
The exact cause of fibroid growth is not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to their accelerated growth. These factors include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Estrogen and progesterone, the female reproductive hormones, play a role in fibroid development and growth. When there is an imbalance between these hormones, such as an excess of estrogen relative to progesterone, it can promote the growth of fibroids.
- Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic component involved in fibroid growth, as they tend to run in families. If you have a family history of fibroids, you may have a higher risk of developing them and experiencing faster growth.
- Age and Hormonal Changes: Fibroids commonly grow during the reproductive years when hormone levels fluctuate. They can grow rapidly during pregnancy when estrogen and progesterone levels are high. Additionally, perimenopause, the transitional phase before menopause, can lead to hormonal fluctuations that can stimulate fibroid growth.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly visceral fat, has been linked to an increased risk of developing and accelerating the growth of fibroids. Adipose tissue produces estrogen, and higher levels of estrogen can contribute to fibroid growth.
- Certain Medications and Hormonal Treatments: Some hormonal medications, such as certain birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), may contain hormones that can promote fibroid growth in some individuals.
- Uterine Trauma or Inflammation: Previous uterine trauma or inflammation due to surgeries, infections, or childbirth complications may trigger the growth of fibroids.
Can Fibroids Shrink Naturally?
If you have been diagnosed with fibroids, you might wonder if these non-cancerous growths can shrink naturally. Fibroids, although stubborn, can indeed shrink naturally with the right approach. Several factors play a crucial role in preventing their growth and promoting their reduction.
Understanding the factors that contribute to fibroid shrinkage is key to exploring effective natural treatment options and avoiding surgery. Let’s explore these factors and natural approaches in detail:
Factors Contributing to Fibroid Shrinkage
- Hormone Balance: Hormonal imbalances, particularly an excess of estrogen or estrogen dominance, can contribute to the growth of fibroids. Therefore, restoring hormone balance is key to preventing their growth and facilitating natural shrinkage.
- Improved Blood Flow and Circulation: Efficient blood flow and circulation are vital for promoting the natural shrinkage of fibroids. Enhanced circulation allows for better oxygen and nutrient delivery to the affected area, supporting healing and reducing fibroid size.
- Liver Detoxification: The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing hormones and eliminating toxins from the body. A healthy and efficient liver function can contribute to fibroid shrinkage.
- Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation can contribute to the growth and development of fibroids. Reducing inflammation can help promote their natural shrinkage.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and contribute to the growth of fibroids. Managing stress is crucial for promoting natural fibroid shrinkage.
- Manage Weight: Excess body weight is associated with an increased risk of fibroids and can exacerbate their symptoms. Maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Fast and Effective Natural Remedies to Shrink Fibroids
If you’re looking for ways to expedite fibroid shrinkage naturally, there are several fast and effective natural remedies you can incorporate into your routine. By combining multiple approaches, you can maximize the chances of achieving optimal results. Let’s explore these methods:
1. Ayurvedic Treatment
Ayurveda, the holistic Indian system of medicine, offers a range of treatments and herbal medicines for fibroids management. Ayurvedic medicines, yoga therapy and deep body detoxification as panchakrama are tailored to an individual’s needs. Ayurvedic treatment for uterine fibroids is effective to balance hormones, manage fibroids symptoms and promote fibroid shrinkage.
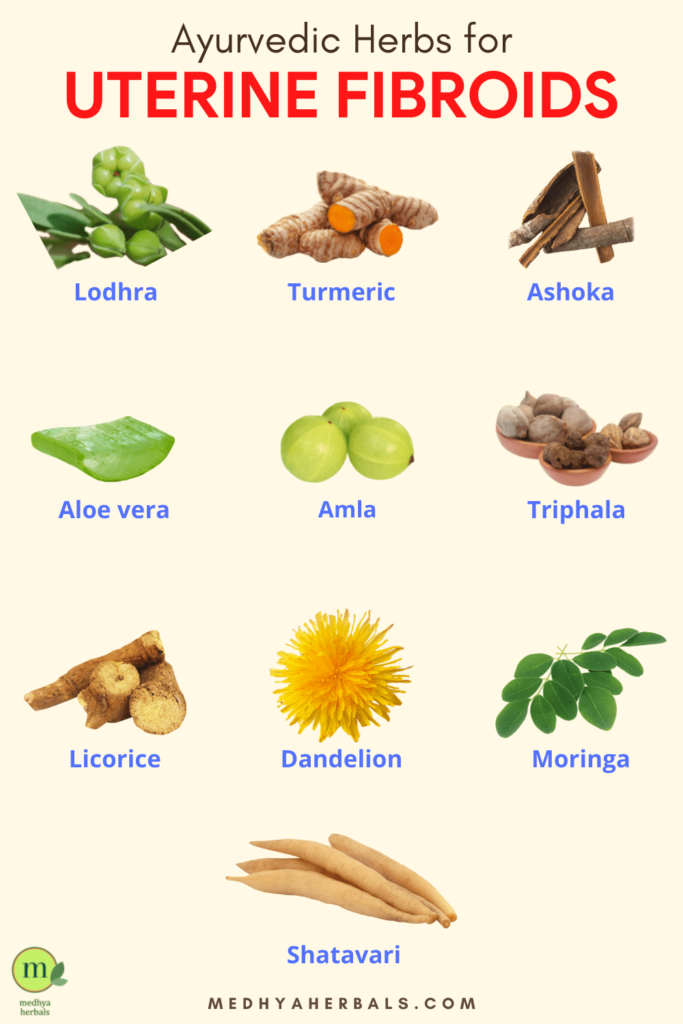

2. Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements have shown promise in promoting fibroid shrinkage. Look for formulations containing herbs like chasteberry, dandelion root, milk thistle, and turmeric. These herbs can help regulate hormones, reduce inflammation, and support the natural healing process.
These herbal supplements can be taken in various forms, such as capsules or teas. Consult with a healthcare professional or Ayurvedic practitioner to determine the right herbal supplements for you.
3. Castor Oil Packs
Applying castor oil packs over the lower abdomen can enhance blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and support fibroid shrinkage. Soak a cloth in high-quality, cold-pressed castor oil and place it on the abdomen. Cover it with a plastic wrap and apply a heating pad for about 30-60 minutes. Practice this method a few times a week for optimal results.
4. Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine
Acupuncture, combined with customized herbal formulas prescribed by trained practitioners, can help promote blood circulation, balance hormones, and support fibroid shrinkage. Acupuncture sessions can stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms, leading to faster results. Consult with a licensed acupuncturist experienced in treating fibroids.
5. Uterine Massage
Uterine massage, performed by a skilled therapist, can help break down adhesions, improve blood flow, and facilitate the shrinkage of fibroids. The therapist applies gentle pressure and circular motions to the lower abdomen to promote circulation and lymphatic drainage. Regular uterine massage sessions can yield noticeable results over time.
6. Stress Reduction Techniques
Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone balance and hinder fibroid shrinkage. Incorporate stress reduction techniques into your daily routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in activities that bring you joy. Managing stress levels supports overall well-being and aids in the natural healing process.

7. Dietary Modifications
Adopting a fibroids diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and aid in fibroid shrinkage. Incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens, can be particularly beneficial.
In addition, emphasize on cruciferous vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and omega-3 fatty acids. While you improve your diet, you should also limit processed foods, red meat, caffeine, and alcohol to reduce inflammation and promote hormonal balance.

8. Exercise and Movement
Regular physical activity helps improve blood circulation, balance hormones, and support overall well-being. Incorporate exercises like brisk walking, yoga for fibroids, swimming, or low-impact aerobics into your routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
9. Good Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for hormone regulation and overall health. Aim for 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to support the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
By combining these natural remedies and approaches, you can create a comprehensive plan to expedite fibroid shrinkage. However, it’s important to note that results may vary, and it’s crucial to be patient and consistent in your efforts. Monitor your symptoms, track your progress, and consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support along the way.
Remember, every individual’s response to treatment is unique, and it’s essential to tailor the approach to your specific needs. With dedication and a holistic approach, you can enhance your chances of achieving fast and effective fibroid shrinkage naturally, empowering yourself on your journey towards improved well-being.
Signs of Shrinking Fibroids
As fibroids begin to shrink naturally, you may notice several signs that indicate positive progress in your treatment. While the specific signs can vary from person to person, here are some common indicators that fibroids are shrinking:
Reduced Menstrual Bleeding
One of the significant symptoms of fibroids is heavy menstrual bleeding. As fibroids shrink, you may observe a noticeable decrease in the amount and duration of your menstrual flow. You may experience lighter periods with fewer clots and a shorter overall duration. This reduction in menstrual bleeding is a positive sign that your fibroids are responding to the treatment.
Decreased Pain and Discomfort
Fibroids often cause pelvic pain, pressure, and discomfort. As the fibroids shrink in size, you may experience a gradual reduction in these symptoms. The intensity and frequency of pain can diminish, leading to improved quality of life and overall well-being.
Improved Urinary and Bowel Function
Large fibroids can exert pressure on the bladder and bowels, leading to urinary frequency, urgency, constipation, or difficulty emptying the bladder. When fibroids shrink, the pressure on these organs is relieved, resulting in improved urinary and bowel function. You may notice a reduction in the frequency of urination, fewer episodes of constipation, and an overall improvement in your urinary and bowel habits.
Regulated Menstrual Cycle
Fibroids can cause irregular menstrual cycles, with variations in cycle length and timing. As the fibroids shrink, you may notice that your menstrual cycle becomes more regular. The intervals between periods may stabilize, and the timing of your menstrual flow may become more predictable.
Decreased Abdominal Swelling
Large fibroids can contribute to abdominal bloating and swelling. As the fibroids shrink, you may observe a reduction in the size of your abdomen. This can lead to a flatter stomach and a decrease in the discomfort associated with abdominal swelling.
Improved Fertility
For women trying to conceive, shrinking fibroids can enhance fertility. As fibroids reduce in size, they exert less pressure on the uterus, allowing for a healthier environment for embryo implantation. This can increase the chances of successful conception and pregnancy.
If you suspect your fibroids are shrinking based on these signs, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments will help track your progress and determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
Medical Interventions for Fibroids
Medical interventions for fibroids can range from hormonal medications to surgical procedures, such as myomectomy (removal of fibroids) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). Your healthcare provider will consider factors such as the size, number, and location of your fibroids, as well as your symptoms, fertility desires, and overall health when discussing treatment options.
Remember, every individual’s situation is unique, and the need for medical intervention may vary. Consulting with an experienced healthcare professional, particularly a gynecologist or a specialist in fibroid management, is essential to develop a personalized plan based on your specific needs and circumstances.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Fibroids: Ensuring Your Well-being
While natural approaches can be effective for managing fibroids, it’s important to be aware of situations that warrant medical attention. Regular check-ups and monitoring are crucial to ensure your well-being and to address any potential complications or concerns. By seeking medical advice when necessary, you can make informed decisions about your fibroid management and take steps towards a healthier and happier life.
Here are some situations in which you should consider consulting with a healthcare professional:
1. Severe Symptoms
If you experience severe symptoms that significantly affect your quality of life, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Symptoms such as heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder, or anemia due to excessive blood loss should not be ignored.
2. Rapid Growth of Fibroids
If you notice a sudden and significant increase in the size of your fibroids, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider. Rapid growth can indicate the need for further evaluation and potential medical intervention.
3. Fertility Concerns
If you are planning to conceive or are experiencing difficulty getting pregnant, it’s advisable to seek medical advice. Fibroids can sometimes interfere with fertility, and a healthcare professional can provide guidance on the best course of action.
4. Suspected Red Flags
If you experience unusual symptoms that could be associated with fibroids, such as severe pain, rapid weight loss, or changes in bowel or bladder habits, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate complications or other underlying conditions that require prompt evaluation and treatment.
5. Impact on Daily Life
If fibroids significantly impact your daily activities, relationships, or emotional well-being, it’s important to discuss your concerns with a healthcare professional. They can help assess the situation and provide appropriate guidance and support.
6. Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Even if you are managing your fibroids naturally, it’s essential to have regular check-ups and monitoring. Your healthcare provider can assess the progression of your fibroids, evaluate their impact on your health, and make informed decisions regarding treatment options if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors that contribute to fibroid shrinkage and adopting natural approaches can play a significant role in managing these growths. Hormone balance, improved blood flow and circulation, liver detoxification, inflammation reduction, and stress reduction are key elements that can support the natural shrinkage of fibroids.
It’s important to note that the timeline for fibroid shrinkage can vary from person to person. Some women may experience noticeable improvements in a few months, while for others, it may take longer. Additionally, not all fibroids may shrink completely, but they can still become smaller and less symptomatic.
At Medhya Herbals, we understand the unique challenges faced by women dealing with fibroids. Our team of experienced Ayurvedic doctors specializes in women’s health and wellness, providing personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. We combine ancient Ayurvedic wisdom with modern medical knowledge to offer holistic and effective solutions.
We invite you to schedule a consultation with our Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals to receive a personalized treatment plan for your fibroids. Our doctors will carefully assess your condition, listen to your concerns, and develop a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes natural fibroid shrinkage. With our guidance and support, you can embark on a journey towards optimal well-being.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Medhya Herbals is here to support you every step of the way, guiding you towards a healthier and fibroid-free life.
FAQ
1. What color is fibroid discharge?
Fibroid discharge typically does not have a specific color. The presence of discharge or abnormal vaginal bleeding can be associated with fibroids, but the color can vary. It can range from clear or white to pink, brown, or even red, depending on various factors such as the menstrual cycle, hormonal changes, and the presence of other underlying conditions. If you notice any changes in your vaginal discharge, including color, consistency, or odor, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
2. Do fibroids come out as clots?
Yes, it is possible for fibroids to cause the passing of clots during menstruation. Fibroids are noncancerous growths that can develop in or around the uterus. They can vary in size and location within the uterine wall. When fibroids are present, they can disrupt the normal flow of menstrual blood, leading to heavier and prolonged periods.
The clots that are passed during menstruation can occur due to the interaction between the fibroids and the lining of the uterus. The fibroids can cause the uterine lining to become thicker, resulting in heavier bleeding. When the blood is expelled from the uterus, it may form clots as it coagulates.
3. How do I know if my fibroid has burst?
Fibroids do not typically burst or rupture. However, in rare cases, a condition called degeneration can occur within a fibroid, which may cause severe pain and lead to symptoms similar to a burst.
Degeneration happens when the blood supply to a fibroid becomes insufficient, resulting in the death of the fibroid tissue. This can lead to acute pain, usually localized to the area of the fibroid. The pain may be sudden, intense, and accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
It’s worth noting that most fibroids do not cause significant symptoms and can be managed through conservative measures or medical treatments. However, if you have concerns about your fibroids or experience any unusual symptoms, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, perform any necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options based on your individual situation.
4. Is it okay to leave fibroids untreated?
In many cases, small fibroids that are not causing any significant symptoms or complications may not require immediate treatment. However, it is important to closely monitor the fibroids and have regular check-ups with a healthcare professional to ensure they are not growing or causing any complications.
The decision to treat or not to treat fibroids depends on various factors, including the size, location, and number of fibroids, as well as the severity of symptoms and their impact on your quality of life. Some women with small fibroids may experience no symptoms at all and may choose to manage them through lifestyle changes, monitoring, and regular check-ups.
However, if fibroids are causing bothersome symptoms such as heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, or fertility issues, or if they are growing rapidly, medical intervention may be necessary. Treatment options can range from medication to manage symptoms, minimally invasive procedures to remove or shrink fibroids, or in more severe cases, surgical removal of the uterus (hysterectomy).
It is important to discuss your specific situation with a healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or an Ayurvedic doctor experienced in fibroid management, to determine the best course of action. They can evaluate your symptoms, perform necessary tests, and provide personalized guidance and treatment options based on your individual needs and preferences. Leaving fibroids untreated without proper monitoring may lead to worsening symptoms or complications over time.
References
- Treatment of Uterine Fibroids Based on Allopathy and Indian System of Medicine
- Current progress of Ayurveda treatments on uterine fibroids: a comprehensive review
- Ayurvedic intervention in the management of uterine fibroids: A Case series
- Al-Hendy, A., & Badr, M. (2014). Can vitamin D reduce the risk of uterine fibroids? Women’s Health, 10(4), 353-358. https://doi.org/10.2217/whe.14.24
- Brakta, S., Diamond, J. S., Al-Hendy, A., Diamond, M. P., & Halder, S. K. (2015). Role of vitamin D in uterine fibroid biology. Fertility and Sterility, 104(3), 698-706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.05.031
- Catherino, W., Eltoukhi, H., & Al-Hendy, A. (2013). Racial and ethnic differences in the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of uterine Leiomyoma. Seminars in Reproductive Medicine, 31(05), 370-379. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1348896
- Fibroids. (2022). Johns Hopkins Medicine, based in Baltimore, Maryland. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/uterine-fibroids
- He, Y., Zeng, Q., Dong, S. Y., Qin, L. Q., Li, G., & Wang, P. (2013). Associations between Uterine Fibroids and Lifestyles Including Diet, Physical Activity and Stress: A Case-control Study in China. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 22(1), 109-117. https://doi.org/10.6133/apjcn.2013.22.1.07
- Medikare, V., Kandukuri, L. R., Ananthapur, A., Deenadayal, M., & Nallari, P. (2011). The genetic bases of uterine fibroids; a review. Journal of Reproduction & Infertility, 12(3), 181-91. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3719293/pdf/JRI-12-181.pdf
- Okolo, S., Gentry, C., Perrett, C., & Maclean, A. (2005). Familial prevalence of uterine fibroids is associated with distinct clinical and molecular features. Human Reproduction, 20(8), 2321-2324. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dei049
- Qin, H., Lin, Z., Vásquez, E., Luan, X., Guo, F., & Xu, L. (2020). Association between obesity and the risk of uterine fibroids: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 75(2), 197-204. https://doi.org/ 10.1136/jech-2019-213364
- Reis, F. M., Bloise, E., & Ortiga-Carvalho, T. M. (2016). Hormones and pathogenesis of uterine fibroids. Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 34, 13-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.11.015
- Schellenberg, R. (2001). Treatment for the premenstrual syndrome with agnus castus fruit extract: Prospective, randomised, placebo controlled study. BMJ, 322(7279), 134-137. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7279.134
- Tinelli, A., Vinciguerra, M., Malvasi, A., Andjić, M., Babović, I., & Sparić, R. (2021). Uterine Fibroids and Diet. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031066
- Ulin, M., Ali, M., Chaudhry, Z. T., Al-Hendy, A., & Yang, Q. (2019). Uterine fibroids in menopause and perimenopause. Menopause, 27(2), 238-242. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0000000000001438
- Uterine fibroids: Symptoms, causes, risk factors & treatment. (2020, August 24). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9130-uterine-fibroids
- Van Die, M., Burger, H., Teede, H., & Bone, K. (2012). Vitex agnus-castus extracts for female reproductive disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials. Planta Medica, 79(07), 562-575. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1327831
- Wise, L. A., & Laughlin-Tommaso, S. K. (2016). Epidemiology of uterine fibroids. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynecology, 59(1), 2-24. https://doi.org/10.1097/grf.0000000000000164
- Zhao, S., Gardner, K., Taylor, W., Marks, E., & Goodson, N. (2015). Vitamin D assessment in primary care: Changing patterns of testing. London Journal of Primary Care, 7(2), 15-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/17571472.2015.11493430


Nice
Indeed awakening the Physician within our bodies by giving it what it requires to function optimally.