Are you trying to conceive but struggling with low progesterone levels? Or are you approaching menopause and concerned about the impact it may have on your fertility? If so, you’re not alone. Many women face hormonal imbalances that can affect their ability to conceive and carry a healthy pregnancy. But the good news is, there’s a simple solution – incorporating progesterone rich foods into your diet.
Progesterone plays a crucial role in regulating menstrual cycles, maintaining pregnancy, and managing menopausal symptoms. Yet, as women approach menopause, their progesterone levels can drop, leading to a range of symptoms that can impact their fertility. But what if we told you that simply by adding certain foods to your diet, you can boost your progesterone levels and improve your chances of conceiving and carrying a healthy pregnancy?

In this blog post, we’ll uncover the top sources of progesterone foods that can help you achieve hormonal balance and boost your fertility. From the tasty fruits and vegetables to the nutritious nuts and seeds, we’ll show you how incorporating these foods into your diet can support your journey to motherhood. So, if you’re ready to learn how you can use food to enhance your fertility and improve your chances of having a healthy pregnancy, keep reading!
What is Progesterone and its Role in the Body?
Progesterone is a hormone produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands. It is a critical hormone in the female reproductive system, playing a vital role in regulating menstrual cycles, preparing the uterus for pregnancy, and maintaining pregnancy. Progesterone also helps to manage menopausal symptoms by balancing the levels of estrogen and other hormones in the body.
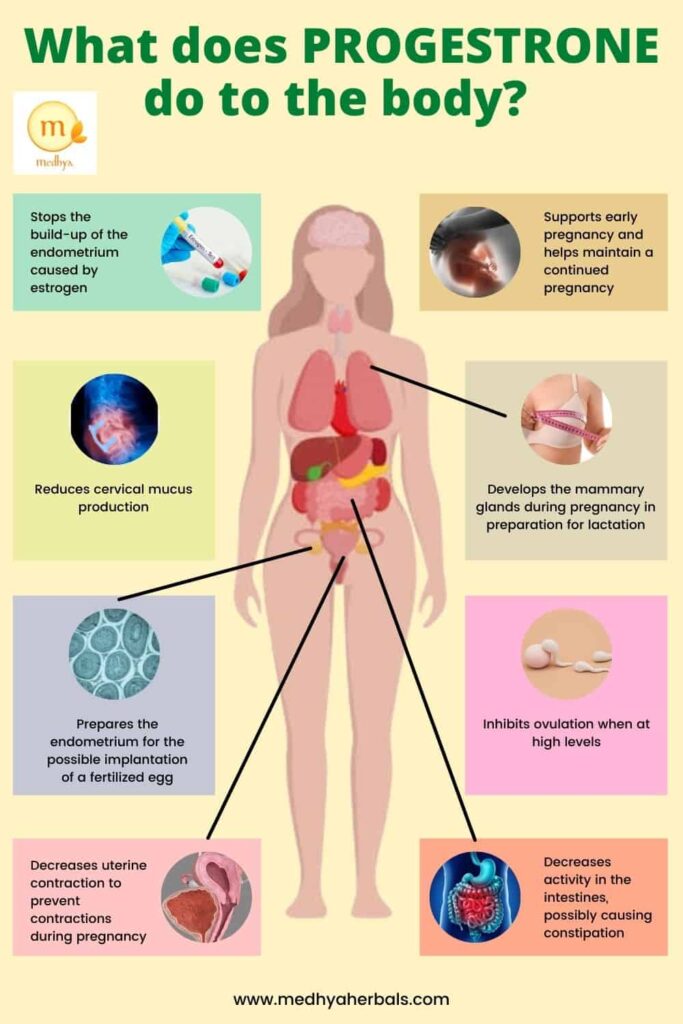
Functions of Progesterone in the Body
Progesterone has several important functions in the female body, including:
- Regulating menstrual cycles: Progesterone helps to regulate the menstrual cycle by preparing the uterus for pregnancy and maintaining the lining of the uterus.
- Maintaining pregnancy: During pregnancy, progesterone levels rise, helping to maintain the pregnancy and prevent the uterus from contracting.
- Balancing hormones: Progesterone helps to balance the levels of estrogen and other hormones in the body, which is important for managing menopausal symptoms and maintaining overall hormonal balance.
Causes of Low Progesterone Levels
Progesterone levels can decline for a variety of reasons, including:
- Age: As women approach menopause, their progesterone levels can decline.
- Stress: Chronic stress can impact hormone levels, including progesterone levels.
- Certain health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can impact progesterone levels.
Low progesterone levels can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and other symptoms of hormonal imbalances, making it important to maintain healthy levels of this hormone.
Progesterone Rich Foods
There are many foods that are rich in progesterone and can help boost your levels of this important hormone. Here are some of the top progesterone rich foods to include in your diet:
- Avocados: Avocados are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and B vitamins, making them a great food for supporting hormonal balance. They also contain phytoestrogens, which can help balance the effects of estrogen in the body and reduce the risk of estrogen dominance.
- Bananas: Bananas are a rich source of potassium, magnesium, and B vitamins, all of which are essential for maintaining healthy hormone levels. They also contain phytoestrogens, which can help balance the effects of estrogen in the body.
- Oranges: Oranges are high in vitamin C, which is important for supporting adrenal function and maintaining healthy hormone levels. They also contain limonoids, which have been shown to have a balancing effect on estrogen levels in the body.
- Papayas: Papayas are a rich source of vitamin C, folate, and potassium, all of which are important for maintaining healthy hormone levels. They also contain papain, an enzyme that has been shown to have a balancing effect on estrogen levels in the body.
- Sweet Potatoes: Sweet potatoes are a great source of complex carbohydrates, fiber, and vitamins and minerals like beta-carotene, vitamin C, and potassium. These nutrients can help support adrenal function and balance hormone levels, especially during pregnancy and menopause.
- Carrots: Carrots are a rich source of beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. This vitamin is important for supporting adrenal function and maintaining healthy hormone levels.
- Broccoli: Broccoli is a great source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals like vitamin C, calcium, and iron. These nutrients can help support adrenal function and balance hormone levels, especially during pregnancy and menopause.
- Spinach: Spinach is a great source of iron, calcium, and vitamins like vitamin C and folate. These nutrients are important for supporting adrenal function and maintaining healthy hormone levels, especially for women during pregnancy and menopause.
- Brazil Nuts: Brazil nuts are a rich source of selenium, a mineral that is important for supporting adrenal function and maintaining healthy hormone levels. They are also a good source of healthy fats, which can help balance hormone levels, especially during menopause.
- Sunflower Seeds: Sunflower seeds are a good source of healthy fats, fiber, and vitamins and minerals like vitamin E and magnesium. These nutrients can help support adrenal function and balance hormone levels, especially for women during menopause and for maintaining healthy fertility.
How to Incorporate Progesterone Foods into Your Diet
Incorporating progesterone rich foods into your diet is an easy and delicious way to boost your progesterone levels and support your overall health and hormone balance. With these tips, you can feel confident in incorporating progesterone rich foods into your diet and supporting your overall health and hormone balance.
Tips for Incorporating Progesterone Rich Foods into Your Diet
Experimenting with new recipes is a great way to keep things interesting and ensure that you’re getting a variety of nutrients from progesterone rich foods. Try incorporating these foods into your meals and snacks in different ways, such as blending them into smoothies, tossing them into salads, stir-frying them, or incorporating them into baked goods.
By making these foods a staple in your diet, rather than just eating them occasionally, you can reap the benefits of their nutrient rich properties. Additionally, opting for organic and non-GMO foods can help reduce your exposure to harmful chemicals and pesticides, so it’s a good idea to make this a priority whenever possible. Here are some tips and meal ideas to help you get started:
- Aim to include a variety of progesterone rich foods in your diet each day, including fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and herbs and spices.
- Make a grocery list: Write down all the progesterone foods you want to try and make a plan to incorporate them into your meals.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods: Aim to include a variety of whole, unprocessed foods in your diet to ensure you’re getting a balanced mix of nutrients.
- Snack on nuts and seeds: Keep a bag of nuts or seeds in your bag or at your desk to snack on throughout the day.
- Use herbs and spices: Use herbs and spices to flavor your meals and add extra nutrition.
Sample Meal Plans for Breakfast, Lunch, and Dinner
- Breakfast: Start your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with sliced bananas, almond butter, and a sprinkle of cinnamon.
- Lunch: Enjoy a salad with mixed greens, carrots, avocado, and grilled chicken or turkey.
- Dinner: Have a stir-fry with sweet potatoes, broccoli, and your choice of protein, seasoned with turmeric and ginger.
Recipe Suggestions for Snacks and Desserts
- Snacks: Make a batch of energy bites with oats, sunflower seeds, and dried fruits.
- Desserts: Indulge in a slice of banana bread made with almond flour, or a sweet potato pie spiced with cinnamon and nutmeg.
Conclusion
Incorporating progesterone rich foods into your diet is an easy and delicious way to support your hormone levels and overall health. With a variety of options to choose from, including fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and herbs and spices, you can find something that fits your tastes and dietary needs.
Whether you’re trying to support your fertility, manage symptoms during menopause, or simply maintain healthy hormone levels, adding these foods to your diet can make a big difference.
If you’re struggling with hormonal imbalances or low progesterone levels, it’s important to make dietary changes to improve your health. If you need help, consider seeking the guidance of a nutrition expert. At Medhya Herbals, we offer personalised nutrition plans to help you achieve optimal health and wellness. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support you on your health journey.
FAQ
What are the benefits of eating progesterone-rich foods?
Eating progesterone-rich foods can help support the production and balance of progesterone in the body, which can regulate the menstrual cycle, prepare the uterus for pregnancy, and maintain a healthy pregnancy. Incorporating these foods into your diet can also help support overall health and well-being.
How can I determine if I have low progesterone levels?
Low progesterone levels can cause menstrual irregularities and infertility, and can be diagnosed through a blood test. If you have concerns about your progesterone levels, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
What are some examples of progesterone-rich foods?
Some examples of progesterone-rich foods include whole grains, leafy greens, nuts and seeds, seafood, fruits such as papaya and cherries, legumes, cruciferous vegetables, herbs such as red raspberry leaf and chasteberry, spices such as ginger and turmeric, and high-quality dairy products such as grass-fed butter, ghee, and whole milk.
How can I incorporate progesterone-rich foods into my diet?
To incorporate progesterone-rich foods into your diet, try adding them to your meals and snacks. For example, add leafy greens to your smoothies or salads, snack on nuts and seeds, and incorporate whole grains into your meals. You can also try incorporating herbs and spices into your cooking or adding them to tea. The key is to eat a balanced and varied diet, including a variety of these foods, to support optimal hormone balance.
Are there any side effects of consuming progesterone-rich foods?
Consuming progesterone-rich foods is generally considered safe and can provide numerous health benefits. However, if you have any concerns or allergies, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet.
What vitamins increase progesterone?
While there is no specific vitamin that directly increases progesterone levels, certain vitamins and nutrients can support the production and balance of this hormone. These include:
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is essential for hormone synthesis and can help support progesterone production.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can support adrenal function, which plays a role in progesterone production.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is involved in hormone synthesis and regulation, and can help support progesterone levels.
- Zinc: Zinc is important for hormone synthesis and can help support progesterone production.
- Essential fatty acids: Essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can help support hormonal balance and overall health.
Which fruit is rich in progesterone?
There is no fruit that is specifically rich in progesterone. Progesterone is a hormone that is produced by the ovaries in women and by the adrenal glands in both men and women, not by fruits. However, incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense fruits into your diet can support overall health and well-being, which can in turn support hormone balance. Some fruits that are particularly high in nutrients and antioxidants include berries, cherries, papaya, and guava. It’s important to eat a balanced and varied diet, including a variety of fruits, to support optimal health.
References
- J.E. Williams, “Textbook of Endocrine Physiology,” Oxford University Press, (2010).
- S.G. Smith, “Progesterone: A Key Regulator of Female Reproductive Function,” Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, vol. 1135, pp. 58-68 (2008).
- A. Rauch, “Progesterone and the Brain,” Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 7, pp. 1-17 (2013).
- J.E. Hall, “Vitamins, minerals and hormones,” Journal of Endocrinology, vol. 180, pp. S1-S14 (2004).
- J.L. Ellington, “Magnesium and Hormonal Function,” Journal of the American College of Nutrition, vol. 25, pp. 179-184 (2006).
- Mayo Clinic: “Progesterone: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects” https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/progesterone/description/drg-20065051
- Harvard Health Publishing: “The role of diet in hormone balance” https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-role-of-diet-in-hormone-balance-2017050310113
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: “Hormones and Menstruation” https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/menstruation/conditioninfo/hormones
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health: “Herbs at a Glance: Chasteberry” https://nccih.nih.gov/health/chasteberry

