If you’ve ever wondered, “Why is my period late?” you’re not alone. Late periods can be a source of concern, confusion, and curiosity for many women. In this article, we will unravel the mysteries surrounding late periods, explore the signs that accompany them, and provide you with valuable insights on what to do when your periods are late but not pregnant.
Late periods can happen to anyone, and they often lead to a flurry of questions. Is it normal to experience delays in your menstrual cycle? What are the signs that your period might be on its way, even if it’s running late? We’re here to address these questions and more. Whether you’re seeking answers to your own experiences or looking to support a loved one, this comprehensive post will empower you with the information needed to identify potential causes and seek appropriate guidance for a healthier, more balanced menstrual cycle.
Here’s Why Your Period May Get Late!
Understanding the underlying causes of late periods is crucial for managing your menstrual health effectively. In this section, we will explore eight primary factors that can contribute to delayed menstruation, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms and conditions that can disrupt the regularity of your menstrual cycle.
1. Hormonal Imbalances
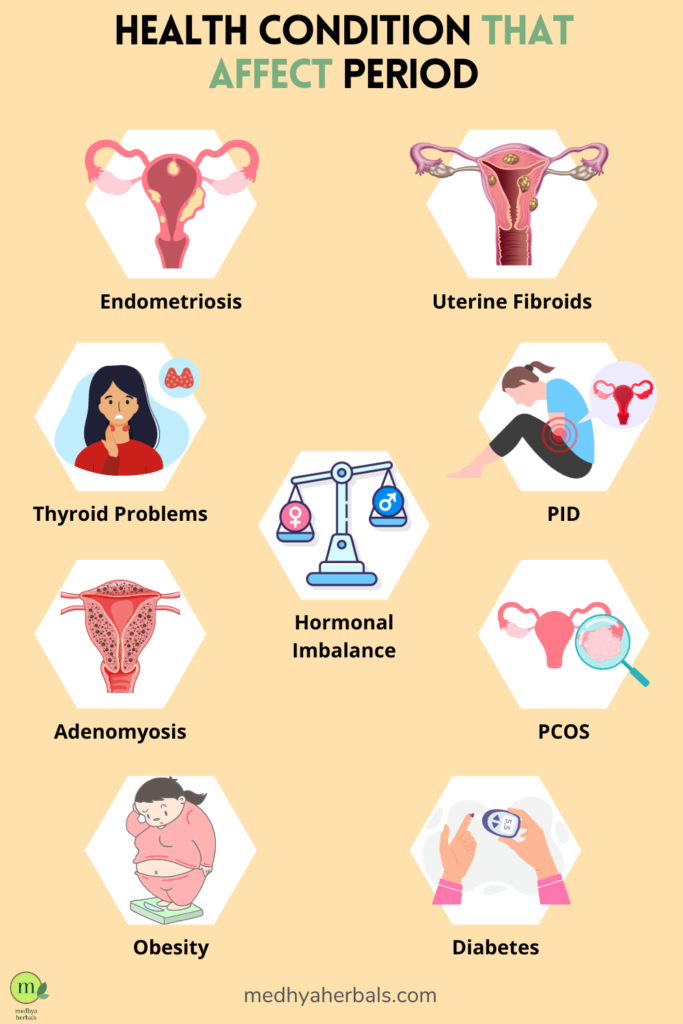
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact the regularity of your menstrual cycle. These imbalances can result from various factors, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or changes in birth control methods. PCOS, in particular, can lead to irregular periods due to elevated androgen levels, affecting the ovaries’ ability to release eggs. Thyroid disorders, on the other hand, can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones, subsequently affecting reproductive hormones and menstrual regularity. Identifying and addressing these hormonal imbalances often involves medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments to restore equilibrium.
2. Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress, anxiety, and emotional factors can have a profound impact on your menstrual cycle. Chronic stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones, leading to late or irregular periods. Additionally, emotional factors such as grief, trauma, or major life changes can also influence the timing of your menstrual cycle. Learning effective stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness, can help mitigate these effects and promote regularity.

3. Psychological Stress
Psychological stress, whether related to work, relationships, or personal challenges, can affect the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and, subsequently, the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis responsible for regulating reproductive hormones. As a result, psychological stress can lead to delayed ovulation or anovulation (lack of ovulation), causing late periods. Practicing stress reduction strategies and seeking support when needed can be beneficial in managing these effects.
4. Extreme Weight Changes
Significant fluctuations in body weight, whether due to rapid weight loss or gain, can disrupt your menstrual cycle. For example, extreme dieting or rigorous exercise routines can lead to reduced body fat, impacting the production of hormones necessary for ovulation. Conversely, obesity can also affect hormonal balance and menstrual regularity. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and a moderate exercise regimen is essential for promoting a regular menstrual cycle.
5. Low Body Weight
Low body weight, often associated with conditions like anorexia nervosa or excessive exercise, can lead to hypothalamic amenorrhea, a condition where menstruation ceases due to the suppression of the HPG axis. In such cases, restoring a healthy weight and adopting a more balanced approach to exercise are crucial for reestablishing hormonal equilibrium and resuming regular periods.
6. Medications and Birth Control
Certain medications, including hormonal birth control methods, can influence the timing of your menstrual cycle. Birth control pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs) can sometimes lead to lighter or even absent periods, especially during continuous or extended-cycle use. Hormonal birth control methods work by regulating hormones to prevent pregnancy. These methods can sometimes lead to lighter or less frequent periods, or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). While this is often expected and not a cause for concern, some women may experience delayed return to regular cycles after getting off birth control pills. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on what to expect and when your menstrual cycle should normalize.
7. Pregnancy
Pregnancy and breastfeeding naturally result in the absence of menstruation. However, there are situations where pregnancy may not be initially detected, leading to apparent late periods. It’s essential to consider the possibility of pregnancy if you’ve been sexually active and your period is late, especially if you’re not actively preventing pregnancy.
8. Breastfeeding and Amenorrhea
Breastfeeding provides essential nourishment for infants and can delay the return of menstruation in some women. This phenomenon, known as lactational amenorrhea, occurs because breastfeeding suppresses the release of certain reproductive hormones, temporarily preventing ovulation and menstruation. While breastfeeding is a natural method of contraception during this period, it’s essential to plan for contraception once fertility returns.
9. Perimenopause and Menopause
Perimenopause is the transitional phase leading to menopause, during which a woman’s reproductive system undergoes significant changes. Irregular periods, including late or missed cycles, are common during perimenopause due to fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone. Menopause, marked by the absence of menstruation for 12 consecutive months, signifies the end of the reproductive years.
During perimenopause, ovarian function gradually declines, leading to hormonal imbalances and irregular periods. These changes can result in late or heavy periods, as well as various menopausal symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings. Managing perimenopausal symptoms often involves lifestyle adjustments and, in some cases, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
10. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions and illnesses can affect the timing of your menstrual cycle. Conditions such as polyps, fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can lead to abnormal bleeding patterns, including late or heavy periods. Infections or systemic illnesses can also disrupt hormonal balance and menstruation.
11. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder characterized by the formation of small cysts on the ovaries. One of its hallmark symptoms is irregular menstrual cycles. Women with PCOS often experience delayed or missed periods due to the elevated levels of androgens, such as testosterone, which can hinder ovulation. This condition can also lead to symptoms like acne, excessive hair growth, and weight gain. Managing PCOS often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications and exercise, as well as medical treatments to regulate hormones and improve menstrual regularity.
Signs of Period Coming Late
Late periods can be accompanied by various signs and symptoms that signal a shift in the menstrual cycle. Recognizing these indicators can help individuals better understand their body and address any concerns they may have.
Signs of Late Periods:
- Missed Period: The most apparent sign is the absence of menstrual bleeding beyond the expected cycle length.
- Change in Menstrual Flow: A delay in periods may be followed by either lighter or heavier bleeding than usual when menstruation does occur.
- Breast Tenderness: Some women experience breast tenderness and swelling just before their period. This symptom can persist if menstruation is delayed.
- Abdominal Bloating: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to water retention and abdominal bloating, which may be more noticeable when periods are late.
- Mood Swings: Hormonal changes can impact mood, causing irritability, mood swings, or heightened emotional sensitivity.
- Cramping: Menstrual cramps, often associated with menstruation, may occur even if periods are delayed. These cramps can be uncomfortable but are not necessarily a sign of pregnancy.
Differentiating Late Period Signs from Pregnancy Symptoms
It’s essential to distinguish between the signs of late periods and those of pregnancy, as they can sometimes overlap. Knowing the difference can help alleviate anxiety and guide appropriate actions.
Signs of Pregnancy:
- Breast Changes: Similar to late periods, pregnancy can cause breast tenderness and enlargement. However, in pregnancy, these changes tend to be more pronounced and persist.
- Nausea and Morning Sickness: While some women experience nausea and vomiting during pregnancy, it’s less common with late periods.
- Positive Pregnancy Test: The most definitive way to confirm pregnancy is through a positive pregnancy test, typically taken a few days after a missed period.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Late Periods
Ayurveda offers a unique perspective on interpreting signs of late periods, emphasizing the balance of doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) and the importance of a woman’s overall well-being.
Ayurvedic Considerations:
- Dosha Imbalances: Ayurveda attributes late periods to imbalances in the doshas. For example, Vata imbalance can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, while Pitta imbalance may cause excessive heat and bleeding. Kapha imbalance may contribute to prolonged periods or delayed periods.
- Lifestyle and Diet: Ayurveda underscores the role of diet and lifestyle in menstrual health. It suggests that certain dietary choices, stress, and physical activity can influence the doshas and affect the menstrual cycle.
- Stress Management: Stress is a significant factor in Ayurveda’s understanding of late periods. It can disrupt the natural rhythms of the body and contribute to Vata imbalances, which can make your periods irregular and painful.
- Herbal Support: Ayurveda offers herbal remedies and dietary recommendations to address dosha imbalances and support healthy menstruation. For instance, warming and grounding herbs are often used to balance Vata.
- Ritucharya (Seasonal Routines): Ayurveda advocates adapting one’s daily and seasonal routines to align with the changing environment. This can help maintain hormonal balance and prevent late periods.
In Ayurveda, addressing late periods involves restoring dosha balance, adopting a balanced lifestyle, and incorporating Ayurvedic herbs and practices as needed. Consultation with an Ayurvedic practitioner can provide personalized guidance based on an individual’s constitution and specific concerns.

What to Do When Periods Are Late But Not Pregnant
Experiencing late periods when not pregnant can be concerning, but there are steps you can take to address the issue while prioritizing your well-being. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Self-Assessment
- Check Your Calendar: Start by tracking your menstrual cycle. Determine whether your period is genuinely late or if it falls within your normal cycle length, which can vary among individuals.
- Pregnancy Test: Take a pregnancy test if there’s any chance you might be pregnant, even if you think it’s unlikely. Pregnancy is a common cause of missed periods.
- Consider Recent Changes: Reflect on any recent lifestyle changes, stressors, dietary alterations, or medication adjustments that might be affecting your menstrual cycle.
Step 2: Self-Care Measures
- Stress Management: High stress levels can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Engage in relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to reduce stress.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure you’re consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Include warming and nourishing foods as recommended by Ayurveda to support hormonal balance.
- Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic herbs like Ashwagandha or Shatavari may help balance hormones and regulate menstruation. Consult an Ayurvedic practitioner for guidance on their use.
- Lifestyle Habits: Evaluate your daily routine and make adjustments to ensure you are getting enough sleep, regular exercise, and maintaining a consistent schedule.
Step 3: Seek Ayurvedic Guidance
While self-assessment and self-care measures are valuable, seeking Ayurvedic guidance from a qualified practitioner is essential for addressing late periods effectively. Here’s why:
The Importance of Professional Ayurvedic Guidance
- Personalized Assessment: An Ayurvedic practitioner can conduct a detailed assessment of your dosha constitution (Prakriti) and identify any imbalances (Vikriti) contributing to late periods.
- Tailored Recommendations: Based on your unique constitution and imbalances, an Ayurvedic practitioner can provide personalized recommendations for herbs, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle modifications.
- Holistic Approach: Ayurveda takes a holistic approach, addressing not only the symptoms but also the root causes of late periods. It aims to restore balance to your entire well-being.
- Safe and Natural Solutions: Ayurvedic remedies are natural and generally free from side effects when used under the guidance of a trained practitioner.
- Long-Term Well-Being: Ayurveda focuses on long-term health and wellness, ensuring that your menstrual health is part of a broader strategy to support your overall well-being.
Facing late periods when not pregnant can be a source of concern, but it’s essential to approach the issue methodically. Start with self-assessment and self-care measures, but don’t hesitate to seek professional Ayurvedic guidance. With the help of an experienced practitioner, you can identify and address the underlying factors contributing to late periods and work toward achieving menstrual harmony and optimal well-being.
Conclusion
We understand that dealing with irregular or delayed periods can be frustrating and concerning. The quest for relief from this condition can be challenging, but it’s important to know that you don’t have to navigate this journey alone. At Medhya Herbals, our team of experienced Ayurvedic doctors is here to offer you a helping hand and a path towards lasting relief.
We want to assure you that Ayurveda, with its holistic approach and focus on addressing root causes, can provide a solution that goes beyond just managing symptoms. Our personalized Ayurvedic treatments are tailored to your unique needs, aiming to restore balance to your menstrual cycle and overall well-being.
Don’t let irregular periods disrupt your life any longer. Take the next step towards a healthier, harmonious menstrual cycle by scheduling a consultation with our Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals. Together, we can uncover the underlying causes of your condition and work towards a permanent solution that brings you lasting relief and a renewed sense of vitality. Your path to a balanced and regular menstrual cycle starts here with Medhya Herbals.
FAQ
What Does It Mean If Your Period Is Late and You Have White Discharge?
If your period is late and you’re experiencing white discharge, it can be an indication of several factors. White discharge, also known as cervical mucus, can vary in consistency and color throughout your menstrual cycle. While it’s usually normal and can be a sign of ovulation or hormonal fluctuations, when coupled with a late period, it may suggest various possibilities. It could be a sign of early pregnancy, an underlying infection, or even a response to changes in your hormonal balance. It’s essential to consider other symptoms you may be experiencing and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause and appropriate course of action.
Why Do I Have Cramps but No Period?
Experiencing abdominal cramps without the onset of your menstrual period can be perplexing. These cramps, often referred to as “phantom” or “false” cramps, can occur due to various reasons. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those in the lead-up to menstruation, can trigger cramping even if your period is delayed or absent. Additionally, factors like digestive issues, stress, or uterine conditions may also contribute to cramping in the absence of menstruation. If you’re concerned about persistent or severe cramps without a period, consulting a healthcare professional can help identify the underlying cause and determine the appropriate steps for relief.
Can Lack of Sleep Cause a Delayed Period?
Yes, a lack of sleep can indeed contribute to a delayed period. Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating various hormonal processes in the body, including those involved in the menstrual cycle. When you consistently experience insufficient sleep, it can lead to disruptions in hormone production and balance, potentially causing irregularities in your menstrual cycle. The stress and physical strain associated with sleep deprivation can also impact the body’s overall hormonal equilibrium, further increasing the likelihood of a delayed period. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help support a regular menstrual cycle and overall well-being.
Can Sadness Make Your Period Late?
Yes, emotional factors like sadness and chronic stress can influence your menstrual cycle and potentially lead to a delayed period. When you experience strong emotions, particularly chronic stress or sadness, it can disrupt the balance of hormones in your body, affecting the timing and regularity of your menstrual cycle. This disruption is often related to the impact of stress on the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which in turn affects the hormones responsible for regulating your periods. While occasional emotional distress may not have a significant impact, chronic or severe emotional stress can contribute to menstrual irregularities, including late periods. Prioritizing self-care, stress management, and seeking support when needed can help promote menstrual regularity and emotional well-being.
Can Your Period Date Change Every Month?
Yes, it’s entirely normal for your period date to change from month to month. Menstrual cycles can vary in length, and it’s common for a woman’s period to arrive earlier or later than expected. Several factors, including stress, hormonal fluctuations, lifestyle changes, and even changes in diet or exercise routines, can influence the length of your menstrual cycle. While some women have relatively consistent cycles, others experience more variability. As long as these changes remain within a certain range and you’re not experiencing other concerning symptoms, such fluctuations are typically considered part of the normal menstrual cycle variability. However, if you notice drastic or persistent changes in your cycle, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying issues.
How Do I Get My Period Back?
Restoring your menstrual cycle, especially if it has been irregular or absent, involves several steps. Firstly, it’s crucial to identify and address the underlying cause, which could be related to factors like stress, extreme weight loss, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to pinpoint the specific reason behind your irregular periods.
To help regulate your menstrual cycle, focus on maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle. This includes consuming a well-rounded diet, managing stress through relaxation techniques, engaging in regular exercise, and ensuring you get adequate sleep. If your irregular periods are due to hormonal imbalances, your healthcare provider may recommend hormonal therapy or other medical interventions. Overall, achieving and maintaining good physical and emotional health plays a key role in promoting a regular menstrual cycle.

