Endometriosis symptoms bring a lot of pain, agony and emotional distress. In fact, excessive period cramps or dysmenorrhea is usually a first sign of endometriosis. It is estimated that Endometriosis affect 1 in 10 women and girls of the reproductive age. It is a growing concern of absenteeism and poor mental health amongst women, specifically during menstruation. Despite its prevalence, endometriosis often goes undiagnosed or misunderstood, leaving many individuals grappling with its challenging symptoms.
While the exact cause of Endometriosis is not yet known, one thing that you must know is that early intervention helps. This is because Endometriosis is progressive in nature. That means, you need to address Endometriosis symptoms in early stages. This will help you to prevent the growth and spread of Endometrial tissues. And hence, avoid multiple health complications that Endometriosis brings.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of endometriosis symptoms, from the common signs to the less-known indicators, providing a comprehensive guide to help individuals recognize, understand, and seek the support they need on their journey to managing this condition. Whether you’re personally affected or seeking to enhance your awareness, join us as we uncover the multifaceted landscape of endometriosis symptoms.
Understanding Endometriosis
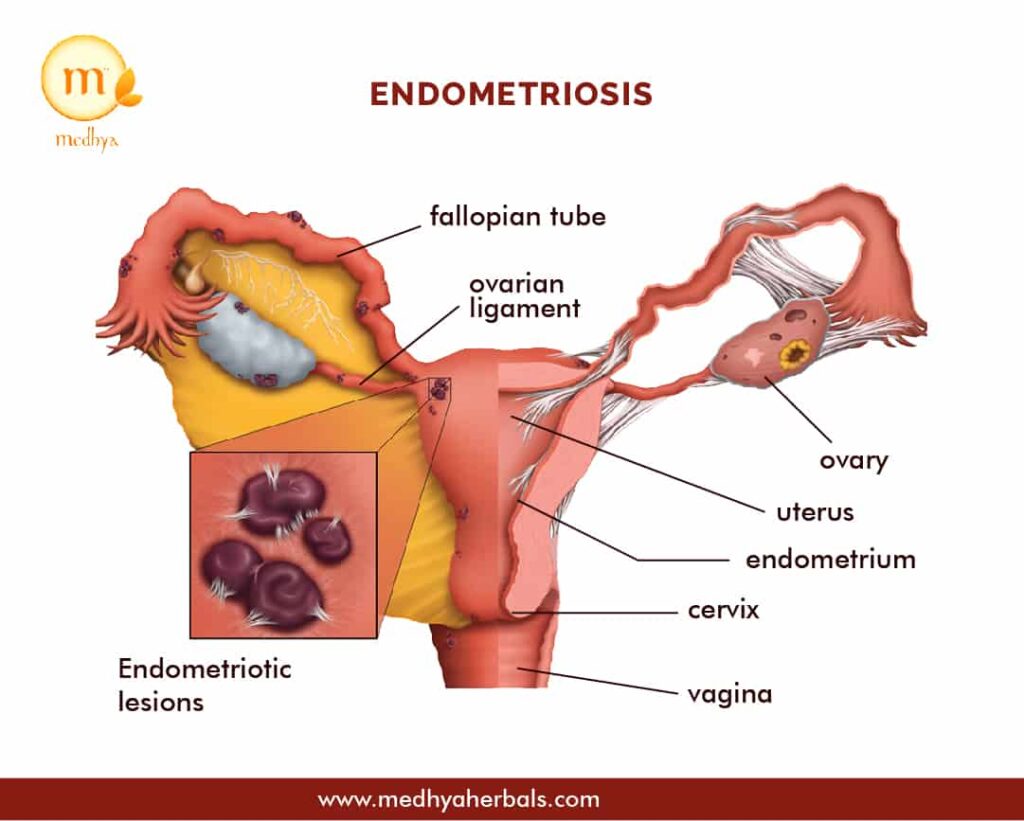
Endometriosis is a chronic medical condition that primarily affects individuals with female reproductive organs. It occurs when tissue resembling the endometrium, which typically lines the inside of the uterus, grows outside the uterus. This condition often manifests with intense and debilitating pain, including severe menstrual cramps and chronic pelvic discomfort throughout the menstrual cycle. Additionally, endometriosis can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, irregular periods, painful bowel movements, and pain during urination.
One of the distressing symptoms associated with endometriosis is “endo belly,” characterized by severe abdominal bloating. Moreover, endometriosis is a leading cause of infertility, as it can adversely affect the functioning of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the reproductive system as a whole, making it challenging for individuals to conceive. It can also result in dyspareunia, causing pain during sexual intercourse. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans are crucial for effectively managing endometriosis and improving an individual’s quality of life and reproductive health.
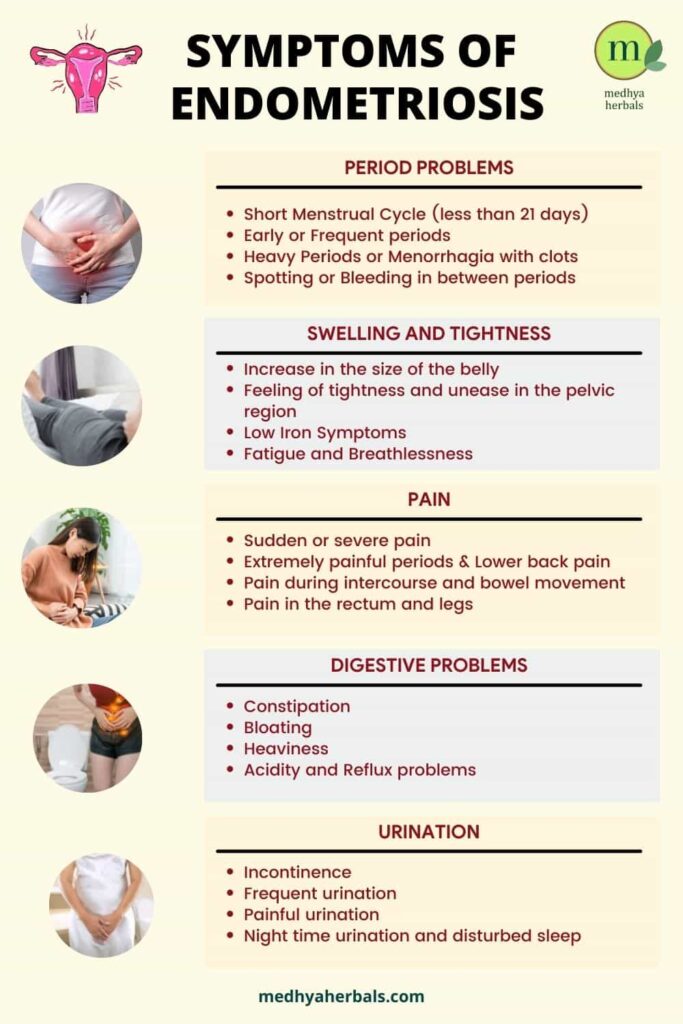
What are the First Signs and Symptoms of Endometriosis?
The first signs of endometriosis are not always the same for all women. It actually depends on the growth and location of the endometrial tissue. That’s why some women experience high intensity symptoms, while for others there aren’t any noticeable signs. Here are the first signs of endometriosis that are often experienced by majority of the women. Any of these symptoms are a sign of normal menstrual cycle or how a woman’s body operates in general.
1. Acute Pain
Growth of endometrial tissues lead to acute pain and cramping in the pelvic cavity. Endometriosis pain usually radiates from lower back area to lower abdomen, thighs, and even to other body parts.
The pain experienced in endometriosis is so bad that the patient is not able to carry out her normal life. Severe pain may be present right before menstruation or continue during the whole cycle. Do note that pain progresses with Endometriosis, meaning the intensity of pain increases if there is more growth and spread of endometriosis.
- Pain in the Uterus
- Lower Back pain
- Pain in lower abdomen area or pelvic cavity
- Dyspareunia or painful intercourse
- Pain is experienced while passing urine or bowel movement
2. Endometriosis Bowel Symptoms – Bloating, Constipation and Gas
One of early signs of endometriosis is frequent bowel problems and digestive issues such as gas, bloating, constipation and diarrhea. This endo symptom is often termed as endo belly. The intensity of endometriosis bloating and abdominal pain in usually increases before and during your period. These symptoms are similar to what a patient experiences in IBS, thus pointing towards a link of Endometriosis and IBS.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Absence of appetite
- Bloating and Gas, which often leads to big endo belly
- Diarrhea or loose stools
3. Irregular Periods
Periods that do not come on time and when it happens, it brings lot of pain and excess bleeding. This is a sure tell-a-tale sign of Endometriosis.
However, that’s not it! All women are different and you may experience different symptoms. Irregular periods can be caused by a multitude of other factors and Endometriosis is one of them.
- Early or Frequent periods
- Long periods that last beyond 7 days
4. Heavy Bleeding during Menstruation
- Clotted blood flow during menstruation
- Heavy Periods or Menorrhagia
- Spotting or Bleeding in between periods
5. Inability to Conceive
Infertility and inability to conceive is commonly observed in Endometriosis. Infertile patients often have no painful symptoms. Usually, endometriosis is only discovered in the course of the diagnostic work-up for infertility.
If you experience these signs and symptoms, do consult with your doctor and take action on your health condition.
Possible Locations of the Endometrial Tissues
- Anywhere outside the uterus
- Ovaries
- Walls of the pelvic cavity
- Fallopian tube: It is frequently reported in patients after menarche (menstrual cycle begins for the first time)
- Gastrointestinal tract: It is estimated to occur in 12–37% of patients with endometriosis. Most common areas are small intestine (cecum and ileum), large intestine (colon) and appendix
- Abdominal wall
- Urinary bladder, ureters, and renal (kidneys)
- Lungs (rare)
- Lower extremities such as on the thigh (rare condition)
- Central Nervous System (rare condition)
- Cutaneous or under the skin, leading to skin lesions and uneven skin (rare condition)
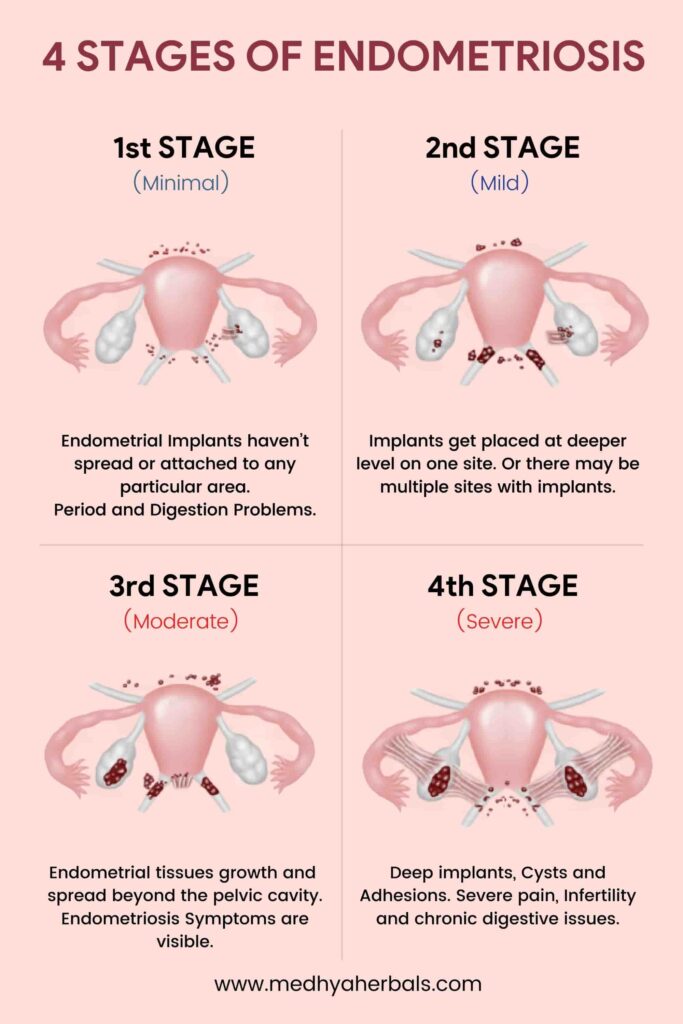
What are The Four Stages of Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a progressive disease. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, there are 4 stages of endometriosis depending on the severity of the symptoms:
1st stage (Minimal)
At this stage, the implants are superficial in nature. This means, they haven’t really attached or grown in any particular area. This is really early stage, at which one can prevent the implants from sticking and growing at one place.
2nd Stage (Mild)
At this stage, the implants have been placed at deeper level on one site. Or there may be multiple sites with implants.
3rd Stage (Moderate)
Typically at this stage a woman starts to exhibit a degree of endometriosis symptoms (apart from pain). This stage usually involves growth and spread of the endometrial tissues beyond the pelvic cavity.
4th Stage (Severe)
At this stage, one experiences many deep implants. There may be large endometrial tissues on one or both ovaries.
One may experience many dense adhesion. Or it may also happen that one has their rectum adhering to the back of the uterus. This leads to severe pain and chronic digestive issues.
What Causes Endometriosis Symptoms?
Understanding the causes of endometriosis is a complex and ongoing area of research in the field of women’s health. While the exact origin of this chronic condition is not fully elucidated, there are several theories and factors that may contribute to its development. In this section, we will explore some of the leading hypotheses and potential triggers that are associated with the onset of endometriosis.
1. Retrograde Menstruation
Retrograde menstruation means that menstrual flow starts to flow upwards rather than exiting through the vaginal canal. This is what happens:
- The endometrial tissues and menstrual blood enters the Fallopian tubes. It then attaches to the nearby organs in the abdomen, and grows like uterine endometrium.
- The menstrual debris and endometrial tissues can spread to other sites in the pelvic cavity or upper body through the Circulatory system and Lymphatic system.
- This causes growth and spread of the endometrial tissues to other body parts, often as far as the head.
2. Poor Immune Function
Usually immune system will remove this menstrual flow debris. But, when it doesn’t function properly, the endometrial tissues stay along and develop into endometriosis.
3. Hormone Imbalance
High estrogen levels and estrogen dominance lead to higher sensitivity of Endometrial tissues to the hormones. That’s why, when you are struggling with hormone imbalance, it makes you more prone to the uncontrolled growth of endometriosis.
4. Poor Diet and Lifestyle
Excessive consumption of Alcohol and Smoking predisposes women to conditions that support endometriosis. Additionally, when your diet is not good then you are more prone to develop nutritional deficiency and hormone imbalances.
5. Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Materials
Endocrine Disrupting Materials (EDC) such as BPA, Dioxins and chemicals in food and environment also creates possibility of endometriosis.
EDC often lead to high estrogen levels and hormone imbalances that further disrupt normal menstrual flow and immune function of a woman.
Who is at the Risk of developing Endometriosis Symptoms?
1. Women with obstructive genital tract disease: This makes them prone to high backward menstrual flow.
2. Long duration of Periods and Short Menstrual Cycle: This makes women prone to attachment and progression of endometrial cells in pelvic cavity.
3. Hormone Imbalance and Excess Estrogen: This aggravates the problem of endometriosis as the cells become more sensitive to hormones in the blood.
4. Autoimmune disorders: Immune system is not able to destroy the abnormal endometrial tissues. They stay intact causing more inflammation.
5. Genetic Factors: If someone close in your family has Endometriosis, it makes you more prone to development of the same.
6. Age Group: Usually, the mean age of a woman at diagnosis of endometriosis is 25–29 years. However, it can also be present in adolescents and in elderly.
It has been observed that approximately half of women (below 20 years), who experience chronic pelvic pain have endometriosis. Also, about 5% of endometriosis cases are seen in postmenopausal women.
Conclusion
Do note that Endometriosis is a progressive and painful disease. But, you can prevent it by pursuing a Healthy Diet and Lifestyle. Act Early to Prevent Health Issues Later!
If you are struggling with endo symptoms and looking for support, then do speak to Medhya Herbal’s Ayurvedic doctors today. Our highly experienced Ayurveda medical practitioners will provide you with a personalized Ayurvedic treatment and step-by step guidance on diet and lifestyle to balance hormones and find relief from Endometriosis symptoms.
Don’t let endo take a toll on your life! There are highly effective natural measures that Ayurveda offers to treat Endometriosis in a safe and non-invasive manner. Start today!
FAQ
What organs can endometriosis affect?
Endometriosis is a disorder in which the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of the uterus. This excess tissue can grow on the ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and other organs in the abdominal cavity. In some cases, it may even spread to the lungs or brain. Endometriosis can cause a variety of symptoms, including pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and infertility. Ayurvedic medicine has been used to treat endometriosis for centuries. The main goal of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation. Herbal supplements, dietary changes, and massage therapy are all commonly used Ayurvedic treatments for endometriosis.
Can a blood test detect endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a disorder in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside of the uterus. This can cause pain, heavy bleeding, and other problems. A blood test can sometimes be used to detect endometriosis, but it is not always accurate. In addition, endometriosis can only be diagnosed definitively by surgery. However, a blood test may be able to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms. As a result, a blood test can be a helpful tool in diagnosing endometriosis.
Does endometriosis show up on an ultrasound?
Endometriosis is diagnosed through a combination of pelvic exam and imaging tests, such as ultrasound. Ultrasound can sometimes detect lesions associated with endometriosis, but the diagnosis is typically confirmed through laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure in which a lighted microscope is inserted through small incisions in the abdomen. This allows the doctor to directly visualize any endometrial lesions present.
Can I check myself for endometriosis?
Unfortunately, you cannot diagnose endometriosis on your own. Endometriosis is a medical condition that can only be diagnosed by a qualified healthcare professional.
If you are experiencing symptoms that could be related to endometriosis, such as painful periods, chronic pelvic pain, pain during sex, or difficulty getting pregnant, it is important to make an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can perform a physical exam, review your medical history, and order tests or imaging studies if necessary to make a diagnosis.
Remember, early detection and treatment of endometriosis can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life, so don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you have concerns about your symptoms.
How is endometriosis diagnosis done?
Endometriosis is a disorder in which the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside of the uterus. This can cause pain, heavy bleeding, and infertility. There is no one test that can definitively diagnose endometriosis, but there are several options that can be used to help identify the condition. One common approach is pelvic examination, which can sometimes reveal lesions or masses associated with endometriosis. Ultrasound exams may also be used, as endometrial tissue appears differently than other tissues on an ultrasound. Additionally, MRI or CT scans can be helpful in identifying endometriosis lesions. In some cases, laparoscopy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. During this procedure, a small camera is inserted into the abdomen through a small incision. This allows the doctor to directly visualize any endometrial tissue growths. Endometriosis is a complex condition, and there is no single test that can be used to diagnose it definitively. However, various diagnostic tools can be used to help identify the condition and rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
References

