Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, is a common, often under-diagnosed and misunderstood condition, affecting a significant portion of the global population. Even more striking is its prevalence in women, with almost two-thirds of IBS sufferers being female. If you’ve found yourself here, you’re likely curious or even concerned about the symptoms of IBS in women, seeking answers to questions that can often feel overwhelming or confusing.
As an Ayurvedic doctor specializing in women’s wellness, I’ve dedicated my work to uncovering and understanding these complex issues. I’ll guide you through the signs and symptoms of IBS in females, offering clear, comprehensible insights derived from years of research and experience in the field of Ayurvedic natural treatment.
In this article, we’ll delve deep into the world of IBS, exploring everything from early signs, misdiagnoses, to dietary triggers and treatment options. We aim to provide answers to all your questions – shedding light on the unique challenges women face when dealing with IBS, how to distinguish it from other conditions, and most importantly, how to manage it effectively. So whether you’re seeking knowledge for yourself, a loved one, or simply to educate yourself further, rest assured, you’re in the right place.
Your journey to understanding and managing IBS starts here, and we’re with you every step of the way. Let’s begin.
Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic condition that impacts the large intestine. It’s characterized by a cluster of symptoms that include abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits – diarrhea, constipation, or both. Unlike more serious intestinal diseases such as Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, IBS doesn’t cause inflammation, ulcers or other damage to the bowel. However, the symptoms can be distressing and have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
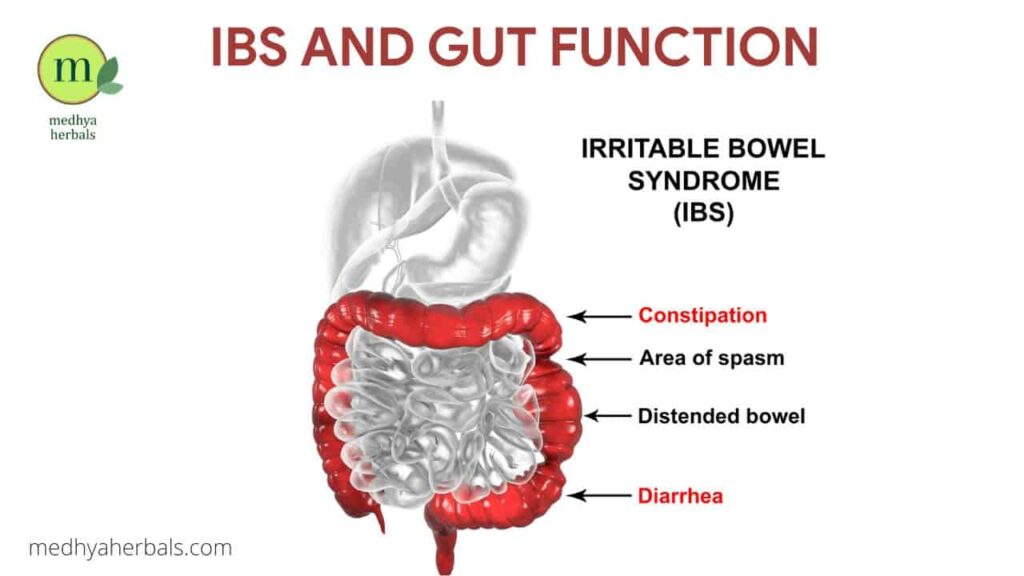
Age of Onset of IBS
IBS can develop at any age, but the symptoms often start in early adulthood. The majority of people are diagnosed before the age of 50. However, the condition is not exclusive to this age range. Some people may experience symptoms later in life, and an onset after the age of 60 is also possible, albeit less common. Regardless of when symptoms begin, IBS is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. Understanding the symptoms of IBS in females can help in earlier detection and treatment, potentially reducing the condition’s impact on quality of life.
The Impact of IBS on Quality of Life
Despite not being life-threatening, IBS can dramatically affect one’s day-to-day life. The unpredictability of the symptoms can lead to anxiety about when they might occur, which can, in turn, exacerbate the condition. It may limit people’s willingness to go out, engage in social activities, or even go to work. The discomfort and inconvenience brought on by the symptoms can also cause emotional distress, adding to the overall burden of the disease.
Early Signs and Symptoms of IBS in Females
Identifying IBS early can be tricky, as the symptoms often overlap with other digestive issues. However, some signs could potentially indicate the onset of IBS. The first signs of having IBS often include recurrent abdominal discomfort or pain that lasts for at least three days per month over the past three months. This pain is usually associated with a change in frequency or form of bowel movements.
Other early signs include alterations in bowel habits, such as frequent diarrhoea or constipation, and changes in the appearance of stool. You may also experience bloating or a feeling of gas, which can be quite uncomfortable. These symptoms may come and go over time. However, if these signs persist, it could be indicative of IBS.
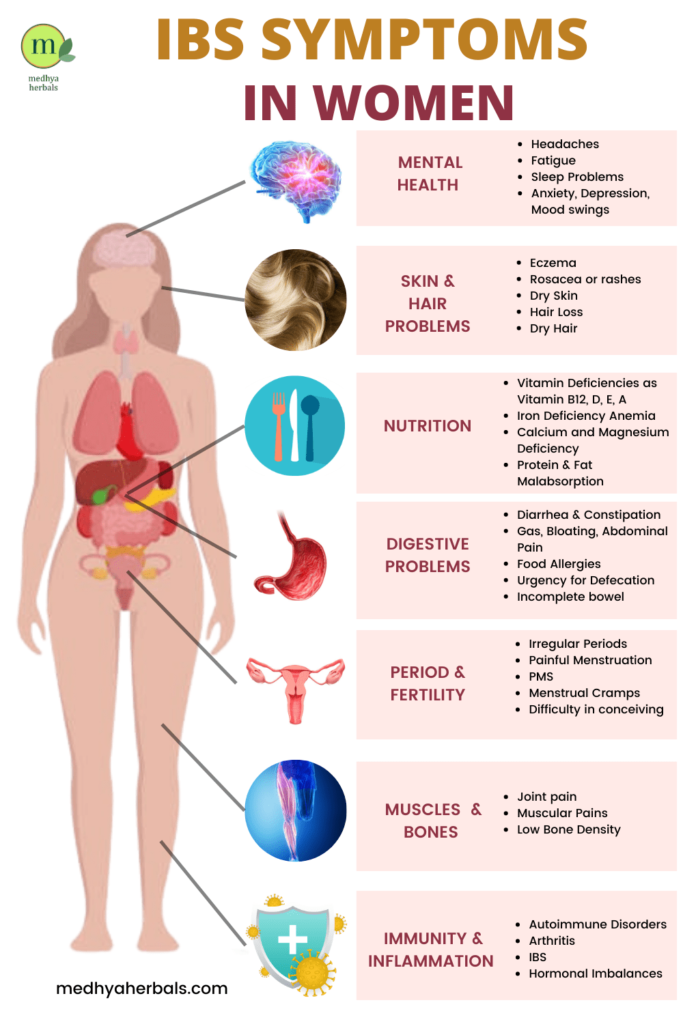
IBS Symptoms in Women
IBS appears to be more common in women than men, with studies indicating that about two-thirds of individuals diagnosed with IBS are women. Hormones are believed to play a role, as the fluctuation of hormone levels during menstrual cycles can exacerbate IBS symptoms in women. Here’s a list of symptoms typically associated with IBS:
- Abdominal pain or cramping that is often relieved by passing wind or feces
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation
- Changes in bowel movements and in the form and appearance of stool
- Bloating and swelling of the stomach
- Excessive gas
- Urgency to defecate
- Feeling that the bowels are not emptying completely
- Mucus in the stool
- Fatigue and difficulty sleeping
- Food intolerance
- Anxiety or depression
For women specifically, these symptoms may be accompanied by:
- Exacerbation of symptoms during or around the menstrual period
- Increased bloating and abdominal discomfort
- Co-existing conditions like fibromyalgia, migraines, and urinary frequency
Please note that these symptoms can vary from person to person, and not everyone with IBS will experience all of these symptoms.

Common Misdiagnoses and How IBS Differs
IBS has a range of symptoms that can overlap with other gastrointestinal disorders, often leading to misdiagnosis. It’s critical to identify the key distinctions to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Conditions That Could Be Mistaken for IBS
1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis fall under IBD. These conditions cause inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms that can closely resemble IBS, like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bloating.
2. Celiac Disease: This is an autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. Its symptoms can mirror IBS, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating.
3. Lactose Intolerance: In this condition, the body is unable to fully digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. This intolerance can cause bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
4. Gastroenteritis: This condition is characterized by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting, similar to IBS.
5. Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. It can cause abdominal pain and bowel symptoms that mimic IBS.
How IBS Differs from These Conditions
While IBS shares some symptoms with the conditions listed above, there are key differences.
IBD vs IBS: IBD causes inflammation and ulceration in the gut that can be seen on scans or during surgery. However, IBS doesn’t cause these physical changes or damage the gut. Instead, it’s a functional disorder, meaning the symptoms don’t have an identifiable cause.
Celiac Disease vs IBS: While both conditions can cause similar gastrointestinal symptoms, Celiac disease is an immune response to gluten, causing damage to the small intestine. IBS doesn’t involve an immune response or cause lasting damage to the digestive tract.
Lactose Intolerance vs IBS: In lactose intolerance, symptoms occur after consuming lactose. In IBS, symptoms may occur without a clear trigger and include more chronic and diverse symptoms like altered bowel habits and abdominal pain.
Gastroenteritis vs IBS: Gastroenteritis is usually acute, caused by an infection, and resolves itself in a few days. IBS, however, is a chronic condition and symptoms last longer, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Endometriosis vs IBS: Endometriosis causes pelvic pain and can affect bowel function, but the pain is typically associated with the menstrual cycle. IBS pain, on the other hand, is often relieved by a bowel movement and is not typically associated with the menstrual cycle.
Understanding these differences is crucial to obtaining the correct diagnosis and, ultimately, the right treatment plan. If you are experiencing persistent digestive discomfort, please seek professional medical advice.
Home Diagnostic Methods for IBS and When to Seek Professional Help
While certain symptoms and patterns can point towards IBS, it’s important to remember that self-diagnosis can be risky due to the condition’s overlap with other serious gastrointestinal disorders. Let’s explore how one might track symptoms at home and when it is crucial to seek professional help.
Checking IBS Symptoms at Home
Home checks for IBS primarily involve observing and recording symptoms. You might want to maintain a symptom diary noting down the following:
- The type of symptoms you experience
- The frequency and duration of these symptoms
- Any changes in bowel habits or appearance of your stools
- Any potential food triggers that seem to exacerbate your symptoms
Using a tool like the Bristol Stool Scale to describe your bowel movements can help identify patterns.
The Accuracy of Home Tests and When to Consult a Doctor
Home tests for IBS do exist, but their reliability can vary, and they should never replace a professional medical diagnosis. Some home tests measure levels of certain markers in the stool or blood that can indicate inflammation, but they cannot diagnose IBS.
It’s essential to consult a doctor if your symptoms persist, significantly impact your quality of life, or if you notice alarming symptoms like unexplained weight loss, rectal bleeding, or iron-deficiency anemia.
Professional Diagnostic Methods for IBS
Doctors use a combination of your medical history, physical examination, and specific criteria for diagnosing IBS, such as the Rome IV criteria. These criteria focus on the presence of recurrent abdominal pain, on average, at least one day per week in the last three months, associated with two or more of the following:
- Related to defecation
- Associated with a change in frequency of stool
- Associated with a change in form (appearance) of stool
For some people, the doctor may recommend further tests to rule out other conditions, such as blood tests, stool tests, or endoscopic procedures.
Regarding stool tests, while they can help rule out infections, inflammatory bowel disease, and other conditions, there is no specific stool test that can definitively diagnose IBS.

Diet and IBS
When it comes to managing IBS, dietary adjustments can play a crucial role. Certain foods can trigger IBS symptoms, while others can help calm them.
Worst Foods and Triggers of IBS Symptoms in Women
The “worst” foods for IBS Diet are those that are most likely to trigger symptoms. This can vary from person to person, but common triggers include:
1. High-fat foods: Foods high in fat can speed up intestinal contractions, leading to diarrhea for some people, or slow them down, causing constipation in others.
2. Dairy products: Lactose present in dairy products can be hard for some individuals with IBS to digest, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
3. Alcohol and caffeinated drinks: These can stimulate the intestines, worsening IBS symptoms.
4. Artificial sweeteners: These can cause diarrhea and gas in some people.
5. Certain fruits and vegetables: Some fruits and vegetables are high in fructans and other fermentable carbs, which can cause bloating, gas, and stomach pain in people with IBS.
Common Triggers for IBS Symptoms in Females
Just like the “worst” foods, triggers can vary greatly among individuals. However, common dietary triggers for IBS in women can include fatty foods, certain types of fiber (like insoluble fiber found in wheat bran), caffeine, alcohol, and large meals. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation can also exacerbate IBS symptoms, as can stress and lack of sleep.
Foods That Help Calm IBS
Diet can also be a tool for managing IBS symptoms. Foods that generally help calm IBS include:
1. Foods low in FODMAPs: FODMAPs are types of carbohydrates that can cause digestive issues in some people. A low-FODMAP diet, which reduces foods like onions, garlic, certain fruits, and wheat, can help manage IBS symptoms.
2. Soluble fiber: Foods with soluble fiber, such as oats, strawberries, and carrots, can help manage constipation and regulate bowel movements.
3. Lean protein: Foods like chicken, fish, and tofu are easy on the digestive system and can help manage symptoms.
4. Peppermint: This herb can help relax the intestines, reducing symptoms like abdominal pain.
Remember, every person with IBS is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to monitor your symptoms and work with a healthcare professional or dietitian to develop a diet plan that suits you.

Conclusion
Living with the symptoms of IBS can be an overwhelming and isolating experience. The unpredictable nature of the condition often adds a layer of anxiety to daily life, making finding the right solution seem like a daunting task. We want to assure you that you’re not alone in this journey, and effective relief is within reach.
At Medhya Herbals, we believe in the power of Ayurveda to provide holistic, root-cause treatments for conditions like IBS. Our experienced Ayurvedic doctors aim to understand the unique needs of each patient, developing personalized treatment plans that address not just the symptoms, but the underlying imbalances causing them. Ayurvedic treatment has the potential to offer a lasting solution, shifting your body back into harmony and providing you with long-term relief.
You don’t have to navigate this path alone. Schedule a consultation with our Ayurvedic doctors at Medhya Herbals today, and take the first step towards reclaiming your health and wellbeing. Let’s work together to make living with IBS a thing of the past for you.
FAQ
Can IBS Be Cured?
IBS a chronic condition that individuals typically manage for the long term. However, while IBS can’t be cured in the traditional sense, many people successfully manage IBS symptoms through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, stress management, and medication. The goal of these interventions is not to eliminate the disease, but to improve quality of life by reducing the frequency and severity of symptoms. It’s also important to note that IBS does not cause lasting damage to the digestive tract or lead to serious disease, such as cancer.
How Long Does It Take for IBS to Go?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is considered a chronic condition, meaning it’s long-term and generally lifelong. The severity and frequency of symptoms can greatly vary over time. Some people may have periods of remission, where their symptoms improve or even disappear for a few weeks, months, or longer. However, there is currently no cure that will completely eliminate IBS. Instead, the focus is on managing the symptoms to improve the quality of life. Everyone is different, and the time it takes to see improvement in symptoms can vary widely from person to person, often depending on factors such as diet, stress levels, and medical treatment. It’s always best to discuss personal symptoms and treatment options with a healthcare provider.
Role of Probiotics in IBS
Probiotics are often referred to as “good” bacteria and are widely used to help restore the natural balance of gut flora. They can aid in digestion and nutrient absorption and can help strengthen the body’s natural defenses.
In terms of IBS, research has suggested that certain strains of probiotics can help reduce symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements. However, not all probiotics are the same, and their effectiveness can vary depending on the specific strain and the individual’s gut microbiome.
In some cases, probiotics may exacerbate IBS symptoms, especially when first started, as the body adjusts to the new bacterial balance. Symptoms can include increased gas and bloating. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new supplement regimen.
IBS and Acid Reflux
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), are distinct conditions but they often occur together. Both are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and can be influenced by similar factors, such as stress, dietary triggers, and changes in gut bacteria. While IBS primarily affects the large intestine, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits, acid reflux is characterized by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation. Effective management of these conditions often involves lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and targeted medications. It’s important to seek professional medical advice if you’re experiencing symptoms of either condition.
What is Best Natural Medication for IBS?
In the realm of natural treatments for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), dietary modifications, probiotics, peppermint oil, and ginger stand out as particularly effective. A low FODMAP diet, which involves reducing intake of certain hard-to-digest carbohydrates, has proven beneficial for many individuals. Probiotics, beneficial gut bacteria found in foods like yogurt or taken as supplements, can help restore gut health and manage IBS symptoms. Peppermint oil, due to its antispasmodic properties, can provide relief from common symptoms such as cramping, bloating, and gas. Lastly, ginger, traditionally used to alleviate digestive problems, can be used to soothe the digestive tract and alleviate symptoms of nausea.
Why Do People Get IBS and Can It Develop Suddenly?
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it’s believed to result from a combination of factors including altered gut motility, visceral hypersensitivity (increased pain sensitivity in the gut), and disruptions in the gut microbiome. Psychological factors like stress and anxiety also play a role. Hormonal changes might explain why IBS is more common in women.
Yes, IBS can develop suddenly. An onset of IBS symptoms can sometimes be traced back to a specific event, such as a gastrointestinal infection or significant life stress.
References
- “The Efficacy of Ayurvedic Medicines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Hindawi, 7 May 2021, https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/6623816/.
- “Ayurvedic and Conventional Treatment for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial.” Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, Elsevier, 1 Jul. 2017, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0975947617300839.
- “Efficacy of Ayurvedic treatment modalities in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A randomized controlled trial.” Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, Elsevier, 1 Oct. 2019, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0975947619301583.
- “Herbal remedies for irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review.” Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Wiley Online Library, 10 May 2021, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jphp.13475.
- “The effect of yoga on irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” Complementary Therapies in Medicine, Elsevier, 1 Oct. 2019, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0965229919302955.
- “Effect of probiotics on Irritable Bowel Syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.” Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, National Institute of Health, 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6738735/.
- “The therapeutic effect of Aloe vera in gastrointestinal disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, National Institute of Health, 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6843916/.
- “Fennel and its potential beneficial effects in critical health conditions.” Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, Elsevier, 2018, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1021949817301897.
- “Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, National Institute of Health, 2014, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4286770/.
- “The effect of ginger in the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” Journal of Functional Foods, Elsevier, 1 Jan. 2021, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464620307185.

