PCOS or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a condition that affects many women of reproductive age. It is characterized by an imbalance of hormones, which can lead to irregular periods and fertility problems in PCOS patients. Thus getting pregnant with PCOS and even pcos pregnancy is often considered to be challenging for majority of the women.
Ayurveda can help to naturally treat the root cause of pcos fertility issues. Ayurveda treatment for PCOS/PCOD (polycystic ovarian disease) focuses on regulating the hormones and boosting the fertility.
Ayurvedic medicine, dietary changes, and yoga are all part of an Ayurveda PCOS treatment to improve the fertility in women with PCOS and increase the chances of a healthier pregnancy outcome.
PCOS Symptoms
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the leading causes of female infertility. It affects about 6 – 15% of women of reproductive age.
Of these women, 73% have anovulation due to PCOS. Absence of ovulation and menstrual irregularity lead to fertility problems and problems with pcos pregnancy.
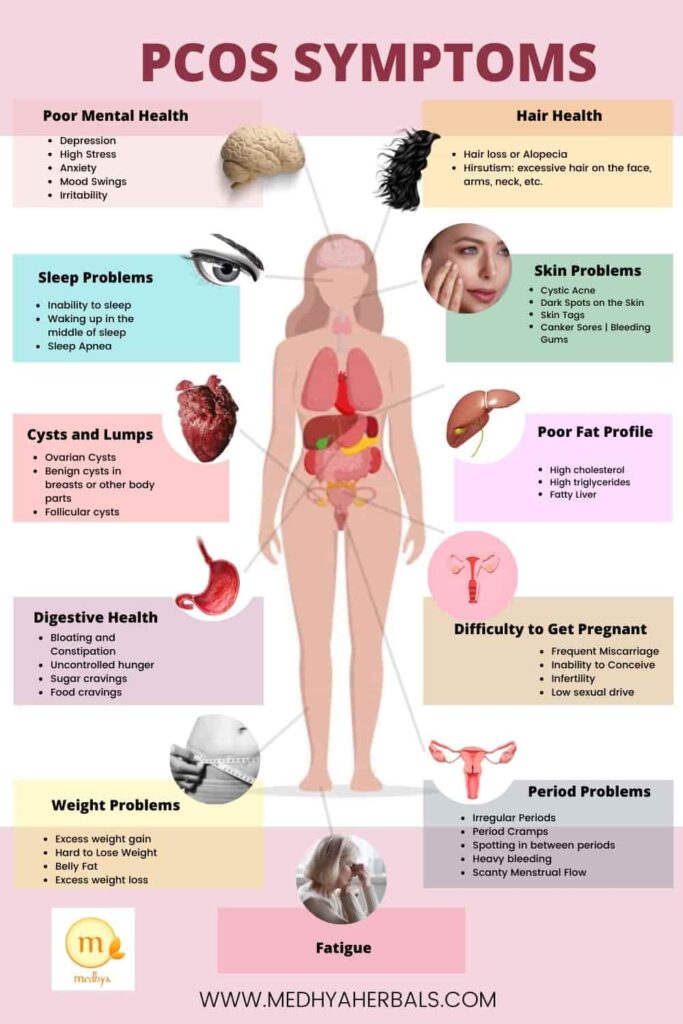
If you are struggling with fertility issues, but are not quite sure about the reason. Then perhaps you should check for the other symptoms of PCOS such as:
- Hirsutism: Excess hair growth an unwanted body hair on the face, chest, abdomen
- Skin problems like extensive acne breakouts (reaching neck, chest, and back), acanthosis nigricans (dark patches on the skin).
- Menstrual period disorder involving menstrual irregularity
- PCOS Hair loss
- Ovarian cyst or cysts on the ovaries
- PCOS Weight Gain
- Mood Swings and Fatigue
- Digestive problems
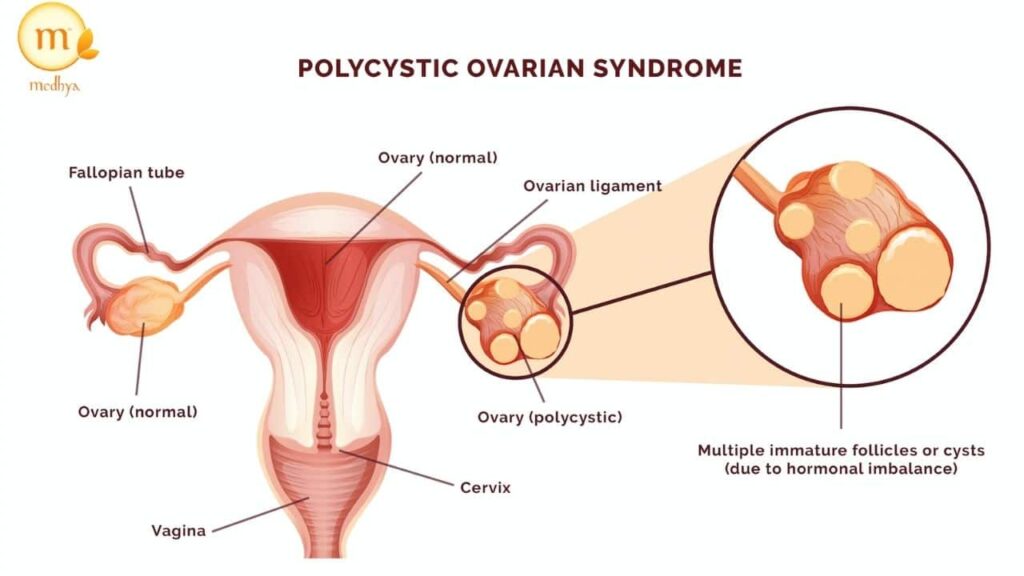
What Causes PCOS Infertility?
Hormonal Imbalance is the leading cause of a pcos patient’s struggles with fertility problems. Here’s what happens:
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Women with PCOS (Polycystic ovarian syndrome) often have higher-than-normal levels of male hormone and high insulin levels. Both of these hormones can cause problems with ovulation and interfere with implantation and early pregnancy. In addition, they suppress female sex hormones such as Estrogen and Progesterone that regulate a woman’s menstrual cycle, thus causing menstrual irregularity in PCOS.
2. Irregular Periods
Your menstrual cycle can be distorted by the irregularity in hormone levels brought about by polycystic ovarian syndrome. In PCOS, your menstrual cycle can be longer than 35 days, meaning your periods do not show up as often as they should. You may get your period in a month and not get it the next two. It is completely unpredictable.
Or you may suffer from amenorrhea, in which there is no menstruation at all. Thus, it becomes difficult to plan conception when you don’t even know when next your period is going to be.
3. Polycystic ovaries
One of the main causes of PCOS infertility is ovulatory dysfunction. In women with PCOS, the ovaries may produce immature eggs that do not develop properly or are not released during ovulation.
PCOS cysts are formed due to these numerous immature eggs in the ovary that were never released. They accumulate like a string of beads giving the appearence of polycystic ovaries.
If your eggs are not maturing, then they can’t get fertilized, thus making it difficult for you to conceive in the first place.
4. Inflammation & Health Conditions
Women with PCOS may also have other health conditions that can affect fertility, such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, or endometriosis. In addition, PCOS is associated with chronic low-grade inflammation, which can contribute to infertility by damaging the reproductive tissues and interfering with ovulation and implantation.
Ayurvedic Fertility Treatment for Getting Pregnant with PCOS
PCOS Fertility treatments like removing the cysts via surgery, taking hormone therapy to treat hormonal imbalance, period or ovulation inducing pills and Oral Contraceptive or birth control pills only act as temporary solutions that do not address the root cause of PCOS infertility. Ayurveda on the other hand offers a permanent and safe solution to reverse PCOS/PCOD.
According to Ayurveda, fertility is determined by three main factors: the quality of the eggs, the quality of the sperm, and the strength of the uterus.
There are a number of different Ayurvedic treatments that can be used to improve each of these factors. For example, herbs such as shatavari and ashwagandha are said to improve egg quality thus treat female infertility, while herbs such as gokshura and tribulus terrestris are thought to treat male infertility by improving sperm quality.
In addition, Ayurvedic massage and yoga can help to strengthen the uterus for a safe pregnancy outcome. Here are the steps that you can take under the direction of an Ayurvedic doctor to boost your fertility and get pregnant with PCOS:
1. Ayurvedic Herbs to Improve Egg Quality & PCOS Fertility
There are many Ayurvedic herbs and medicines that boost fertility and regular ovulation.

- Shatavari: This a rich source of vitamins and minerals. It has antioxidant properties so that it can protect the reproductive system. It increases insulin sensitivity and boosts fertility as a whole.
- Guduchi: This Ayurvedic herb helps to reduce blood sugar levels and manage high blood pressure. Aside this, it helps boost immunity, treat liver conditions and sex drive in females.
- Kachnar Guggulu: It is rich in flavonol glycosides. These compounds help regulate hormones, improve fertility and reduce uterine disorders generally.
- Ashwagandha (Withania Somnifera): This Ayurvedic herb helps to rejuvenate the female reproductive system. It also supports adrenal glands and improves sleep.
- Bibhitaki: Bibhitaki helps to improve sugar metabolism, thus reducing the risk of diabetes in a PCOS patient. In addition, it improves digestion and nutrient levels in the body.
- Basti (Herbal Enema): This helps to regulate imbalanced vata dosha, in order to ‘get things moving’.
- Panchakarma therapy: This is an Ayurvedic detoxification process to get rid of excess kapha dosha, improve fertility and immunity.
- Fertility Yoga therapy.
2. PCOS Fertility Diet
The importance of eating good food is highly underrated these days.
Most people think you’re alright as long as you’ve stuffed your stomach full of something. They believe if it has just the right texture and is the right temperature and all that, then they have ‘eaten food.’
But food is more than that. Food is the fuel the body runs on, and the body includes the reproductive system. The body extracts what it needs from the food you eat and discards the waste.
If it does not get the right type of nutrients in the right proportions at the right time, then it leads to multiple health issues related to fatigue, skin, hair, menstrual cycle and fertility problems.
This is not to say that you should not enjoy your meals, nor is it saying you should not eat what you like. Rather, it is to remind you that the primary purpose of food is nutrition.
A Diet to Boost Fertility and Vitality – Get Pregnant with PCOS Naturally
Multiple research studies and our own client testimonials indicate that your diet is one of the most powerful tools to your fight against PCOS infertility.
Diet and exercise are the two best recommendations for managing PCOS. Sticking to them improves symptoms considerably. Your chances of conception are also increased.
Adopt a diet that includes:
- Foods with low glycemic index;
- Lots of fruits and vegetables;
- Healthy fats;
- Proteins;
- Natural, unprocessed foods.
If you’re trying to conceive with PCOS, then you should stay away from:
- Sugar;
- Cigarettes;
- Coffee;
- Alcoholic beverages;
- Soda.
Ayurveda recommends following foods to boost your fertility
Ayurveda is that medical science that certainly knows about keeping your body systems balanced. Here are some recommendations:
- Ghee and Sesame Seeds – they contain the right kind of fats that promote ovulation and improve quality of eggs.
- Turmeric – improves circulation to all organs, including womb and ovaries (your egg making factories).
- Mung Beans – a good source of protein packaged along with fiber and antioxidants
- Cinnamon – makes your stomach feel fuller for longer, so you don’t have to eat so much so often. It also regulates menstrual period.
- Leafy greens – they are rich in magnesium, which helps to improve fertility.
Here you will find a detailed post on Ayurvedic natural ways to support and boost fertility.
You should get to understand the PCOS diet and how it works. It will definitely help in your quest to get pregnant with PCOS.
Remember, it is about you trusting your instincts and taking charge of your own body.
3. PCOS Weight loss and Regular Exercise
Now you’re wondering, “What does exercise have to do with my chances of getting pregnant with PCOS? Has another study linked exercise with PCOS pregnancy success rate?”
Not just another research, but plenty of research.
As earlier stated, when a good PCOS exercise routine is combined with the appropriate PCOS diet plan, then you can greatly improve your PCOS symptoms.
Exercise helps in many different ways. For example, if you understand how PCOS works, you would have heard about insulin resistance.
Now, if you carry out exercises that build muscles, the new muscle cells help to lower blood sugar metabolism.
That way, you have some control over insulin resistance. The liver also begins to produce less insulin if it senses that your cells now use insulin better.
When you have less insulin in you, then you will also produce fewer male hormone. All in all, your PCOS symptoms begin to improve.
Exercise at least 30 minutes daily if you can help it. Focus your efforts on strength training and muscle building, and less on cardio exercises like running, etc.
In any case, ensure you are losing weight. Here you can find best exercise to lose weight with PCOS and a free 7 days exercise plan.
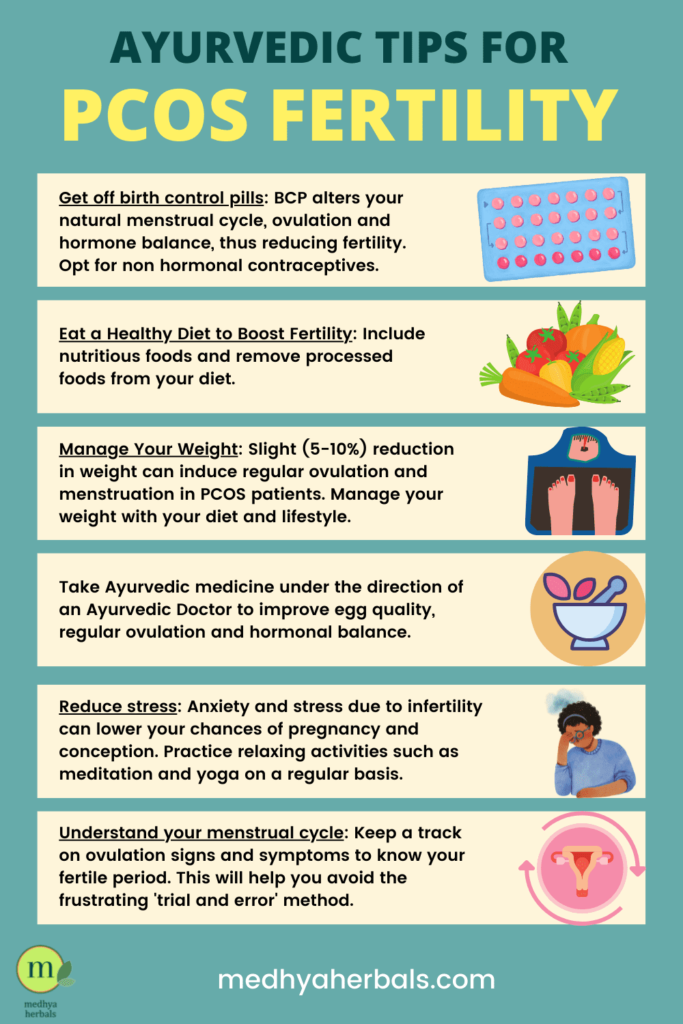
4. If you’re on birth control pills, get off!
Many women are prescribed birth control pills, even from as early as adolescence, either to make menstruation easier, to cure acne, or for some other reason.
However, these birth control pills artificially mask hormonal imbalance symptoms through additional hormones they supply. These hormones also take over the body’s natural hormonal processes.
So, you see that if you are aiming for getting pregnant with PCOS, then taking birth control pills will only mess up your chances even more.
If you’re not in a hurry, but you know you want to have babies sometime in the future, then you need to step off that train now. Your body will have ample time to adjust. If you use it for contraceptive purposes, then try non-hormonal means.
5. Reduce Stress
PCOS puts you in a delicate situation. Your hormones will be further thrown into a state of imbalance if you’re stressed up.
This is because, excess stress releases much higher amount of hormone Cortisol, which further disturbs your natural hormone balance.
Excess Cortisol also suppresses your immune system and triggers high level inflammation in the body.
Your PCOS symptoms often arise due to a toxic combination of high stress and chronic inflammation in the body. Hence, it is vital that you treat the root cause and manage your stress levels.
6. Learn to track Ovulation
Understand your menstrual cycle better and keep a track on ovulation signs and symptoms to know your fertile period. This will help you avoid the frustrating ‘trial and error’ method.
Tracking ovulation at home can be a helpful tool for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) who are trying to conceive. While PCOS can make ovulation tracking more challenging, there are several methods that can be used to track ovulation at home:
- Basal body temperature (BBT) charting: This involves taking your temperature first thing in the morning before getting out of bed and tracking it on a chart to identify changes in temperature that indicate ovulation. While BBT charting can be helpful for some women with PCOS, it may not be reliable for those with very irregular cycles.
- Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs): These are urine tests that detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs just before ovulation. However, OPKs may not be accurate for women with PCOS who have high baseline levels of LH.
- Cervical mucus monitoring: This involves observing changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle. As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus typically becomes thinner and more stretchy, similar to the consistency of egg whites.
- Menstrual cycle tracking: Keeping track of the dates of your periods can help you estimate when ovulation is likely to occur. However, this method may be less reliable for women with irregular cycles.
- Fertility tracking apps: There are several apps available that can help you track ovulation based on your menstrual cycle data, symptoms, and other factors. While these apps can be helpful, it’s important to remember that they are not foolproof and may not be accurate for women with PCOS.
Takeaway
Dr. Randine Lewis, author of “The Infertility Cure” said something interesting, and here it is:
“If you have been told you are infertile, I have one message for you: There is no such thing as infertility; it is a myth. Rarely have I met a woman of childbearing age with all her reproductive organs intact who isn’t capable of bearing children. As long as the anatomical structures are present, a medical diagnosis of ‘infertility’ is often a fallacy.”
Even for women without PCOS, it will surprise you to know that 85% of couples don’t conceive till after a year of trying. Not to talk of someone trying to get pregnant with PCOS.
Remember that getting pregnant with PCOS is possible! And that you can overcome PCOS infertility! Here’s to life, to future, and to good health.
Here you can consult with Medhya’s Ayurvedic Doctor to get your PCOS treatment plan involving prescription for Ayurvedic medicine, diet, yoga and lifestyle guidelines.
FAQ
1. How to predict ovulation with PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can affect women of childbearing age. The condition is characterized by the development of small cysts on the ovaries, as well as an imbalance of sex hormones. PCOS can make it difficult to become pregnant, as ovulation may be irregular or may not occur at all. However, there are some methods that women with PCOS can use to help predict when they are likely to ovulate. One way to track ovulation is to use a basal body temperature (BBT) chart. This involves taking your temperature first thing in the morning, before you get out of bed, and recording it on a chart. You will need to do this every day for several months in order to establish a pattern. Another way to predict ovulation is to keep track of changes in your cervical mucus. Around the time of ovulation, your cervical mucus will become thin and stretchy, like egg white. By tracking these changes, you may be able to better predict when you are likely to ovulate. If you have concerns about PCOS or are having difficulty conceiving, it is important to speak with your doctor and thus work on a treatment plan that is according to your health symptoms.
2. Can infertility from PCOS be treated?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can affect women of childbearing age. The condition is characterized by an imbalance of reproductive hormones, which can lead to the development of cysts on the ovaries and irregular or absent menstrual periods. PCOS can also cause fertility problems, weight gain, and other health issues. Although there is no cure for PCOS, it is possible to manage the condition and have a healthy pregnancy. Ayurvedic medicine offers a holistic approach to managing PCOS and optimizing fertility. Herbal supplements, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications can all help to regulate hormone levels and support reproductive health. With the help of an experienced Ayurvedic practitioner, it is possible to have a healthy pregnancy despite PCOS.
3. How fertile are you with PCOS?
If you have PCOS, you may be wondering how fertile you are. The good news is that most women with PCOS are able to conceive with the help of fertility treatments. However, PCOS can make it more difficult to get pregnant, and you may need to try for longer before you are successful. There are several factors that affect fertility in women with PCOS, including age, weight, and the severity of the condition. With treatment and a healthy lifestyle, most women with PCOS are able to have a successful pregnancy. If you are trying to conceive, talk to your doctor about your fertility options.
4. How likely is infertility with PCOS?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects a woman’s hormonal balance, causing her to ovulate irregularly or not at all. For some women, PCOS will cause their ovaries to produce too many eggs. This can make it difficult to get pregnant. Other women with PCOS may have a hard time ovulating. This means that they may not release an egg every month. This can also make it difficult to get pregnant. PCOS can also cause an increase in androgens and insulin resistance, which can lead to problems with fertility. In fact, women with PCOS have a 30-40% chance of being infertile. While there is no cure for PCOS, there are treatments available that can help to improve fertility. If you are struggling to conceive, it is important to speak to your doctor about your options. Ayurvedic medicine offers a number of herbal remedies that can help to regulate hormone levels and improve fertility in women with PCOS.
5. Does PCOS fertility improve with age?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can affect women of childbearing age. The defining feature of PCOS is the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, which can lead to an imbalance of reproductive hormones. This can result in a variety of symptoms, including irregular periods, weight gain, fertility problems, and acne. While there is no cure for PCOS, fertility may improve with age. As women with PCOS get older, they are more likely to ovulate regularly and have successful pregnancies. In addition, the risk of miscarriage and preeclampsia decreases as women with PCOS age. However, PCOS can still cause fertility problems later in life, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you are trying to conceive.
6. How does PCOS affect my fertility after 35?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that can affect fertility. The condition is characterized by an imbalance of sex hormones, which can lead to the development of small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can cause a number of symptoms, including irregular periods, excess hair growth, and weight gain. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it is believed to be related to insulin resistance. Women with PCOS are at an increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease. The condition can also make it difficult to get pregnant. PCOS affects fertility by interfering with ovulation. In some cases, medication or surgery may be necessary to restore fertility. However, many women with PCOS are able to conceive without treatment. If you have PCOS and are over the age of 35, it is important to consult with a fertility specialist to discuss your treatment options.
7. Do you ovulate monthly with PCOS?
Women with PCOS may have irregular periods, and may not ovulate every month. This is because PCOS is associated with hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle. In some cases, women with PCOS may not ovulate at all.
However, it is important to note that not all women with PCOS will experience the same symptoms. Some women with PCOS may have regular menstrual cycles and ovulate regularly, while others may have irregular periods and struggle to ovulate. The severity of PCOS symptoms can also vary from person to person.
8. Can you ovulate naturally with PCOS?
Yes, it is possible for women with PCOS to ovulate naturally, although it may be less frequent and less predictable than for women without PCOS. However, with proper management and lifestyle changes, many women with PCOS are able to improve their ovulation and menstrual cycles. This may include weight loss (if overweight or obese), regular exercise, a healthy diet, and medications such as metformin or clomiphene citrate to stimulate ovulation.
In some cases, women with PCOS may require assisted reproductive technologies such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) to conceive.
References

