Every woman experiences her menstrual cycle in a unique way, but when does it cross the line from normal to problematic? Period problems, from irregular cycles to painful menstrual cramps, affect millions of women worldwide. It’s estimated that nearly 30% of women experience menstrual disorders, yet many remain unaware of what constitutes a healthy period.
In this comprehensive guide, we dive deep into the world of menstrual health. We’ll unveil the signs of menstrual abnormalities, explore the most common period problems, and help you understand when your menstrual symptoms might be hinting at something more serious. We’ll also shed light on how factors like stress, sleep, and age can influence your cycle.
As an experienced Ayurvedic doctor, specializing in women’s health, I am here to empower you with the information you need to take charge of your menstrual health. I promise to guide you through the confusing maze of period problems with clear, easy-to-understand language, backed by Ayurvedic principles and modern medical knowledge.
Whether you’ve been feeling period symptoms but not seeing the blood, or worrying about why your period dates change every month, we’ve got you covered. So, get ready to embark on a journey of discovery about your body, because understanding is the first step towards healthier, happier periods.
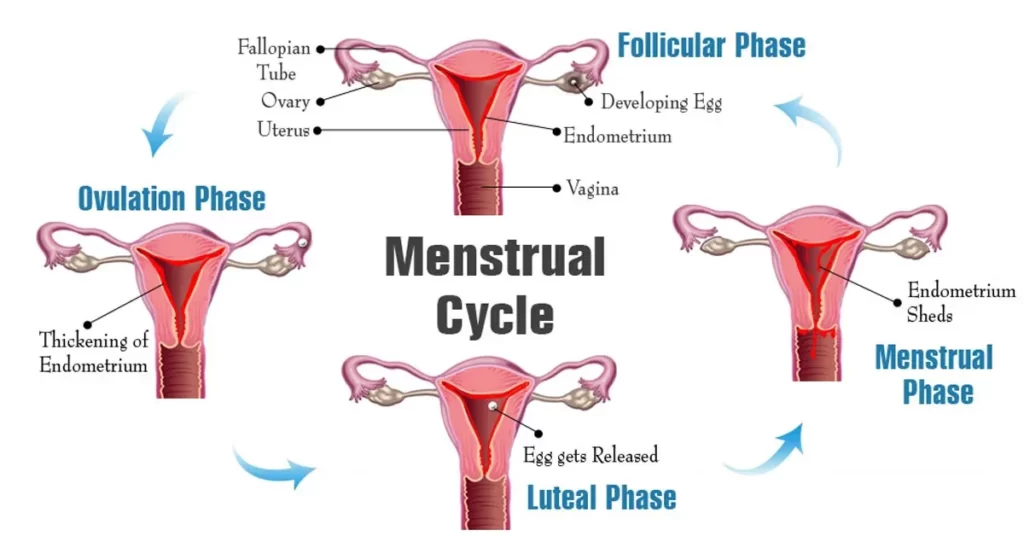
Understanding Regular Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a natural monthly process that a woman’s body goes through in preparation for possible pregnancy. It involves a series of changes in hormone levels, leading to the development and release of an egg from the ovaries. If the egg isn’t fertilized, the lining of the uterus, or womb, is shed through the vagina. This shedding is what we commonly refer to as a period.

Signs of a Healthy Period
Understanding what a regular menstrual cycle looks like is the first step towards recognizing if there’s an issue. Here are four common period symptoms that indicate regular menstruation:
- Menstrual Bleeding: This is the most noticeable symptom of menstruation. A typical menstrual cycle lasts between 21 and 35 days, with periods usually lasting between 2 to 7 days. The bleeding is often heavy in the first couple of days before gradually lightening.
- Mild Cramps: Mild to moderate cramping, often in the lower abdomen or back, is another common symptom. This is due to the contraction of the uterus as it sheds its lining.
- Mild Bloating: Some women might experience mild bloating or water retention. This is caused by the hormonal changes that occur during menstruation.
- Mood Changes: Hormonal fluctuations can also cause mood swings, mild depression, or irritability in the days leading up to the period.
However, this seemingly straightforward process can sometimes go awry, leading to a variety of period problems. These can range from minor irregularities that require little to no treatment, to more significant disorders that can impact a woman’s fertility and overall health.
Symptoms and Signs of Period Problems
Menstrual abnormalities can manifest in several ways. Here are some of the most common signs that something might be off with your menstrual cycle:
- Irregular periods: This can mean periods that come too frequently (less than 21 days apart), not often enough (more than 35 days apart), or even not at all for several months.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding: Also known as menorrhagia, this involves bleeding that’s so heavy it requires you to change your pad or tampon every hour for several consecutive hours.
- Painful periods: Severe or increasing pain during your period, known as dysmenorrhea, can also be a sign of an underlying problem.
- Changes in blood appearance: This could include blood clots larger than a quarter or menstrual flow that’s noticeably thicker or thinner than usual.
Common Side Effects of Menstrual Disorders
Bad periods or menstrual disorders can lead to a range of side effects, including:
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Bloating or water retention
- Severe mood swings
- Fatigue or lethargy
- Disturbances in regular activities due to period symptoms
When to Seek Help: Recognizing Serious Menstrual Problems
While variations in menstrual cycles are common, there are certain instances when these changes may indicate a more serious issue. You should consider seeking medical advice if you experience any of the following:
- Your periods suddenly stop for more than 90 days, and you’re not pregnant
- Your periods become very irregular after having had regular, monthly cycles
- Your period occurs more frequently than every 21 days or less frequently than every 35 days
- You’re bleeding for more than seven days
- You’re bleeding more heavily than usual or using more than one pad or tampon every one to two hours
- You bleed between periods
- You have severe pain during your period
Causes of Period Problems
As we delve into the topic of period problems, it’s crucial to understand the root causes of menstrual disorders. These conditions can stem from a multitude of factors, each unique to the individual’s body and lifestyle. From hormonal imbalances to structural issues within the reproductive system, the causes can be as varied as the symptoms themselves.
Health Conditions That Can Disrupt Regular Menstruation
Several conditions can disrupt the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Here are the common ones:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can cause periods to become infrequent or stop altogether. Women with PCOS might also experience other symptoms like excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, leading to painful and heavy periods.
- Uterine Fibroids: These non-cancerous growths in the uterus can cause heavy bleeding and longer menstrual cycles.
- Uterine Polyps: These are small, soft growths in the lining of the uterus. They can lead to irregular menstrual bleeding, periods that are unusually heavy or long, or bleeding between periods.
- Adenomyosis: This condition happens when the tissue that normally lines the uterus starts to grow into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can lead to longer, heavier periods and severe menstrual cramps.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, so any imbalance can disrupt this process. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, significant weight loss or gain, certain medications, or conditions like thyroid disorders.
The Impact of Stress on Menstruation
Stress, both physical and emotional, can have a significant impact on the menstrual cycle. High levels of stress can lead to changes in hormonal balance, which can in turn delay or even stop menstruation. This is because the body diverts its focus towards managing stress, often at the expense of processes like the menstrual cycle.
A “stress period” might be lighter or heavier than usual, come late, or be missed altogether. Additionally, you might notice an increase in other premenstrual symptoms like mood swings, bloating, and headaches. If you’re experiencing stress-related menstrual changes, it’s crucial to seek ways to manage stress effectively and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
The Role of Sleep in Menstrual Health
Sleep plays a vital role in regulating many of our body’s processes, including the menstrual cycle. Lack of sleep, or poor-quality sleep, can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, potentially leading to irregular periods, heavier or lighter bleeding, or worsened premenstrual symptoms.
Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring you get enough high-quality sleep can help keep your menstrual cycle on track. If you’re struggling with sleep and noticing changes in your menstrual cycle, it’s worth discussing these symptoms with a healthcare provider.
Age-Related Menstrual Irregularities
As women age, it’s normal for their menstrual cycle to undergo changes. Teenagers often experience irregular periods as their bodies adjust to new hormonal rhythms. It’s also common for menstrual cycles to shorten in your 20s and 30s, and then lengthen again in your 40s.
As women approach menopause (usually in their late 40s to early 50s), periods can become irregular before eventually stopping altogether. Any significant changes or symptoms, particularly those that cause distress or disrupt daily life, should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Common Types of Menstrual Disorders: What You Need to Know
Understanding menstrual disorders can be challenging given the variety of conditions. However, here are five common disorders that many women experience:
- Amenorrhea: This is the absence of menstruation. It can be primary (if menstruation hasn’t begun by age 16) or secondary (if menstruation stops for three months or more). Common causes include weight changes, excessive exercise, stress, and certain medical conditions.
- Dysmenorrhea: This refers to painful periods that can interfere with daily activities. Primary dysmenorrhea is pain caused by the menstrual cycle itself, while secondary dysmenorrhea is caused by an underlying condition like endometriosis.
- Menorrhagia: This is a condition characterized by heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, or polyps.
- Oligomenorrhea: This refers to infrequent menstrual periods, with cycles typically longer than 35 days. It can be caused by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), stress, excessive exercise, or certain medical conditions.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS): This involves a group of symptoms like mood swings, tender breasts, food cravings, and fatigue that occur in the week or two before your period.
Decoding Period Symptoms: From Clots to Colors
Menstrual blood can vary in color, consistency, and volume, which can provide important clues about your health.
- Jelly-like Blood: This is often a sign of normal clotting. When the flow is heavy, blood can coagulate into a jelly-like substance. However, if the clots are larger than a quarter or happen frequently, it’s worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
- Heavy/Clotty Periods: Some clotting is normal, especially during the heaviest days of your period. However, passing large clots or having a heavier period than usual could be a sign of menorrhagia, a condition characterized by heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Watery Periods: If your menstrual blood seems thinner or more watery than usual, it might be due to dietary changes, exercise, or hormonal imbalances. If you’re also experiencing other symptoms or if the change is significant, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional.
- Color of Period Blood: Menstrual blood can range from bright red to dark brown. Bright red blood is usually fresh, while darker blood is often older blood that’s been in the uterus longer. However, if your period is consistently a different color (like pink or gray), it could indicate an issue like hormonal imbalances or an infection.
Normal Pad Usage and Identifying Infected Period Blood
The number of pads a woman uses can vary based on the flow of her period. On average, it’s normal to use 3-6 pads or tampons per day. However, if you’re soaking through one pad or tampon every hour for several consecutive hours, it could be a sign of menorrhagia.
Infected period blood is not a common occurrence, but signs of an infection could include a foul smell, fever, severe pain, or unusual color. If you suspect an infection, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.
Seeking Medical Help for Period Problems
Seeking medical help can seem daunting, but it’s important to remember that menstrual disorders are common and treatable. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, or if you’re simply concerned about your menstrual health, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice.
Healthcare professionals can provide a thorough diagnosis, offer advice, and outline treatment options. These may include lifestyle modifications, medication, or even surgery for more serious conditions. It’s always better to seek help sooner rather than later, as early intervention can often lead to more effective treatment.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of period problems can be confusing and overwhelming, not to mention the discomfort and distress that can come with these conditions. We understand how challenging it can be to find effective, long-lasting relief. You’re not alone in this journey, and it’s important to remember that help is available.
At Medhya Herbals, we believe in addressing the root cause of health issues. Our team of experienced Ayurvedic doctors can provide personalized treatment plans tailored to your unique needs and symptoms. Ayurvedic treatment can offer a holistic approach to menstrual health, going beyond temporary relief to provide a more permanent solution.
Don’t let period problems keep you from living your life to the fullest. Schedule a consultation with our Ayurvedic doctors today and start your journey towards improved menstrual health. With Ayurveda’s holistic approach and our personalized care, we’re confident that we can help you find the relief you’ve been seeking.
FAQ
Period Symptoms Without Bleeding
Sometimes, women might experience period symptoms like bloating, cramps, and mood swings but not actually bleed. This could be due to factors like stress, weight changes, or hormonal imbalances that disrupt the menstrual cycle. However, if this happens regularly or if you’re experiencing other concerning symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional.
Understanding Abnormal Period Cycles
A typical menstrual cycle lasts between 21 and 35 days, with the period itself lasting between 2 to 7 days. If your cycle is consistently shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days, it could be a sign of an abnormal period cycle. Other signs of abnormal cycles include: periods that last longer than a week, bleeding or spotting between periods, severe pain during your period, or sudden changes in the amount of blood you lose during your period. Any of these symptoms warrant a discussion with your healthcare provider to determine if there’s an underlying problem.
Can I have a period without blood?
While it may seem unusual, it is possible to experience a “period” without blood, often referred to as an anovulatory cycle or a hormonal withdrawal bleed. This typically happens when hormonal fluctuations cause the usual symptoms of a period, such as bloating, cramping, or mood swings, without the usual shedding of the uterine lining. This can occur due to stress, drastic weight changes, certain medical conditions, or hormonal contraceptives. However, if this happens frequently, it’s important to seek medical advice, as it could indicate an underlying health issue.
How long after missed period should I worry?
Missing a period can be alarming, but it’s not always a cause for immediate concern. Menstrual cycles can vary and may be influenced by factors such as stress, changes in weight, exercise habits, or illness. However, if you have missed your period for three consecutive cycles or more, or if your period is more than 90 days late, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you are sexually active and your period is late, it could be a sign of pregnancy, and a pregnancy test might be warranted. As with any health concern, when in doubt, it’s always best to seek professional advice.
Why do I feel like I’m having my period but I’m not bleeding?
Experiencing period-like symptoms without bleeding can be perplexing. This can often occur due to hormonal changes in the body. Conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or a hormonal imbalance can cause your body to mimic symptoms of a period, like cramping, bloating, or mood swings, without actual menstrual bleeding. Stress or significant changes in weight or exercise routines can also disrupt your hormonal balance and lead to these symptoms. If you’re consistently experiencing period symptoms without bleeding, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying health issues.
Why did my cycle change from 28 to 35 days?
A change in the menstrual cycle from 28 to 35 days can be perplexing and concerning, but it’s often linked to hormonal imbalance in the body. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone play a vital role in regulating the menstrual cycle, and any fluctuations in these hormone levels can cause changes in the cycle’s length. Various factors can trigger these hormonal shifts, including stress, significant weight loss or gain, certain medications, or underlying health conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Even natural life changes like entering perimenopause can alter the menstrual cycle. It’s essential to recognize that while a one-time change may not be a cause for alarm, consistent changes in your cycle should prompt a discussion with a healthcare provider, who can conduct proper evaluations and offer personalized treatment to restore hormone balance.
References
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menstrual-cramps/symptoms-causes/syc-20374938
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/breast_health/normal_breast_development_and_changes_85,P00151
- https://www.yourperiod.ca/normal-periods/symptoms-of-menstruation/
- https://youngwomenshealth.org/2013/10/31/pms/
- https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Premenstrual-Syndrome-PMS
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/menstrual-cycle/premenstrual-syndrome
- http://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/prostaglandins/
- https://dx.doi.org/10.5468%2Fogs.2017.60.1.100
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S019096220123641X
- https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/health-and-wellness/menstruation/what-can-i-do-about-cramps-and-pms

